EX-99.1
Published on August 13, 2025

Kiora Pharmaceuticals, Inc. NASDAQ: KPRX 13 Aug 2025 | Corporate Overview H.C. Wainwright 5th Annual Ophthalmology Virtual Conference

2 Forward Looking Statements Some of the statements in this presentation are "forward-looking" and are made pursuant to the safe harbor provision of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These "forward-looking" statements include statements relating to, among other things, the development and commercialization efforts and other regulatory or marketing approval efforts pertaining to Kiora's development-stage products, including KIO-301 and KIO-104, as well as the success thereof, with such approvals or success may not be obtained or achieved on a timely basis or at all, the potential ability of KIO-301 to restore vision in patients with RP, the expecting timing of enrollment, dosing and topline results for the ABACUS study, the ability to develop KIO-301 for Choroideremia and Stargardt Disease and KIO-104 for retinal inflammatory diseases, the ability to utilize strategic relationships to develop certain product candidates, Kiora’s ability to maintain the listing of our common stock on a national securities exchange, and Kiora's ability to achieve the specific milestones described herein. These statements involve risks and uncertainties that may cause results to differ materially from the statements set forth in this presentation, including, among other things, the ability to conduct clinical trials on a timely basis, the ability to obtain any required regulatory approvals, market and other conditions and certain risk factors described under the heading "Risk Factors" contained in Kiora's Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on March 25, 2025, or described in Kiora's other public filings. Kiora's results may also be affected by factors of which Kiora is not currently aware. The forward-looking statements in this presentation speak only as of the date of this presentation. Kiora expressly disclaims any obligation or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to such statements to reflect any change in its expectations with regard thereto or any changes in the events, conditions, or circumstances on which any such statement is based, except as required by law.
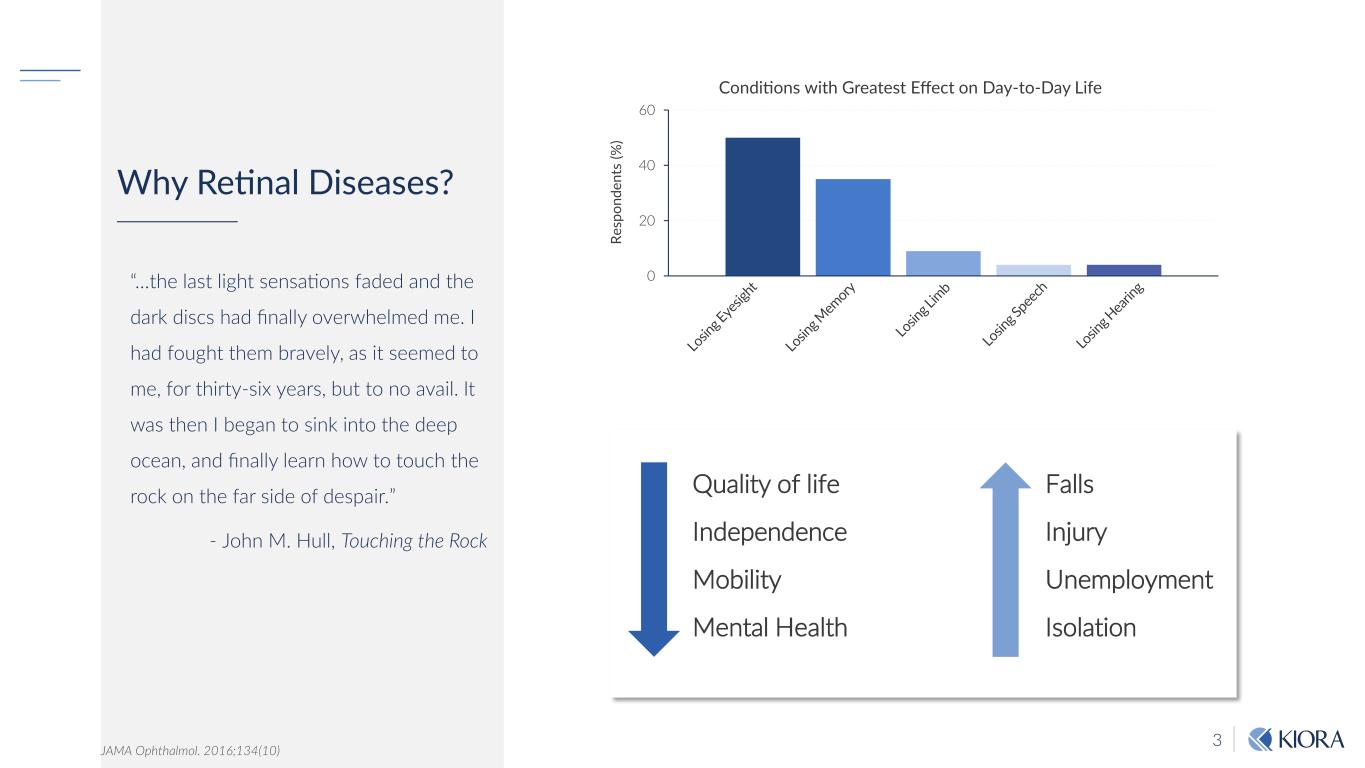
3 Why Retinal Diseases? “…the last light sensations faded and the dark discs had finally overwhelmed me. I had fought them bravely, as it seemed to me, for thirty-six years, but to no avail. It was then I began to sink into the deep ocean, and finally learn how to touch the rock on the far side of despair.” - John M. Hull, Touching the Rock JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(10) 0 20 40 60 Re sp on de nt s (% ) Conditions with Greatest Effect on Day-to-Day Life Quality of life Independence Mobility Mental Health Falls Injury Unemployment Isolation
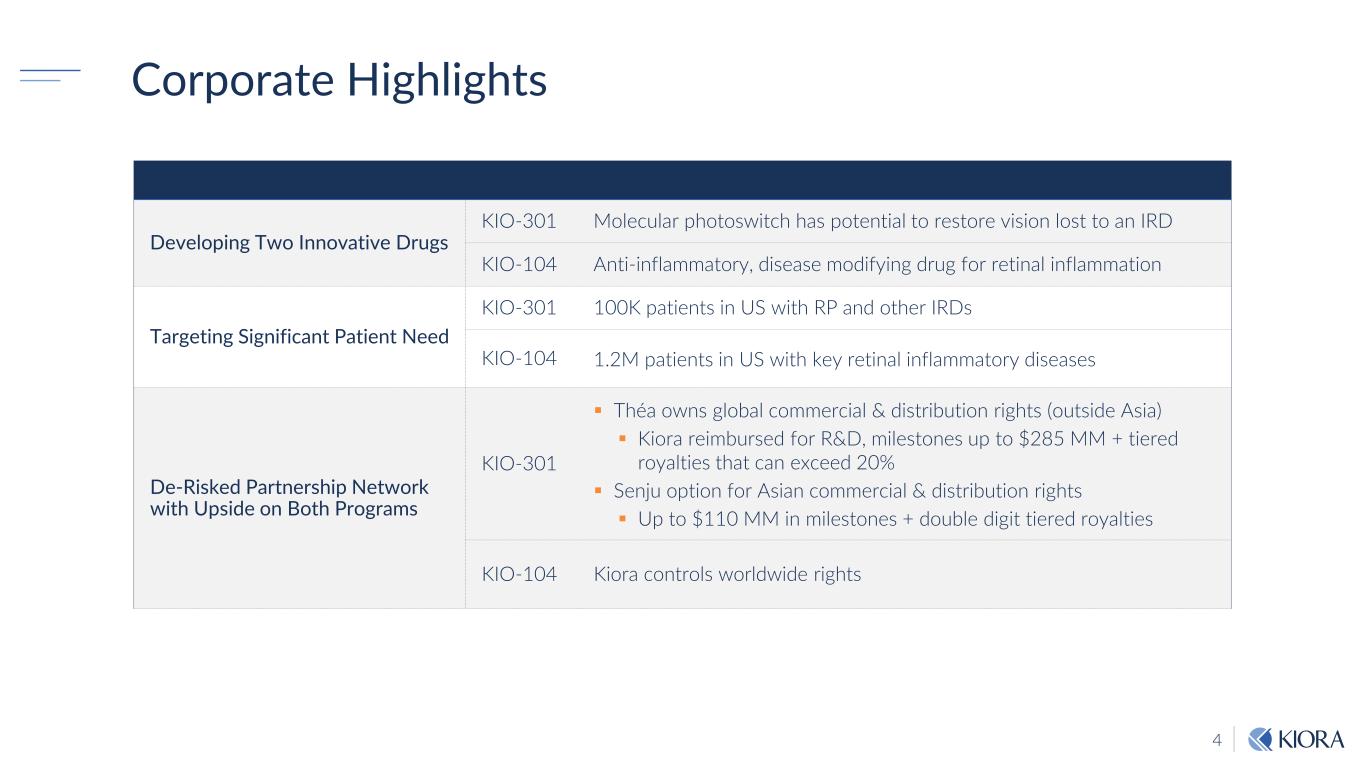
4 Corporate Highlights Developing Two Innovative Drugs KIO-301 Molecular photoswitch has potential to restore vision lost to an IRD KIO-104 Anti-inflammatory, disease modifying drug for retinal inflammation Targeting Significant Patient Need KIO-301 100K patients in US with RP and other IRDs KIO-104 1.2M patients in US with key retinal inflammatory diseases De-Risked Partnership Network with Upside on Both Programs KIO-301 Théa owns global commercial & distribution rights (outside Asia) Kiora reimbursed for R&D, milestones up to $285 MM + tiered royalties that can exceed 20% Senju option for Asian commercial & distribution rights Up to $110 MM in milestones + double digit tiered royalties KIO-104 Kiora controls worldwide rights
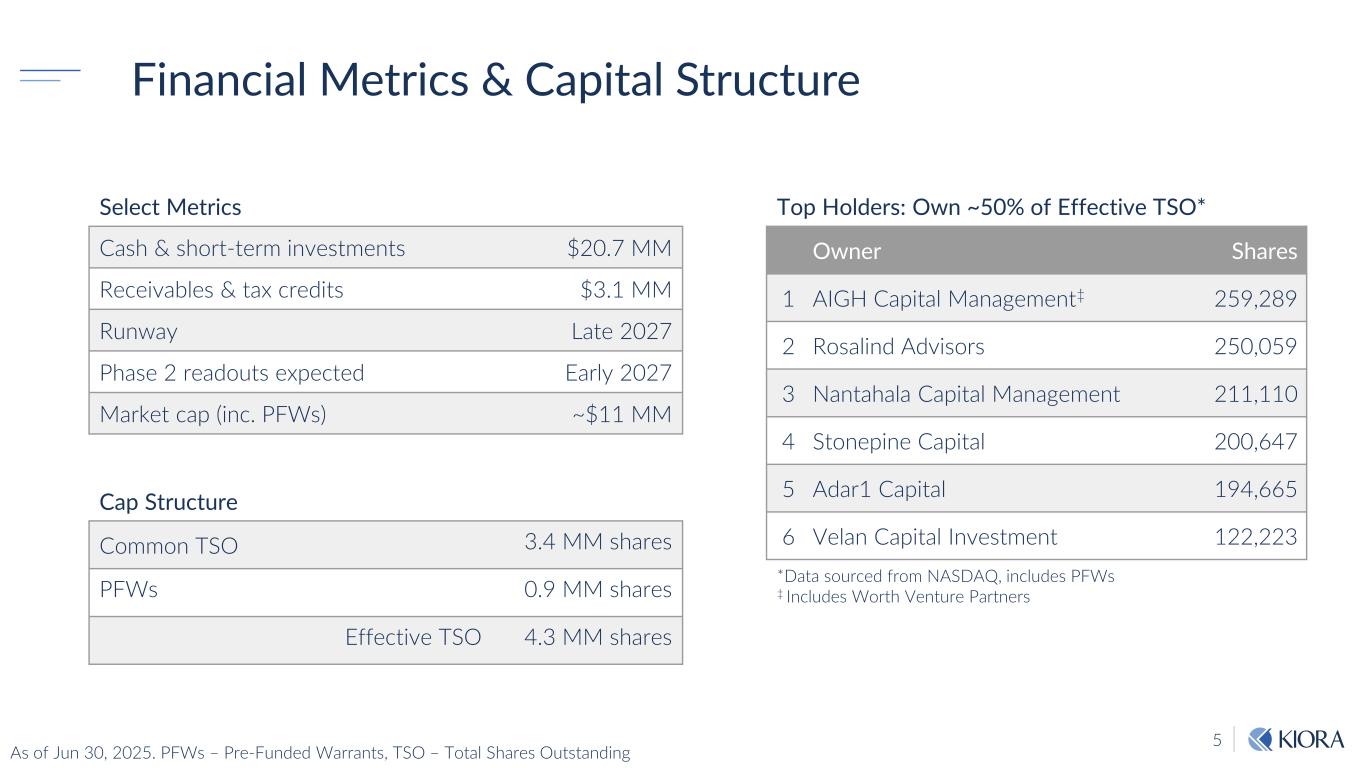
5 Financial Metrics & Capital Structure Cash & short-term investments $20.7 MM Receivables & tax credits $3.1 MM Runway Late 2027 Phase 2 readouts expected Early 2027 Market cap (inc. PFWs) ~$11 MM Common TSO 3.4 MM shares PFWs 0.9 MM shares Effective TSO 4.3 MM shares Owner Shares 1 AIGH Capital Management‡ 259,289 2 Rosalind Advisors 250,059 3 Nantahala Capital Management 211,110 4 Stonepine Capital 200,647 5 Adar1 Capital 194,665 6 Velan Capital Investment 122,223 Top Holders: Own ~50% of Effective TSO*Select Metrics Cap Structure *Data sourced from NASDAQ, includes PFWs ‡ Includes Worth Venture Partners As of Jun 30, 2025. PFWs – Pre-Funded Warrants, TSO – Total Shares Outstanding

6 Targeting the Retina to Slow, Stop, or Restore Vision Loss Development Pipeline of Proprietary Small Molecule Therapeutics Product Indication Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Commercial Rights KIO-301 Intravitreal Retinitis Pigmentosa (Mutation Agnostic)* Théa Open Innovation (global less Asia) Senju Pharmaceutical holds exclusive option rights in key Asian countries Choroideremia Stargardt Disease KIO-104 Intravitreal Retinal Inflammation Kiora Pharmaceuticals Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy * - Orphan Disease Designation granted in the USA and EU

7 KIO-301 Small Molecule Targeting Vision Restoration Inherited Retinal Diseases
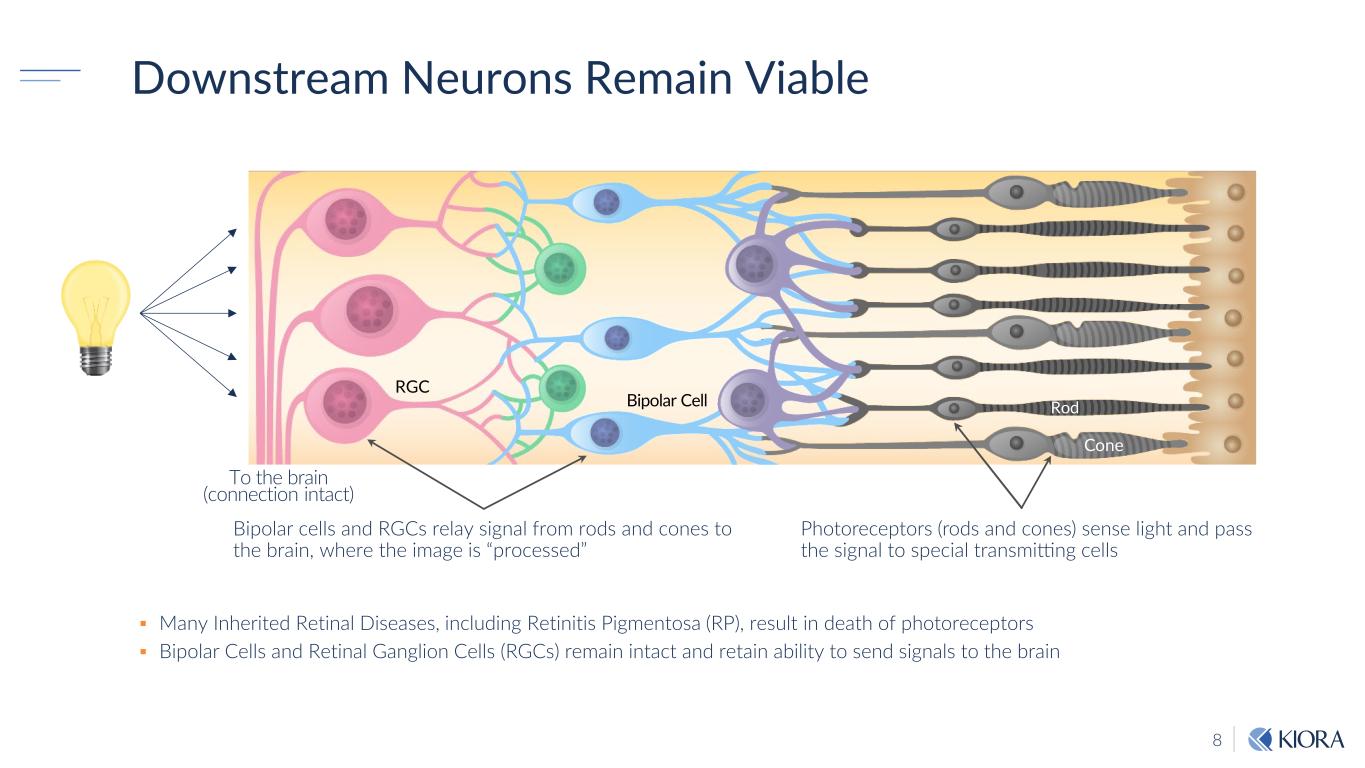
8 Downstream Neurons Remain Viable Many Inherited Retinal Diseases, including Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP), result in death of photoreceptors Bipolar Cells and Retinal Ganglion Cells (RGCs) remain intact and retain ability to send signals to the brain Photoreceptors (rods and cones) sense light and pass the signal to special transmitting cells Bipolar cells and RGCs relay signal from rods and cones to the brain, where the image is “processed” RGC Bipolar Cell To the brain (connection intact) Cone Rod
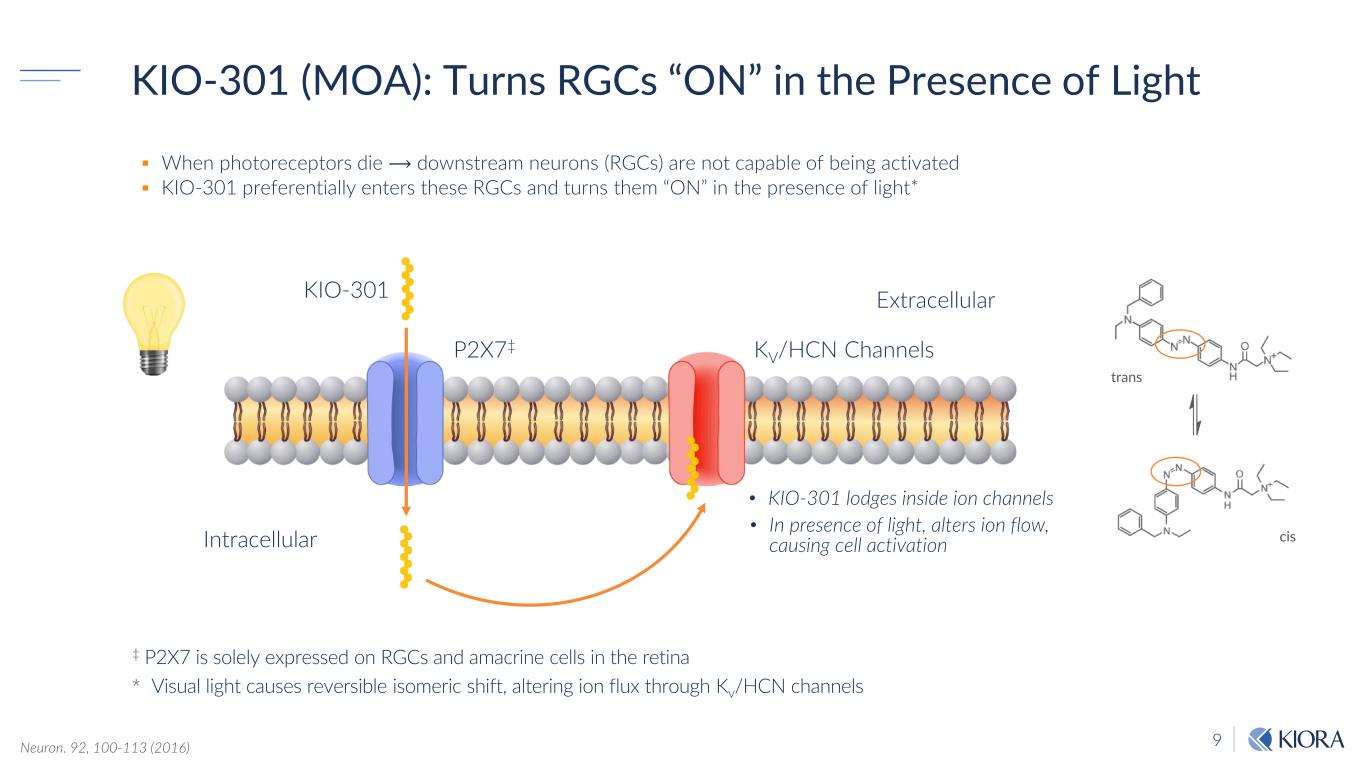
9Neuron. 92, 100-113 (2016) trans cis When photoreceptors die ⟶ downstream neurons (RGCs) are not capable of being activated KIO-301 preferentially enters these RGCs and turns them “ON” in the presence of light* ‡ P2X7 is solely expressed on RGCs and amacrine cells in the retina * Visual light causes reversible isomeric shift, altering ion flux through Kv/HCN channels Intracellular KIO-301 P2X7‡ Extracellular KV/HCN Channels • KIO-301 lodges inside ion channels KIO-301 (MOA): Turns RGCs “ON” in the Presence of Light • In presence of light, alters ion flow, causing cell activation
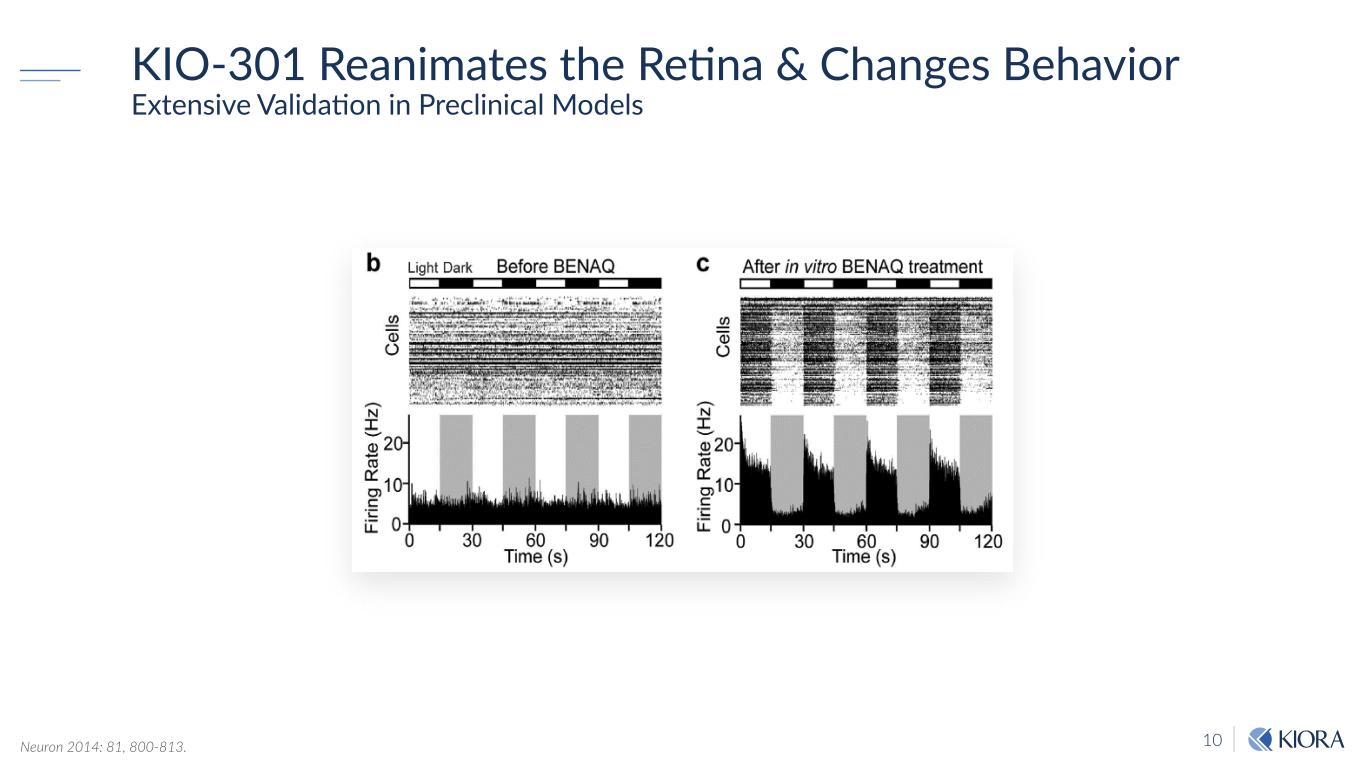
10 KIO-301 Reanimates the Retina & Changes Behavior Extensive Validation in Preclinical Models Neuron 2014: 81, 800-813.
11 Market Opportunity ~100k patients in US (Provider: Retina Specialists [~3k]) Estimated total cost to US healthcare system in 2019: $3.7B Clinical Presentation Night blindness, reduced visual field range and eventual loss of central vision Visual acuity declines 50% of patients are not qualified to drive by age 37 and legally blind by 55 Etiology 50+ genetically distinct subtypes from 150+ mutations Inherited disease Retinitis Pigmentosa A Disease with No Available Treatments Normal Vision Vision Declines over Time IOVS: Visual Field Progression in Retinitis Pigmentosa, AAO, Clin Ophtha 2021,:15. 2855–2866.
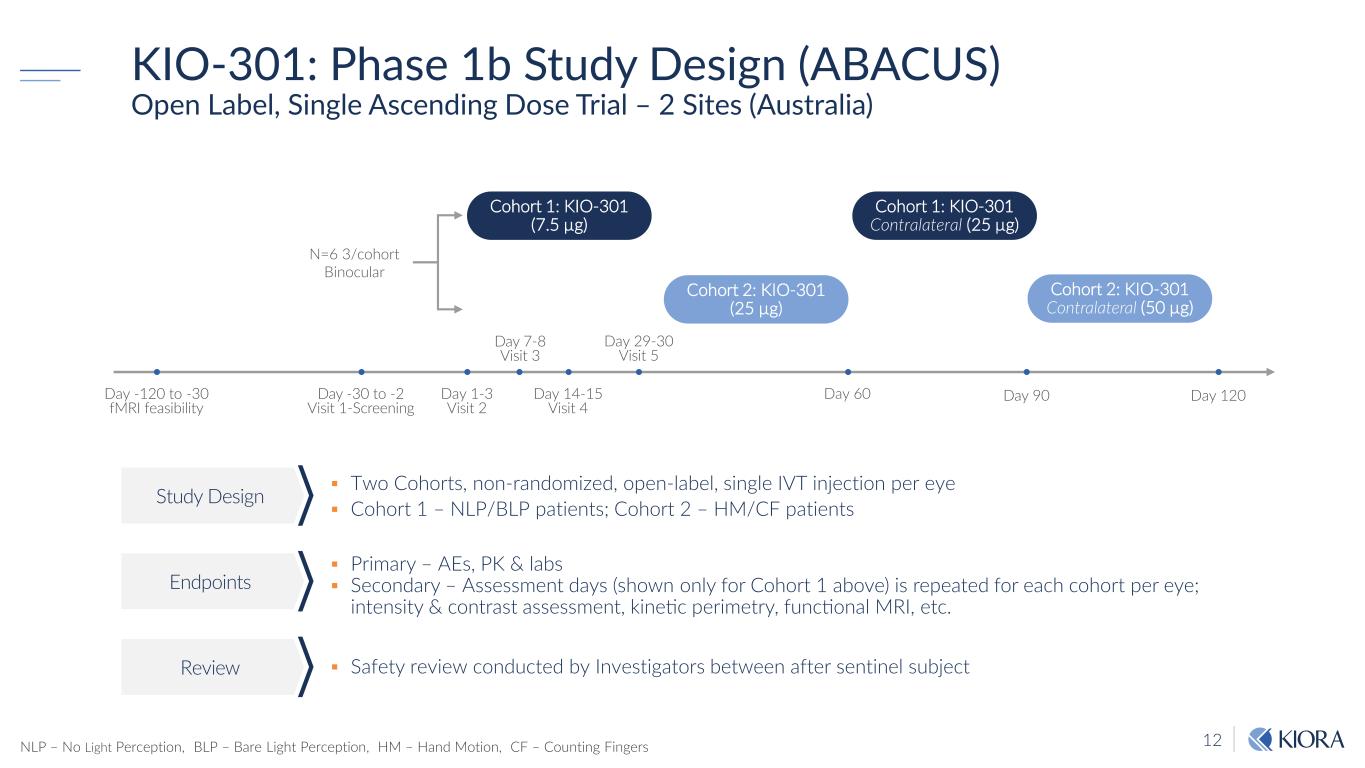
12 KIO-301: Phase 1b Study Design (ABACUS) Open Label, Single Ascending Dose Trial – 2 Sites (Australia) Two Cohorts, non-randomized, open-label, single IVT injection per eye Cohort 1 – NLP/BLP patients; Cohort 2 – HM/CF patients Primary – AEs, PK & labs Secondary – Assessment days (shown only for Cohort 1 above) is repeated for each cohort per eye; intensity & contrast assessment, kinetic perimetry, functional MRI, etc. Safety review conducted by Investigators between after sentinel subject Study Design Endpoints Review N=6 3/cohort Binocular Day 90 Cohort 1: KIO-301 (7.5 µg) Day -30 to -2 Visit 1-Screening Day 29-30 Visit 5 Day 60 Day 120 Cohort 1: KIO-301 Contralateral (25 µg) Cohort 2: KIO-301 (25 µg) Cohort 2: KIO-301 Contralateral (50 µg) Day 1-3 Visit 2 Day 7-8 Visit 3 Day 14-15 Visit 4 Day -120 to -30 fMRI feasibility NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception, HM – Hand Motion, CF – Counting Fingers
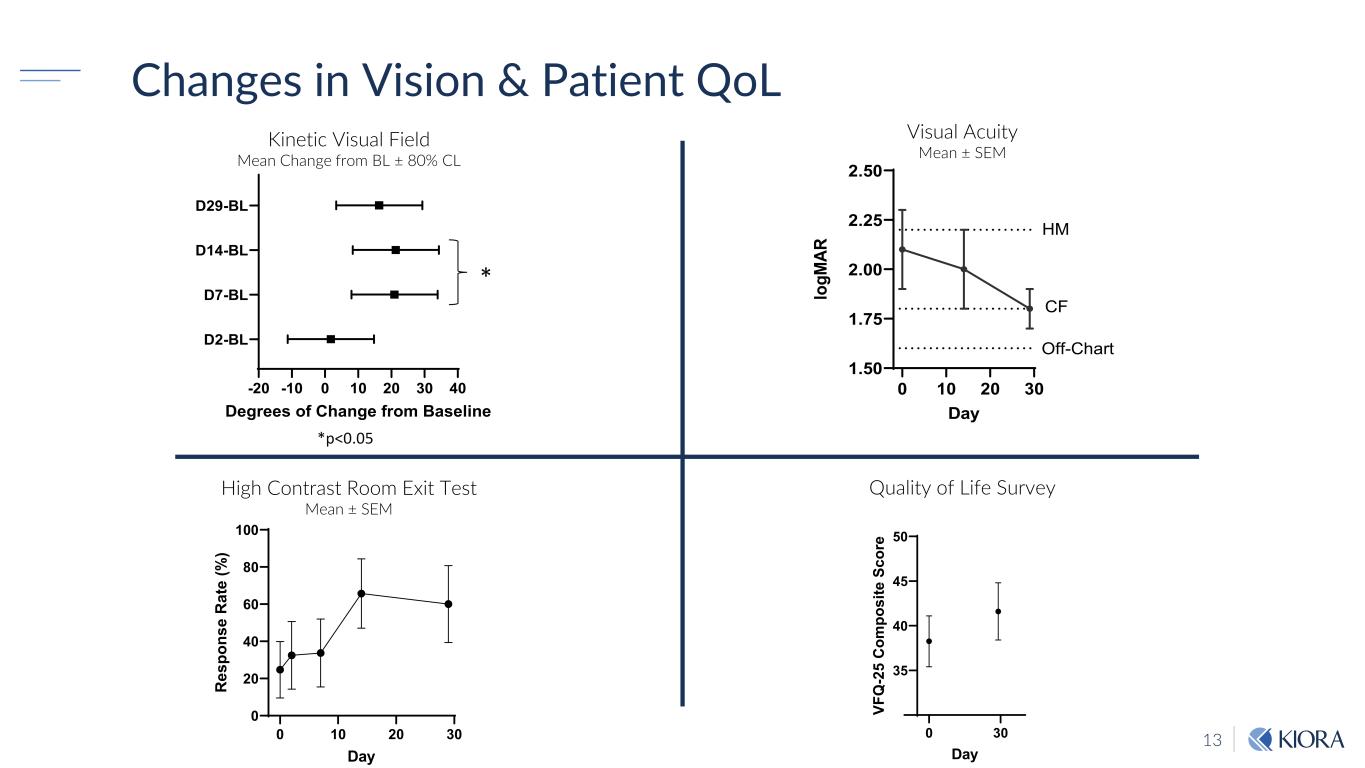
13 Changes in Vision & Patient QoL -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 D2-BL D7-BL D14-BL D29-BL Degrees of Change from Baseline * *p<0.05 0 10 20 30 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 Day lo gM AR Off-Chart CF HM 0 30 35 40 45 50 Day VF Q -2 5 C om po si te S co re 0 10 20 30 0 20 40 60 80 100 Day R es po ns e R at e (% ) Kinetic Visual Field Mean Change from BL ± 80% CL Visual Acuity Mean ± SEM High Contrast Room Exit Test Mean ± SEM Quality of Life Survey
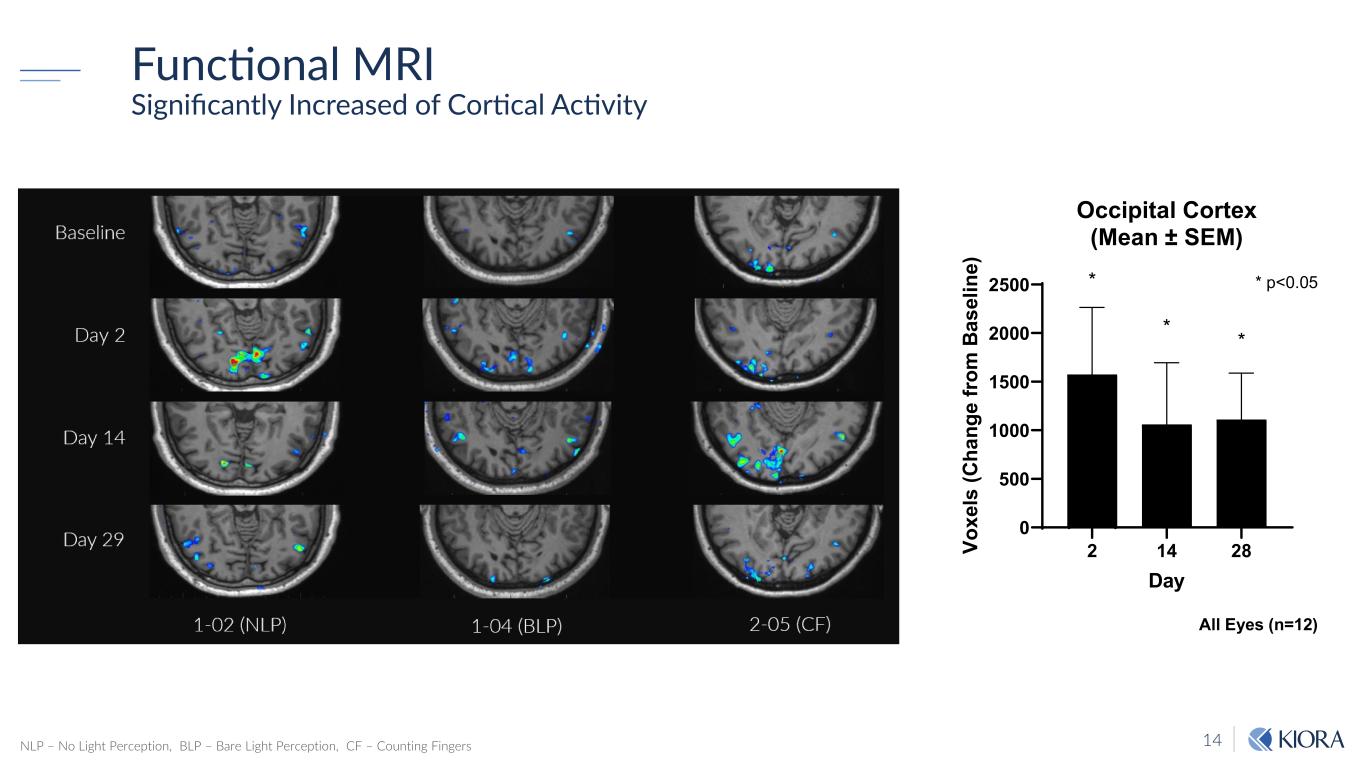
14 Functional MRI Significantly Increased of Cortical Activity NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception, CF – Counting Fingers 2 14 28 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 Occipital Cortex (Mean ± SEM) Day Vo xe ls (C ha ng e fro m B as el in e) * * * * p<0.05 All Eyes (n=12)

15 Patient Testimonials www.youtube.com/@kiorapharma Additional videos available at https://kiorapharma.com/inherited-retinal-diseases/
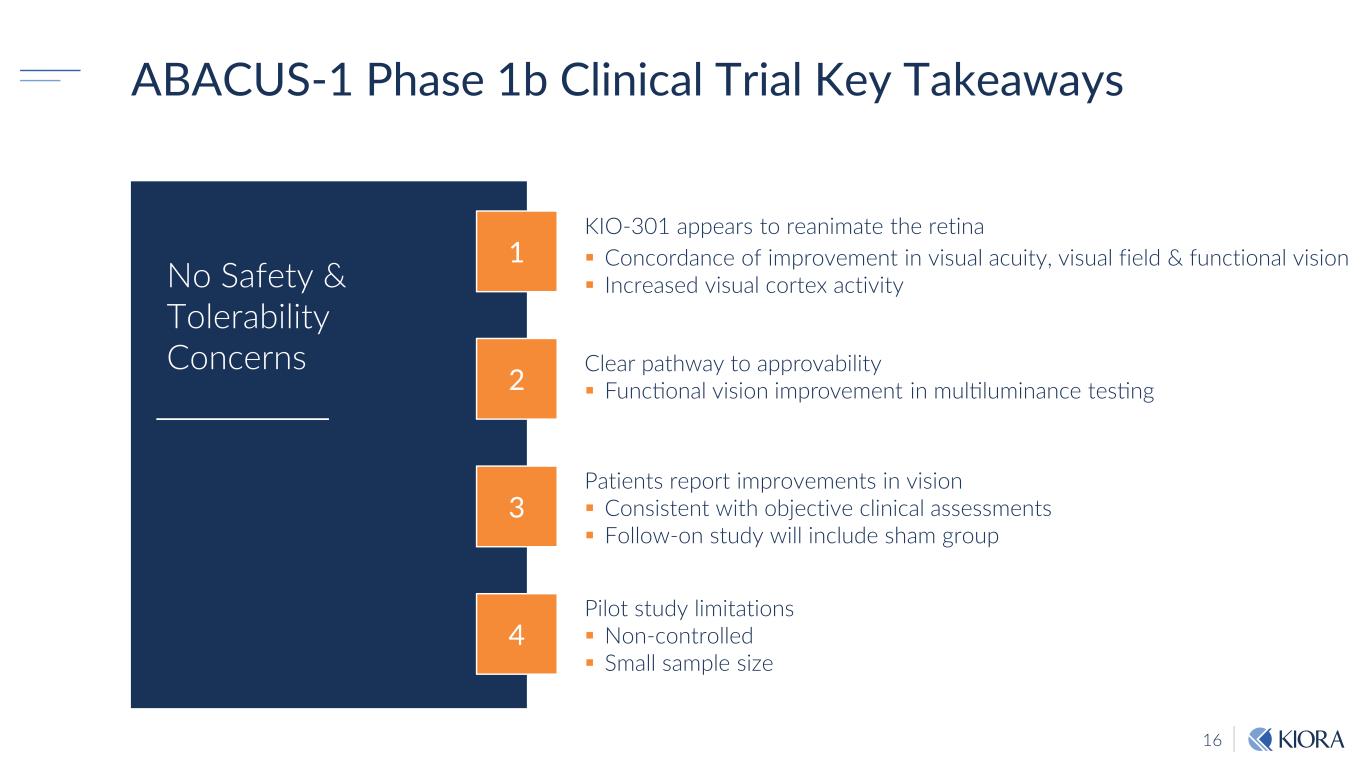
16 ABACUS-1 Phase 1b Clinical Trial Key Takeaways Patients report improvements in vision Consistent with objective clinical assessments Follow-on study will include sham group Pilot study limitations Non-controlled Small sample size Clear pathway to approvability Functional vision improvement in multiluminance testing KIO-301 appears to reanimate the retina Concordance of improvement in visual acuity, visual field & functional vision Increased visual cortex activity 4 3 2 1 No Safety & Tolerability Concerns
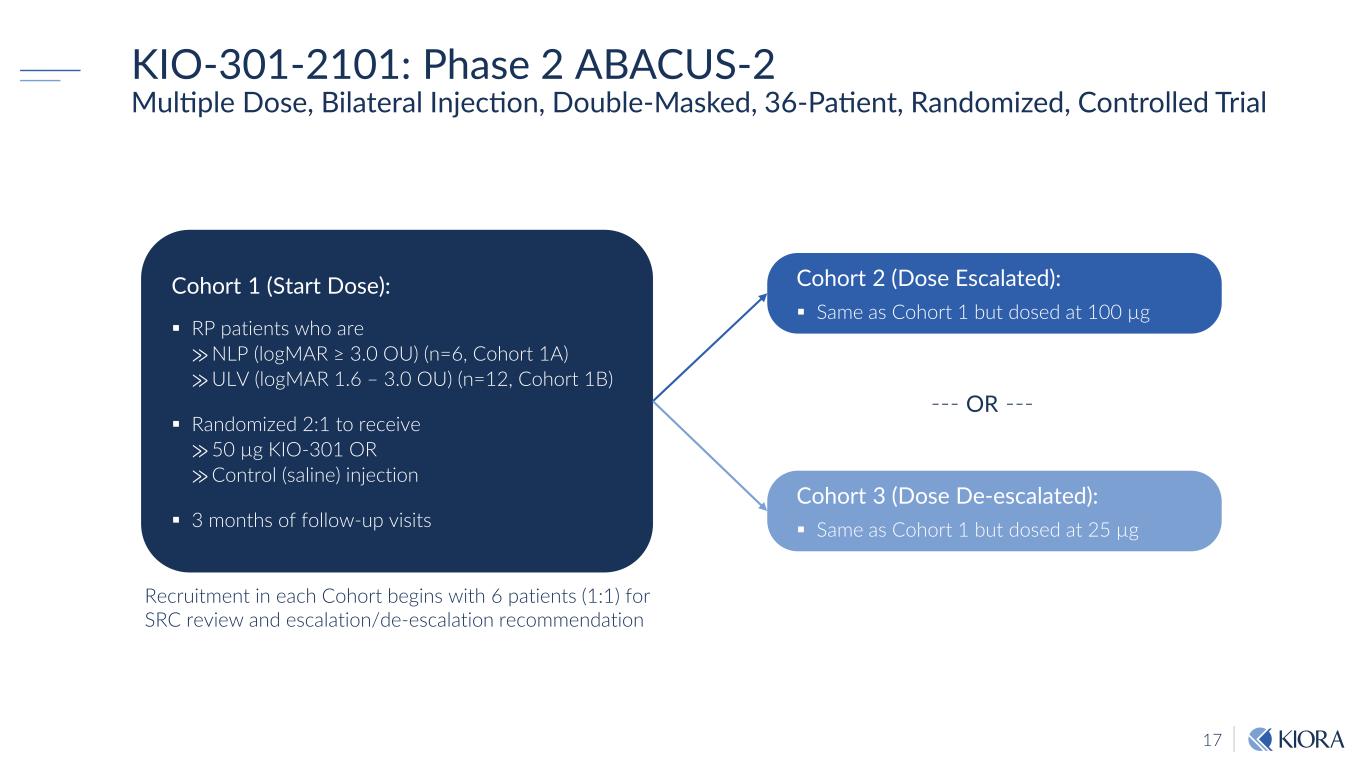
17 KIO-301-2101: Phase 2 ABACUS-2 Multiple Dose, Bilateral Injection, Double-Masked, 36-Patient, Randomized, Controlled Trial Recruitment in each Cohort begins with 6 patients (1:1) for SRC review and escalation/de-escalation recommendation Cohort 2 (Dose Escalated): Same as Cohort 1 but dosed at 100 µg Cohort 1 (Start Dose): RP patients who are ⨠NLP (logMAR ≥ 3.0 OU) (n=6, Cohort 1A) ⨠ULV (logMAR 1.6 – 3.0 OU) (n=12, Cohort 1B) Randomized 2:1 to receive ⨠50 µg KIO-301 OR ⨠Control (saline) injection 3 months of follow-up visits Cohort 3 (Dose De-escalated): Same as Cohort 1 but dosed at 25 µg --- OR ---

18 KIO-104 Intravitreal Small Molecule DHODH Inhibitor Steroid-Sparing Approach to Retinal Inflammation
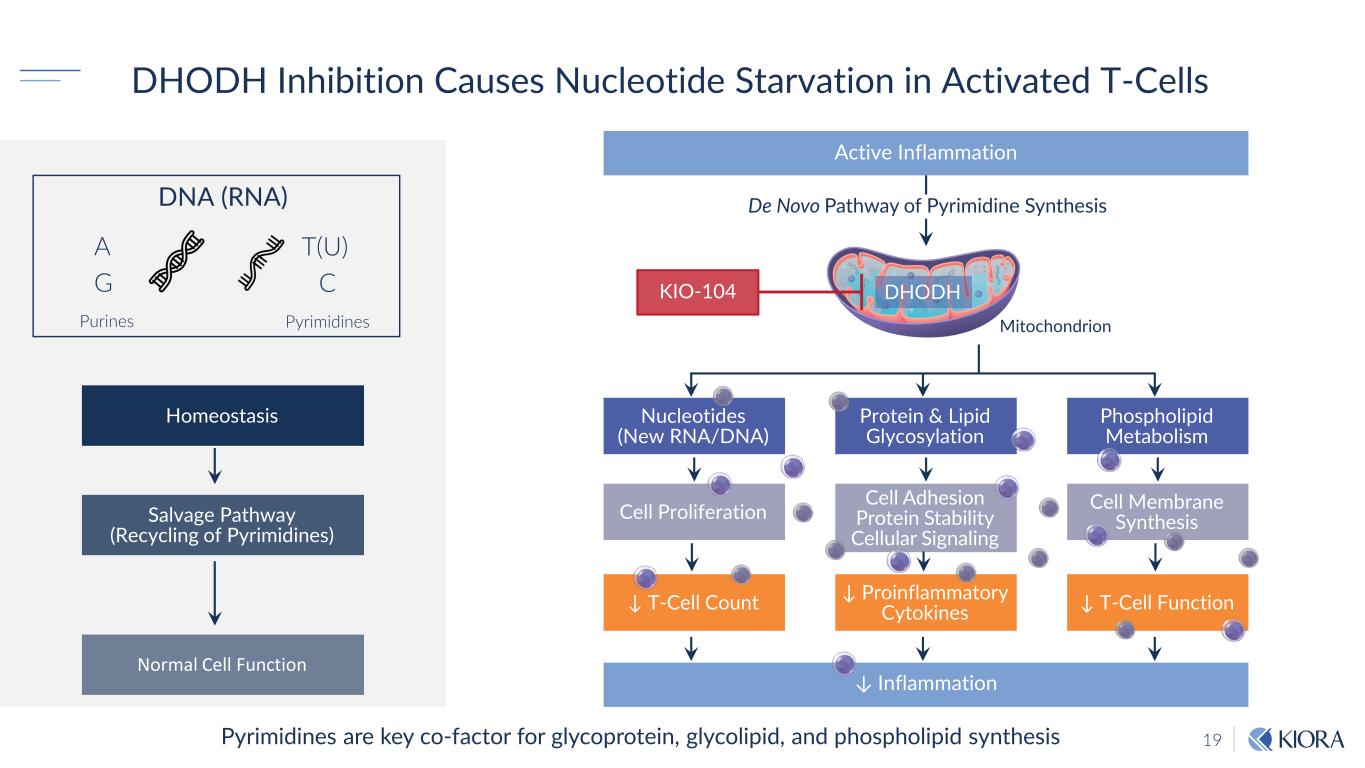
19 DHODH Inhibition Causes Nucleotide Starvation in Activated T-Cells Pyrimidines are key co-factor for glycoprotein, glycolipid, and phospholipid synthesis Homeostasis Normal Cell Function Salvage Pathway (Recycling of Pyrimidines) Active Inflammation De Novo Pathway of Pyrimidine Synthesis Nucleotides (New RNA/DNA) Protein & Lipid Glycosylation Phospholipid Metabolism ↓ T-Cell Count ↓ Proinflammatory Cytokines ↓ T-Cell Function Cell Proliferation Cell Adhesion Protein Stability Cellular Signaling Cell Membrane Synthesis ↓ Inflammation DHODH Mitochondrion KIO-104 DNA (RNA) A G T(U) C Purines Pyrimidines
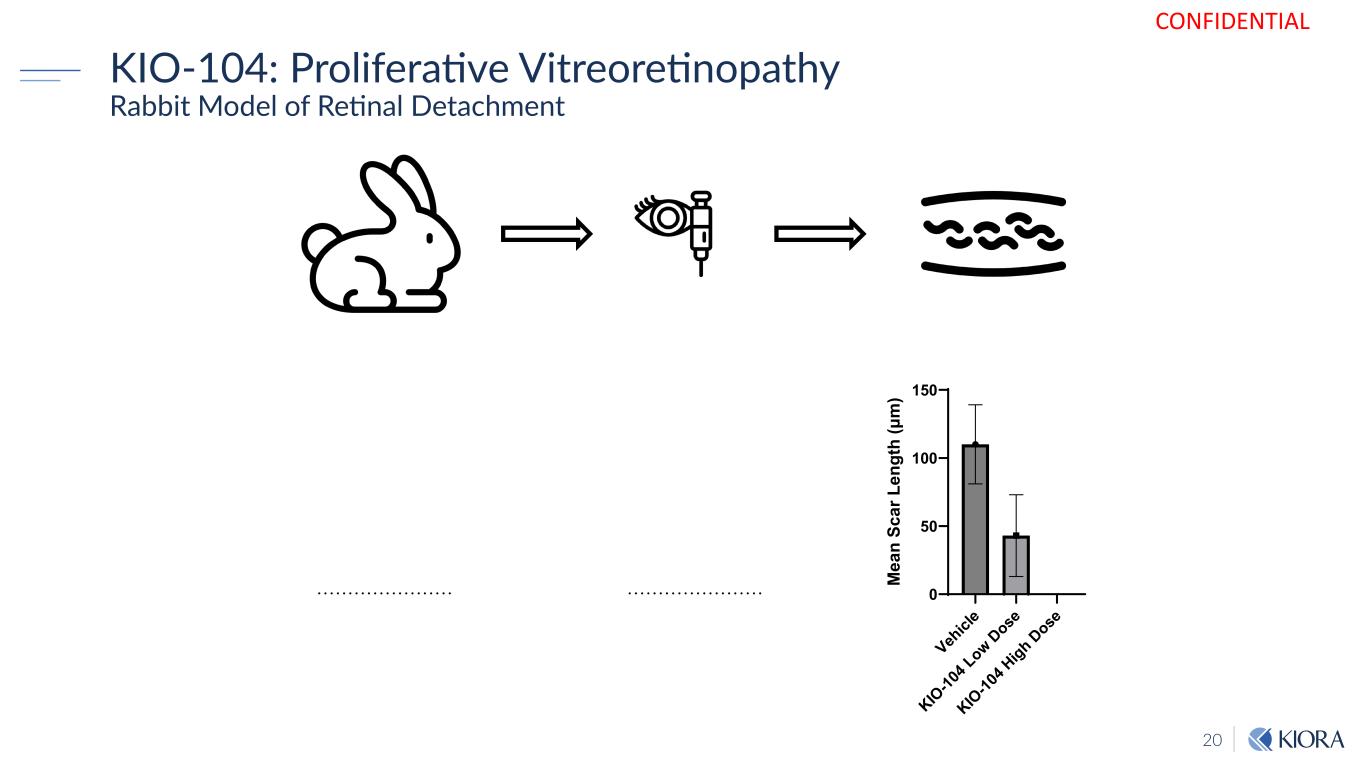
20 KIO-104: Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy Rabbit Model of Retinal Detachment CONFIDENTIAL Veh icl e KIO -10 4 L ow Dose KIO -10 4 H igh Dose 0 50 100 150 M ea n Sc ar L en gt h (μ m )
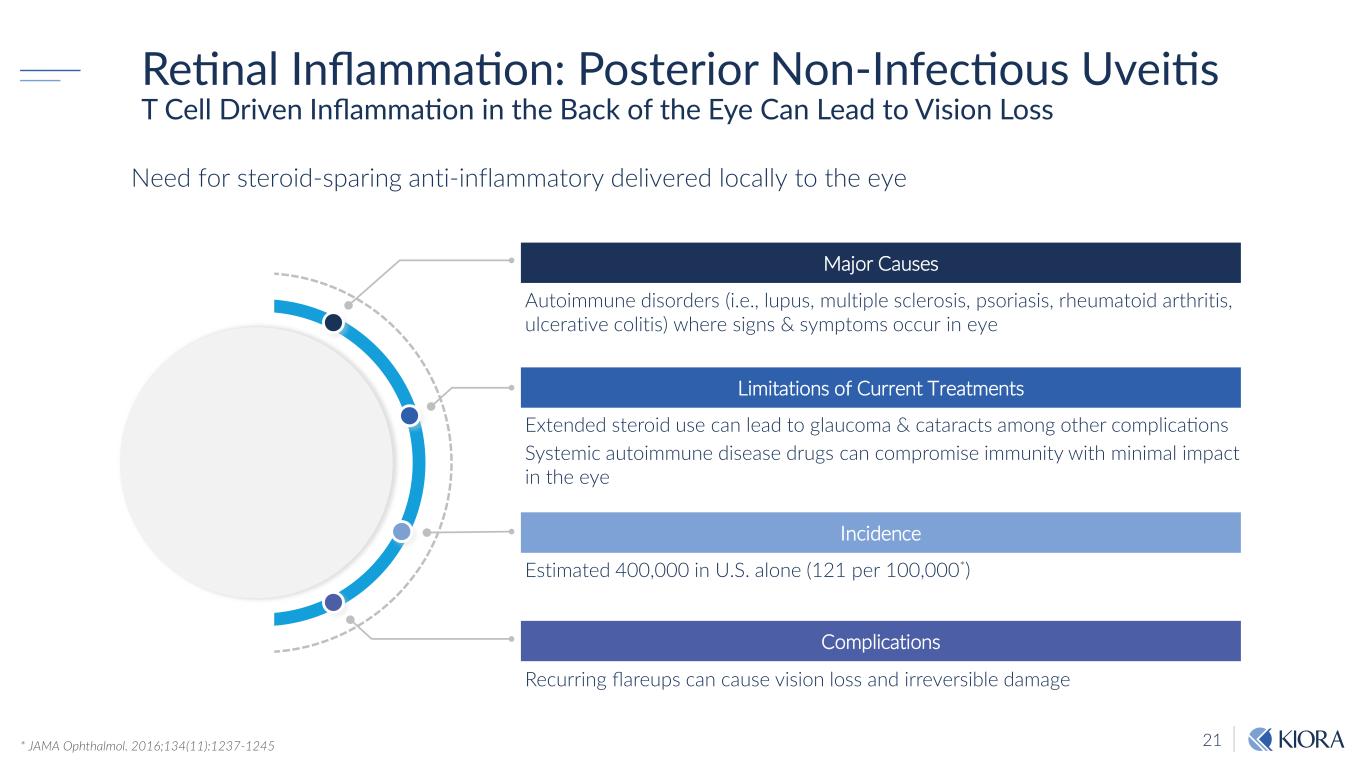
21 Need for steroid-sparing anti-inflammatory delivered locally to the eye Retinal Inflammation: Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis T Cell Driven Inflammation in the Back of the Eye Can Lead to Vision Loss Major Causes Autoimmune disorders (i.e., lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis) where signs & symptoms occur in eye Limitations of Current Treatments Extended steroid use can lead to glaucoma & cataracts among other complications Systemic autoimmune disease drugs can compromise immunity with minimal impact in the eye Incidence Estimated 400,000 in U.S. alone (121 per 100,000*) Complications Recurring flareups can cause vision loss and irreversible damage * JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(11):1237-1245

22 Phase 1/2a SAD Study Design Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis Safety and tolerability Improvement of inflammation Blood PK of KIO-100 Single intravitreal injection of 300ng, 600ng, and 1200ng Patients with chronic, posterior non-infectious uveitis Prospective, open label, multi-center, dose escalating, 4 patients in each Cohort, 12 patients in total Duration [Study Days] -14 -7 0 2 7 14 21 28 Tasks Screening / Baseline KIO-104 Injection Exam Exam Exam Exam Exam Study Design Objectives KIO-104 Administration
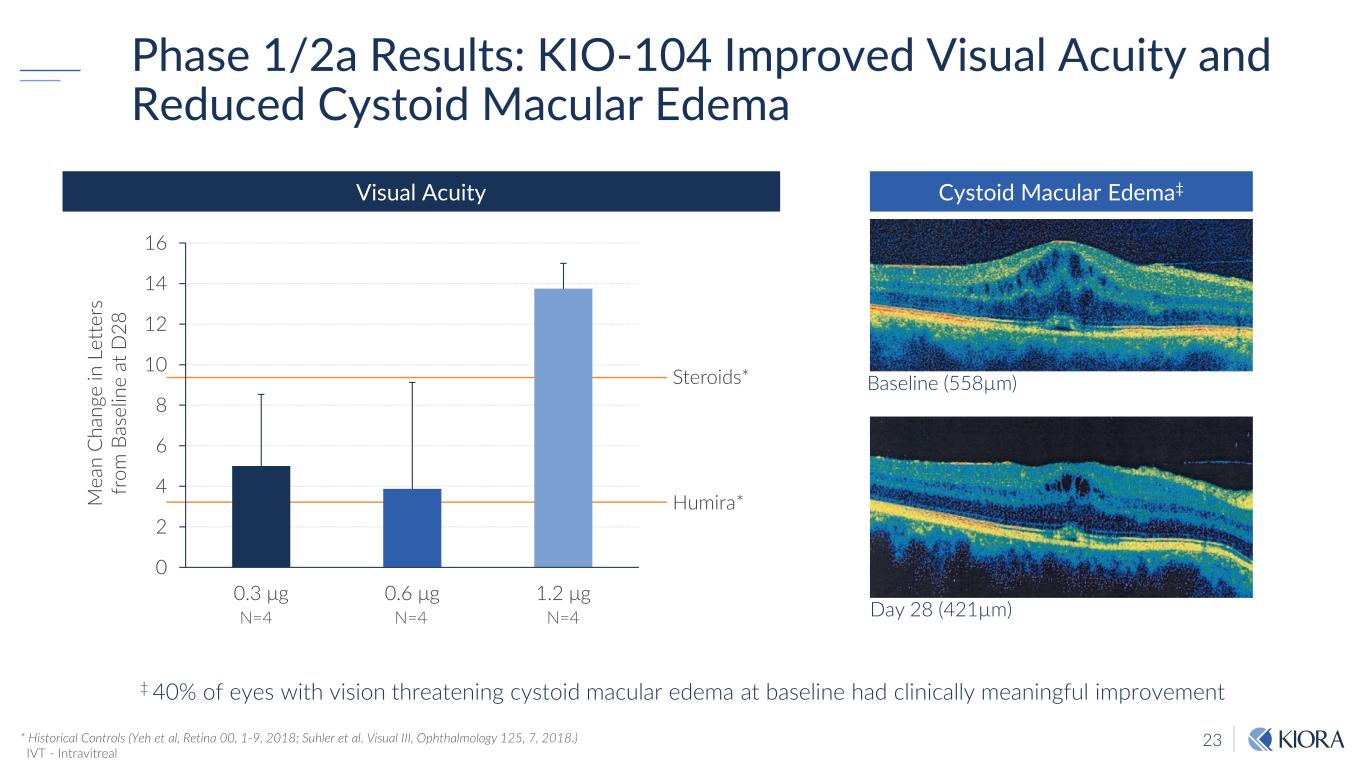
23 Phase 1/2a Results: KIO-104 Improved Visual Acuity and Reduced Cystoid Macular Edema * Historical Controls (Yeh et al, Retina 00, 1-9, 2018; Suhler et al. Visual III, Ophthalmology 125, 7, 2018.) IVT - Intravitreal 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 0.3 μg 0.6 μg 1.2 μg Steroids* Humira*M ea n C ha ng e in L et te rs fr om B as el in e at D 28 N=4 N=4 N=4 Visual Acuity Day 28 (421µm) Baseline (558µm) Cystoid Macular Edema‡ ‡ 40% of eyes with vision threatening cystoid macular edema at baseline had clinically meaningful improvement
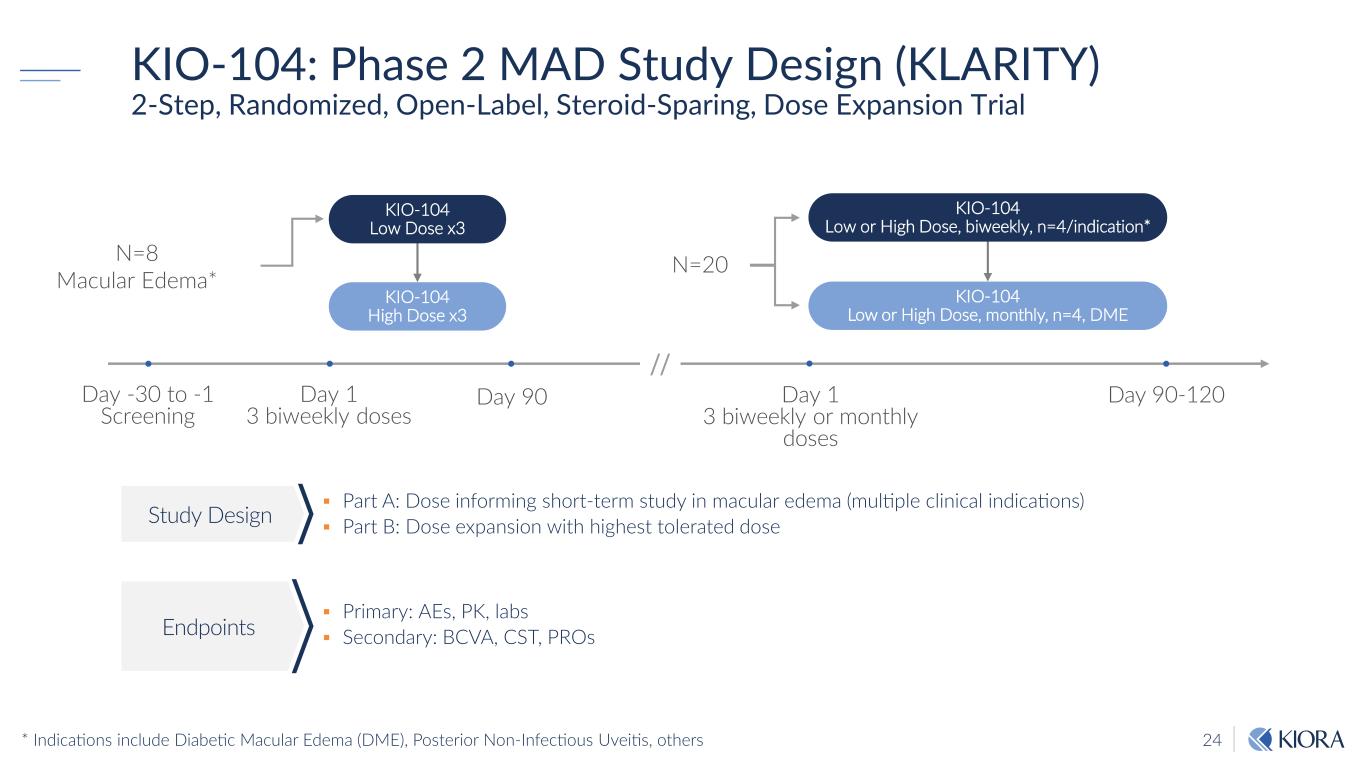
24 KIO-104: Phase 2 MAD Study Design (KLARITY) 2-Step, Randomized, Open-Label, Steroid-Sparing, Dose Expansion Trial Part A: Dose informing short-term study in macular edema (multiple clinical indications) Part B: Dose expansion with highest tolerated dose Primary: AEs, PK, labs Secondary: BCVA, CST, PROs Study Design Endpoints N=8 Macular Edema* KIO-104 Low Dose x3 KIO-104 Low or High Dose, biweekly, n=4/indication* KIO-104 High Dose x3 KIO-104 Low or High Dose, monthly, n=4, DME N=20 Day 1 3 biweekly doses Day 90-120Day 90 Day 1 3 biweekly or monthly doses Day -30 to -1 Screening // * Indications include Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis, others

Thank You NASDAQ: KPRX