EX-99.2
Published on October 29, 2024

Kiora Pharmaceuticals, Inc. NASDAQ: KPRX Q4 2024 | Corporate Overview

2 Forward Looking Statements Some of the statements in this presentation are "forward-looking" and are made pursuant to the safe harbor provision of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These "forward-looking" statements include statements relating to, among other things, the development and commercialization efforts and other regulatory or marketing approval efforts pertaining to Kiora's development-stage products, including KIO-301 and KIO-104, as well as the success thereof, with such approvals or success may not be obtained or achieved on a timely basis or at all, the potential ability of KIO-301 to restore vision in patients with RP, the expecting timing of enrollment, dosing and topline results for the ABACUS study, the ability to develop KIO-301 for Choroideremia and Stargardt Disease and KIO-104 for posterior non-infectious uveitis, the ability to utilize strategic relationships to develop certain product candidates, Kiora’s ability to maintain the listing of our common stock on a national securities exchange, and Kiora's ability to achieve the specific milestones described herein. These statements involve risks and uncertainties that may cause results to differ materially from the statements set forth in this presentation, including, among other things, the ability to conduct clinical trials on a timely basis, the ability to obtain any required regulatory approvals, market and other conditions and certain risk factors described under the heading "Risk Factors" contained in Kiora's Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on March 25, 2024, or described in Kiora's other public filings. Kiora's results may also be affected by factors of which Kiora is not currently aware. The forward-looking statements in this presentation speak only as of the date of this presentation. Kiora expressly disclaims any obligation or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to such statements to reflect any change in its expectations with regard thereto or any changes in the events, conditions, or circumstances on which any such statement is based, except as required by law.

3 Developing Treatments for Retinal Diseases Improve Sight in Patients with Severe Vision Loss and High Unmet Needs Patient Perspective Individual’s burden of disease Physicians Perspective Efficient, cost-effective treatments Societal Perspective 70% of blind patients are unemployed

4 Why Retinal Diseases? “…the last light sensations faded and the dark discs had finally overwhelmed me. I had fought them bravely, as it seemed to me, for thirty-six years, but to no avail. It was then I began to sink into the deep ocean, and finally learn how to touch the rock on the far side of despair.” - John M. Hull, Touching the Rock JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(10) 0 20 40 60 Re sp on de nt s (% ) Conditions with Greatest Effect on Day-to-Day Life 0 5 10 15 20 25 Re sp on de nt s (% ) Rankings of Worst Conditions
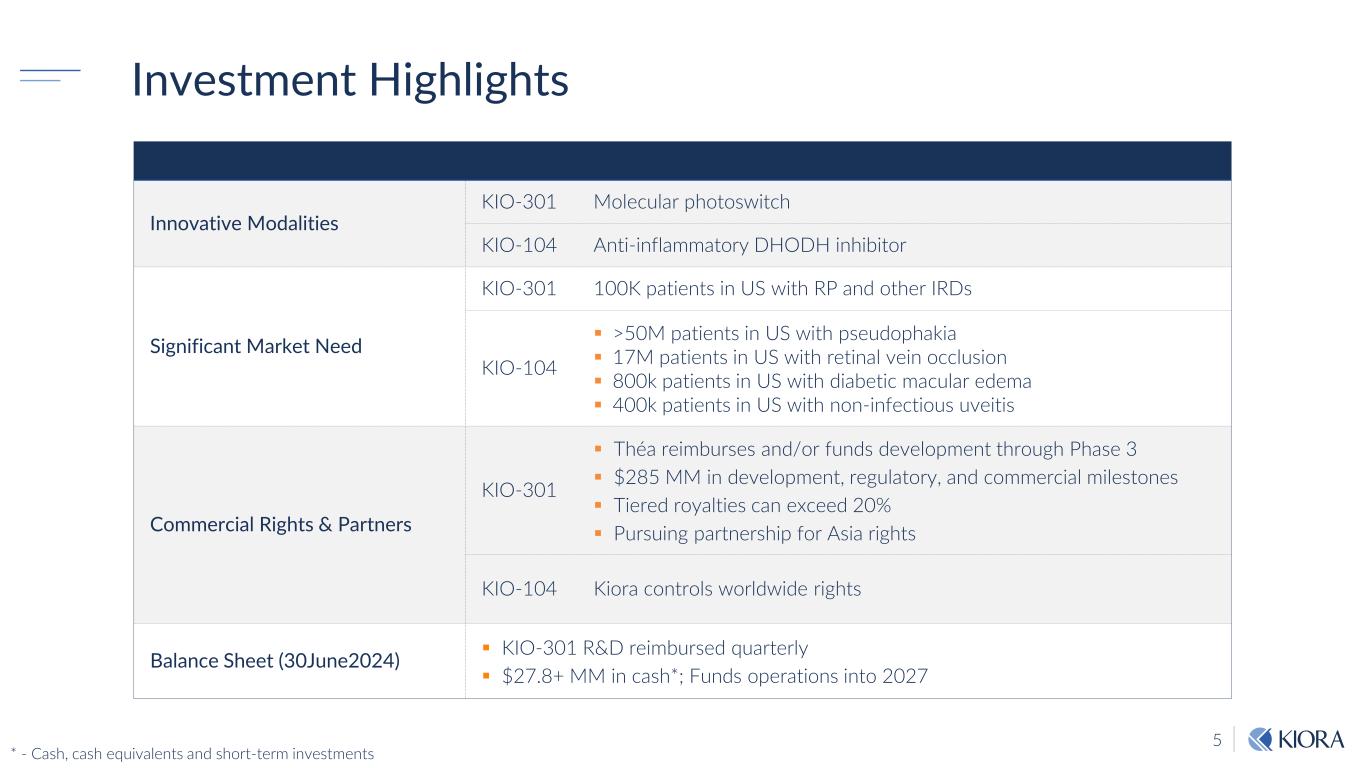
5 Investment Highlights Innovative Modalities KIO-301 Molecular photoswitch KIO-104 Anti-inflammatory DHODH inhibitor Significant Market Need KIO-301 100K patients in US with RP and other IRDs KIO-104 >50M patients in US with pseudophakia 17M patients in US with retinal vein occlusion 800k patients in US with diabetic macular edema 400k patients in US with non-infectious uveitis Commercial Rights & Partners KIO-301 Théa reimburses and/or funds development through Phase 3 $285 MM in development, regulatory, and commercial milestones Tiered royalties can exceed 20% Pursuing partnership for Asia rights KIO-104 Kiora controls worldwide rights Balance Sheet (30June2024) KIO-301 R&D reimbursed quarterly $27.8+ MM in cash*; Funds operations into 2027 * - Cash, cash equivalents and short-term investments

6 Targeting the Retina to Slow, Stop, or Restore Vision Loss Development Pipeline of Proprietary Small Molecule Therapeutics Product Indication Preclinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 Commercial Rights KIO-301 Intravitreal Retinitis Pigmentosa (Mutation Agnostic)* Théa Open Innovation (global less Asia) Choroideremia Stargardt Disease KIO-104 Intravitreal Retinal Inflammation Kiora Pharmaceuticals Proliferative Vitreoretinopathy * - Orphan Disease Designation granted in the USA and EU

7 KIO-104 Intravitreal Small Molecule DHODH Inhibitor Steroid-Sparing Approach to Retinal Inflammation
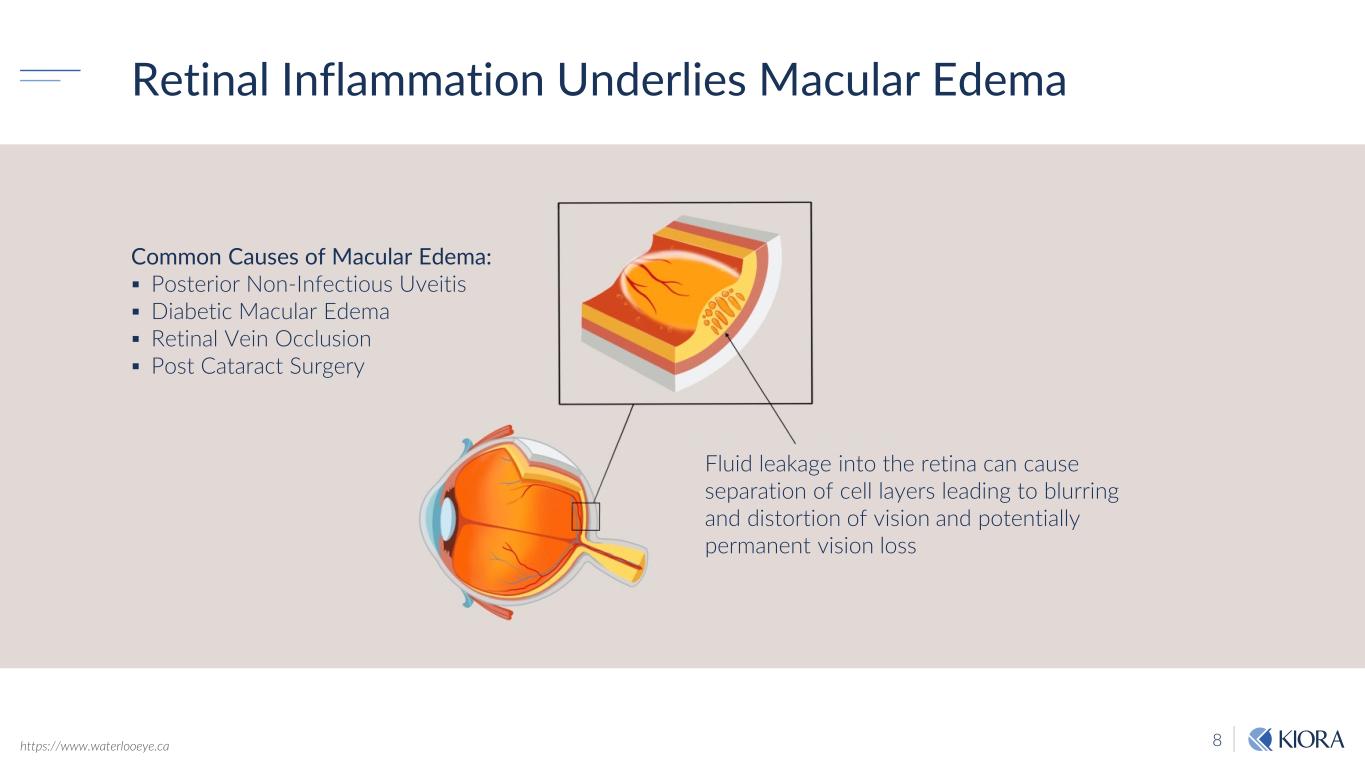
8 Retinal Inflammation Underlies Macular Edema Fluid leakage into the retina can cause separation of cell layers leading to blurring and distortion of vision and potentially permanent vision loss https://www.waterlooeye.ca Common Causes of Macular Edema: Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis Diabetic Macular Edema Retinal Vein Occlusion Post Cataract Surgery

9 T-cells are known to play a fundamental role in inducing ocular inflammation Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH) inhibitors are well established, disease-modifying agents in autoimmune conditions KIO-104 Mechanism of Action DHODH inhibition reduces the cellular pyrimidine pool resulting in: Reduction of T-cell proliferation Downregulation of cellular messengers (IL-17, IFN-ɤ, VEGF, etc.) Dihydroorotate Orotate / Pyrimidines KIO-104 Inhibits DHODH Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH) Dihydroorotate Orotate / Pyrimidines DHODH necessary for production of pyrimidines Pyrimidines necessary for T-cell production and normal cell function Dihydroorotate Dehydrogenase (DHODH) Normal Process By inhibiting DHODH, one reduces ocular inflammation KIO-104 Clinical Aim KIO-104 Inflammation Reduces Inflammation

10 Need for steroid-sparing anti-inflammatory delivered locally to the eye Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis: a T-Cell Driven Disease Retinal Inflammation in the Back of the Eye Can Lead to Vision Loss Major Causes Autoimmune disorders (i.e., lupus, multiple sclerosis, psoriasis, rheumatoid arthritis, ulcerative colitis) where signs & symptoms occur in eye Limitations of Current Treatments Extended steroid use can lead to glaucoma, cataracts among other complications Systemic autoimmune disease drugs can compromise immunity with minimal impact in the eye Incidence Estimated 400,000 in U.S,. alone (121 per 100,000*) Complications Recurring flareups can cause vision loss and irreversible damage * JAMA Ophthalmol. 2016;134(11):1237-1245
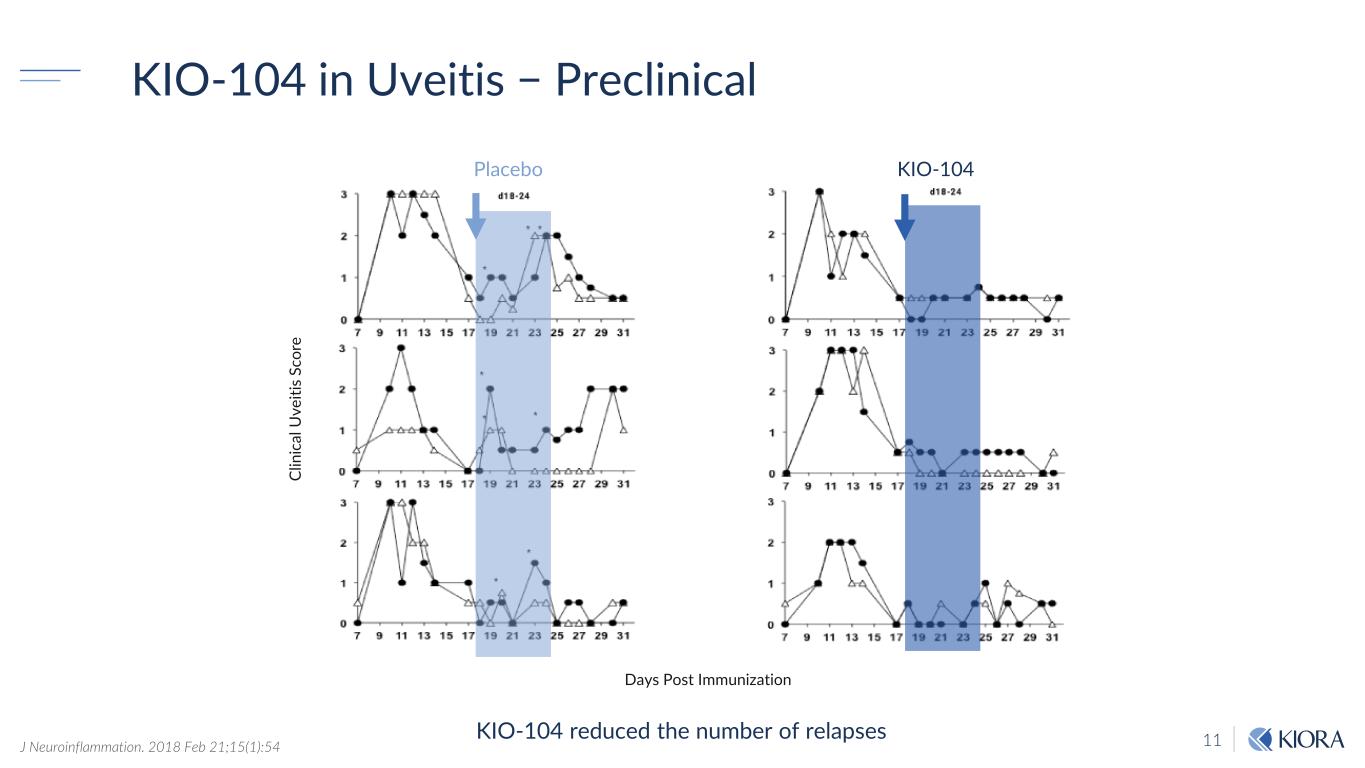
11 KIO-104 in Uveitis − Preclinical KIO-104 reduced the number of relapses Placebo Days Post Immunization Cl in ic al U ve iti s Sc or e KIO-104 J Neuroinflammation. 2018 Feb 21;15(1):54

12 Phase 1/2a Study Design Safety and tolerability Improvement of inflammation Blood PK of KIO-100 Single intravitreal injection of 300ng, 600ng, and 1200ng (any systemic therapy at enrollment was continued) Patients with chronic, posterior non-infectious uveitis Prospective, open label, multi-center, dose escalating, 4 patients in each Cohort, 12 patients in total Duration [Study Days] -14 -7 0 2 7 14 21 28 Tasks Screening / Baseline KIO-104 Injection Exam Exam Exam Exam Exam Study Design Objectives PaniJect Administration

13 KIO-104 Phase 1/2a Results Safety & Tolerability ✓ No SAE ✓ Excellent tolerability at all doses Pharmacokinetics ✓ KIO-100 was not detected in the peripheral blood at any time
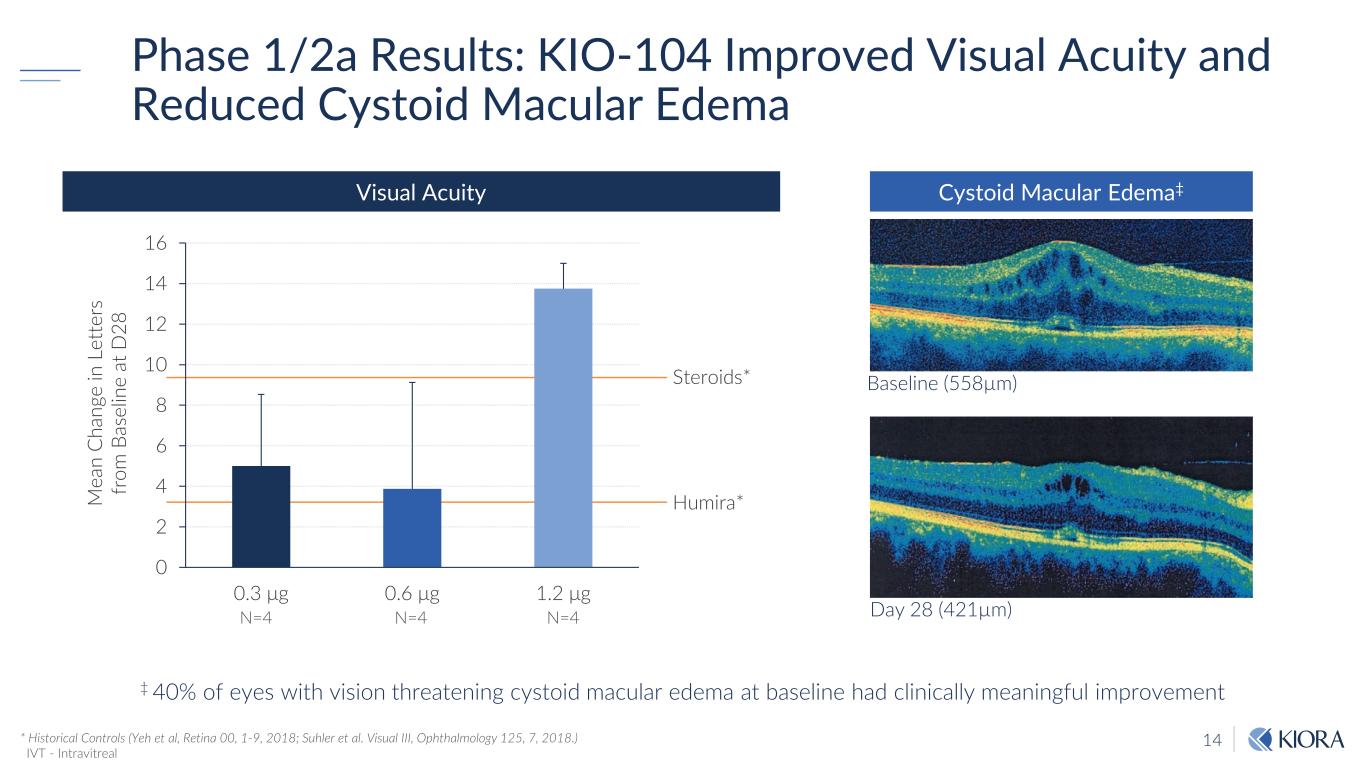
14 Phase 1/2a Results: KIO-104 Improved Visual Acuity and Reduced Cystoid Macular Edema * Historical Controls (Yeh et al, Retina 00, 1-9, 2018; Suhler et al. Visual III, Ophthalmology 125, 7, 2018.) IVT - Intravitreal 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 0.3 μg 0.6 μg 1.2 μg Steroids* Humira*M ea n C ha ng e in L et te rs fr om B as el in e at D 28 N=4 N=4 N=4 Visual Acuity Day 28 (421µm) Baseline (558µm) Cystoid Macular Edema‡ ‡ 40% of eyes with vision threatening cystoid macular edema at baseline had clinically meaningful improvement
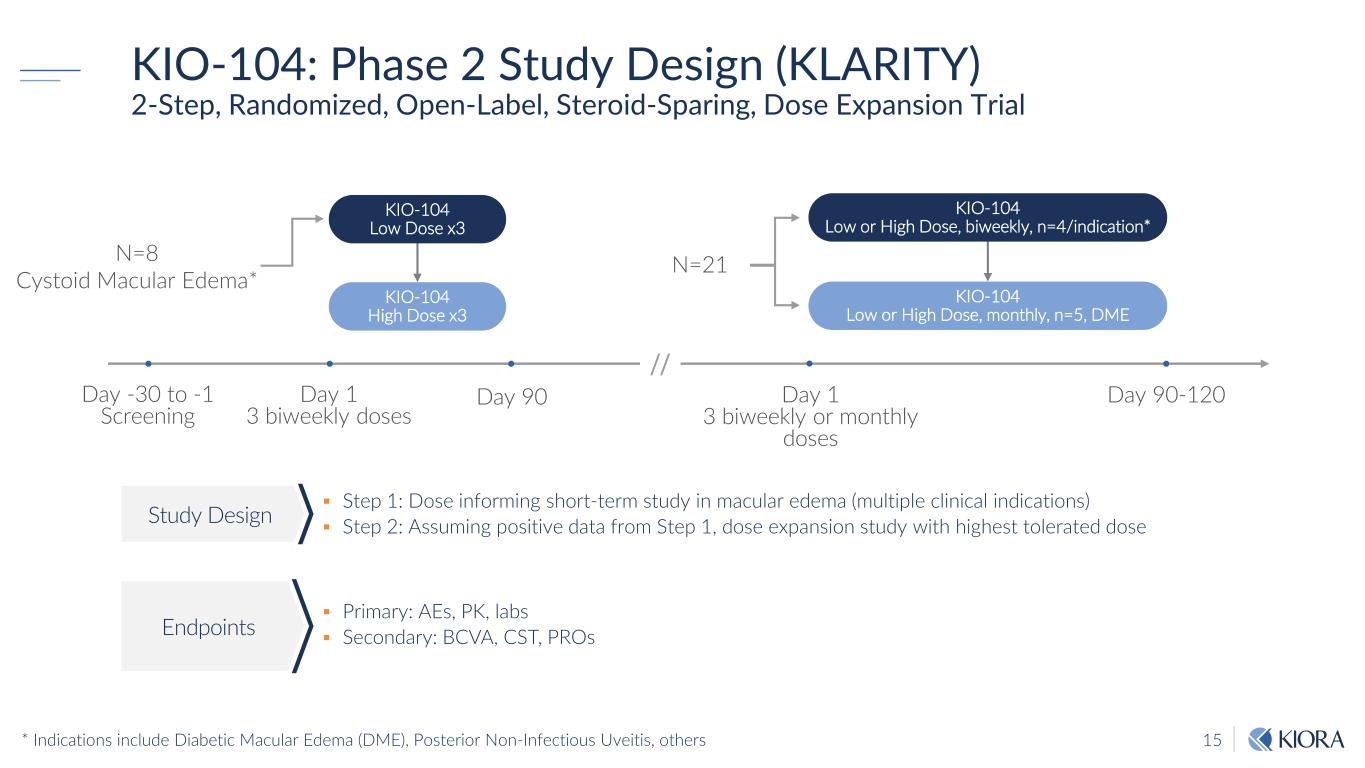
15 KIO-104: Phase 2 Study Design (KLARITY) 2-Step, Randomized, Open-Label, Steroid-Sparing, Dose Expansion Trial Step 1: Dose informing short-term study in macular edema (multiple clinical indications) Step 2: Assuming positive data from Step 1, dose expansion study with highest tolerated dose Primary: AEs, PK, labs Secondary: BCVA, CST, PROs Study Design Endpoints N=8 Cystoid Macular Edema* KIO-104 Low Dose x3 KIO-104 Low or High Dose, biweekly, n=4/indication* KIO-104 High Dose x3 KIO-104 Low or High Dose, monthly, n=5, DME N=21 Day 1 3 biweekly doses Day 90-120Day 90 Day 1 3 biweekly or monthly doses Day -30 to -1 Screening // * Indications include Diabetic Macular Edema (DME), Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis, others

16 KIO-301 Small Molecule Targeting Vision Restoration Inherited Retinal Diseases

17 Inherited Retinal Diseases (IRDs) Lead to Loss of Vision Healthy Vision Rods and cones, the photoreceptors of the retina, process light and relay an electrical signal to downstream cells One of these cell types, retinal ganglion cells (RGCs), transmit the signal to the visual cortex The visual cortex is the part of the brain where vision is perceived Damage from IRDs IRDs, including Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP), result in progressive degeneration and loss of function of rods and cones This causes continuous impairment of vision that often leads to blindness Importantly, many IRDs do not affect the RGCs Rods & Cones Light RGCs Rods & Cones Light RGCs
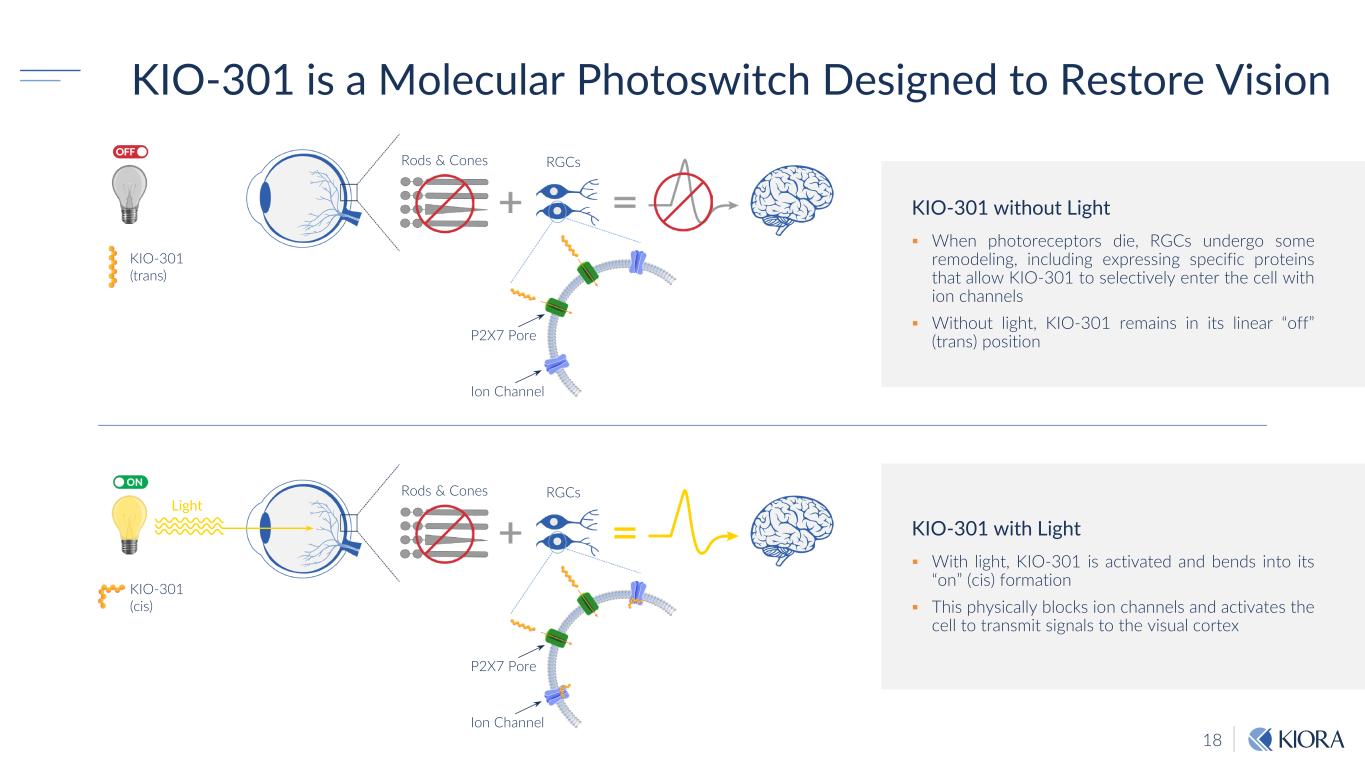
18 KIO-301 is a Molecular Photoswitch Designed to Restore Vision KIO-301 without Light When photoreceptors die, RGCs undergo some remodeling, including expressing specific proteins that allow KIO-301 to selectively enter the cell with ion channels Without light, KIO-301 remains in its linear “off” (trans) position KIO-301 with Light With light, KIO-301 is activated and bends into its “on” (cis) formation This physically blocks ion channels and activates the cell to transmit signals to the visual cortex Rods & Cones RGCs KIO-301 (trans) P2X7 Pore Ion Channel Rods & Cones Light RGCs KIO-301 (cis) P2X7 Pore Ion Channel

19 KIO-301 Reanimates the Retina & Changes Behavior Extensive Validation in Preclinical Models Neuron 2014: 81, 800-813. Behavioral study used a homologue molecule to KIO-301 API
20https://taiwanird.com.tw/ Inherited Retinal Disease Landscape Leber Congenital Amaurosis (LCA) Cone-Rod Dystrophy (CRD) Color Vision Defects (CVD) Stargardt Disease (SD) Vitreo-retinopathy Bietti Crystalline Dystrophy (BCD) Retinoschisis Choroideremia (CHM) Congenital Night Blindness (CNB) Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP)
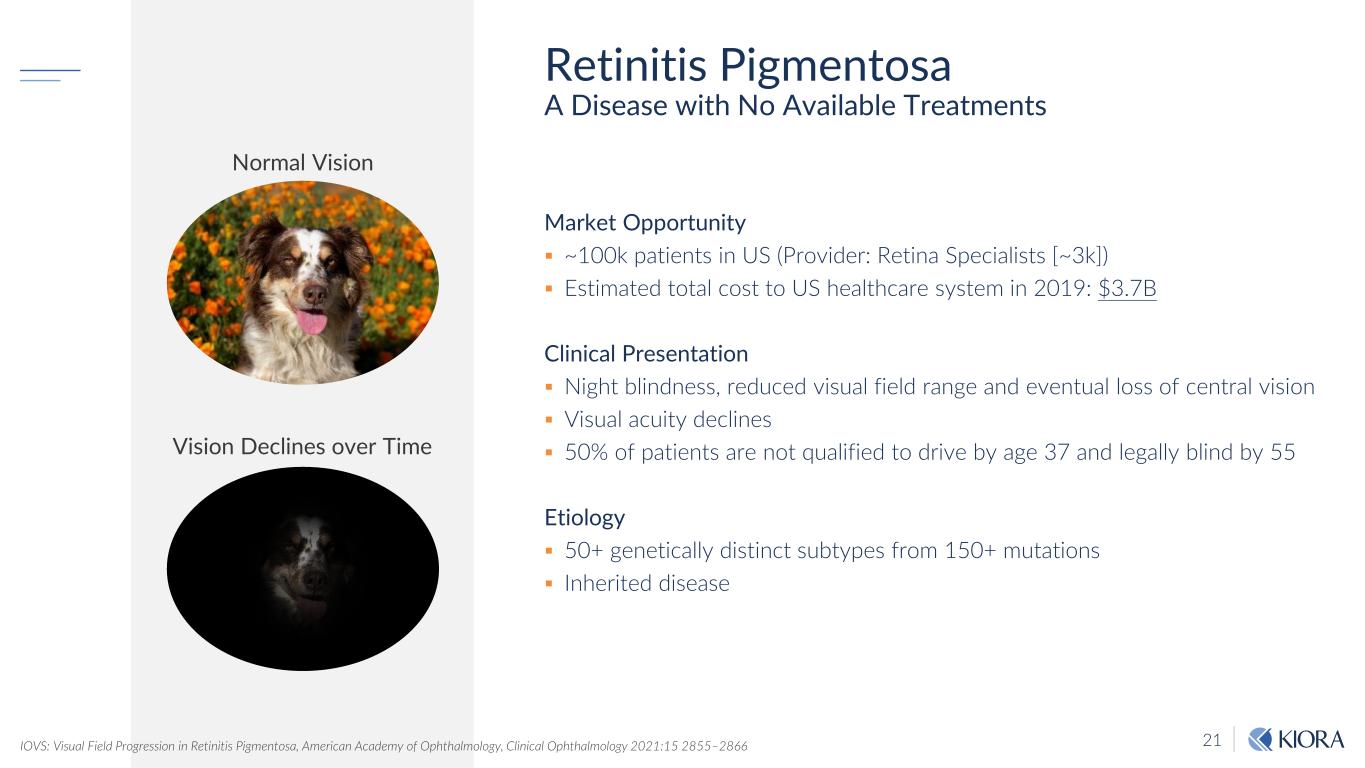
21 Market Opportunity ~100k patients in US (Provider: Retina Specialists [~3k]) Estimated total cost to US healthcare system in 2019: $3.7B Clinical Presentation Night blindness, reduced visual field range and eventual loss of central vision Visual acuity declines 50% of patients are not qualified to drive by age 37 and legally blind by 55 Etiology 50+ genetically distinct subtypes from 150+ mutations Inherited disease Retinitis Pigmentosa A Disease with No Available Treatments Normal Vision Vision Declines over Time IOVS: Visual Field Progression in Retinitis Pigmentosa, American Academy of Ophthalmology, Clinical Ophthalmology 2021:15 2855–2866
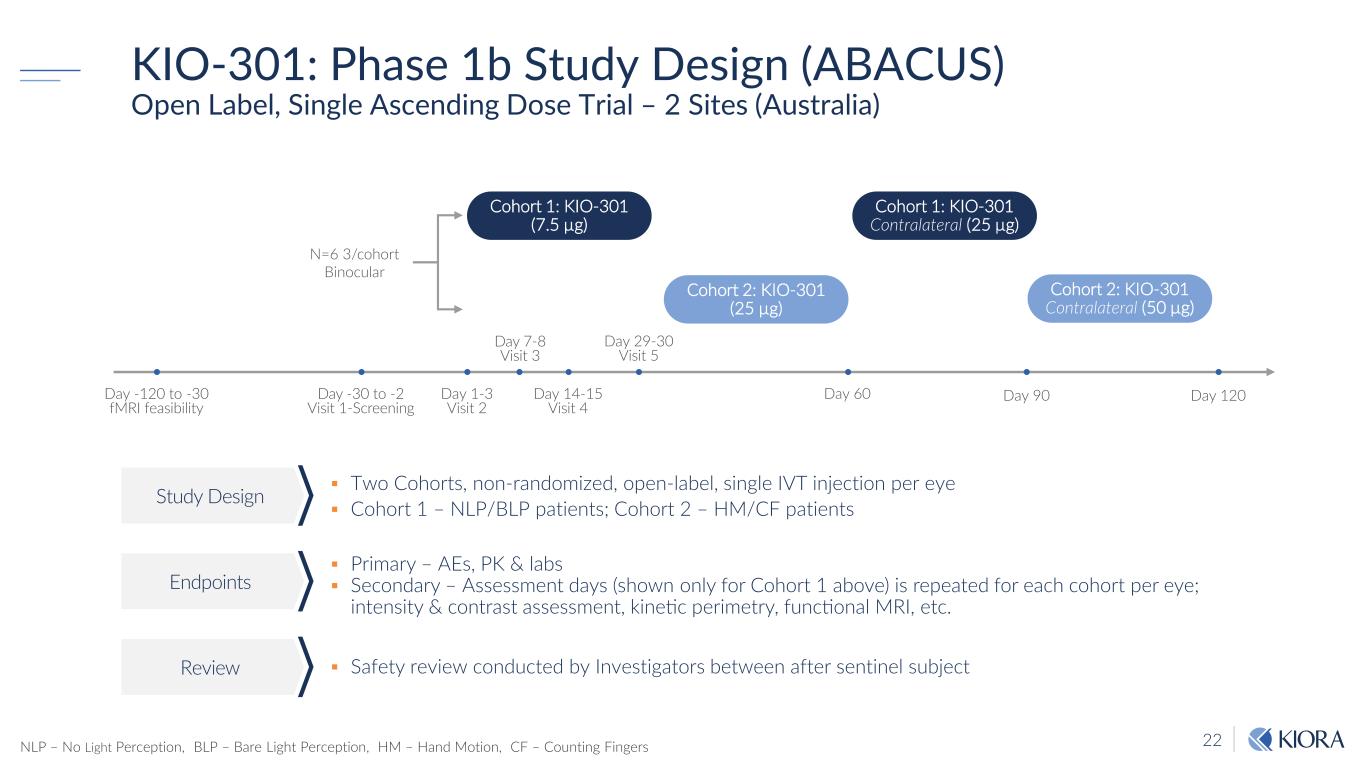
22 KIO-301: Phase 1b Study Design (ABACUS) Open Label, Single Ascending Dose Trial – 2 Sites (Australia) Two Cohorts, non-randomized, open-label, single IVT injection per eye Cohort 1 – NLP/BLP patients; Cohort 2 – HM/CF patients Primary – AEs, PK & labs Secondary – Assessment days (shown only for Cohort 1 above) is repeated for each cohort per eye; intensity & contrast assessment, kinetic perimetry, functional MRI, etc. Safety review conducted by Investigators between after sentinel subject Study Design Endpoints Review N=6 3/cohort Binocular Day 90 Cohort 1: KIO-301 (7.5 µg) Day -30 to -2 Visit 1-Screening Day 29-30 Visit 5 Day 60 Day 120 Cohort 1: KIO-301 Contralateral (25 µg) Cohort 2: KIO-301 (25 µg) Cohort 2: KIO-301 Contralateral (50 µg) Day 1-3 Visit 2 Day 7-8 Visit 3 Day 14-15 Visit 4 Day -120 to -30 fMRI feasibility NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception, HM – Hand Motion, CF – Counting Fingers
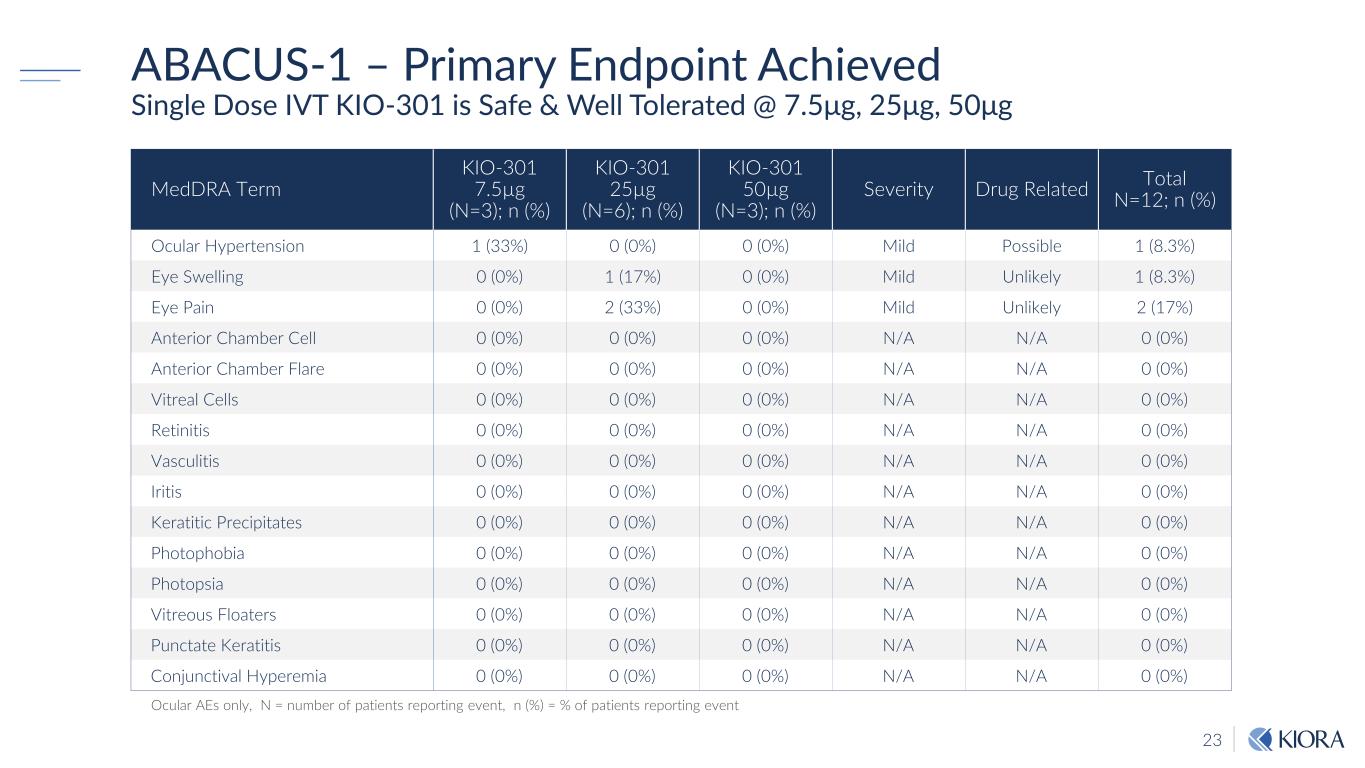
23 ABACUS-1 – Primary Endpoint Achieved Single Dose IVT KIO-301 is Safe & Well Tolerated @ 7.5μg, 25μg, 50μg MedDRA Term KIO-301 7.5µg (N=3); n (%) KIO-301 25µg (N=6); n (%) KIO-301 50µg (N=3); n (%) Severity Drug Related Total N=12; n (%) Ocular Hypertension 1 (33%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) Mild Possible 1 (8.3%) Eye Swelling 0 (0%) 1 (17%) 0 (0%) Mild Unlikely 1 (8.3%) Eye Pain 0 (0%) 2 (33%) 0 (0%) Mild Unlikely 2 (17%) Anterior Chamber Cell 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Anterior Chamber Flare 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Vitreal Cells 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Retinitis 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Vasculitis 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Iritis 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Keratitic Precipitates 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Photophobia 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Photopsia 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Vitreous Floaters 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Punctate Keratitis 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Conjunctival Hyperemia 0 (0%) 0 (0%) 0 (0%) N/A N/A 0 (0%) Ocular AEs only, N = number of patients reporting event, n (%) = % of patients reporting event
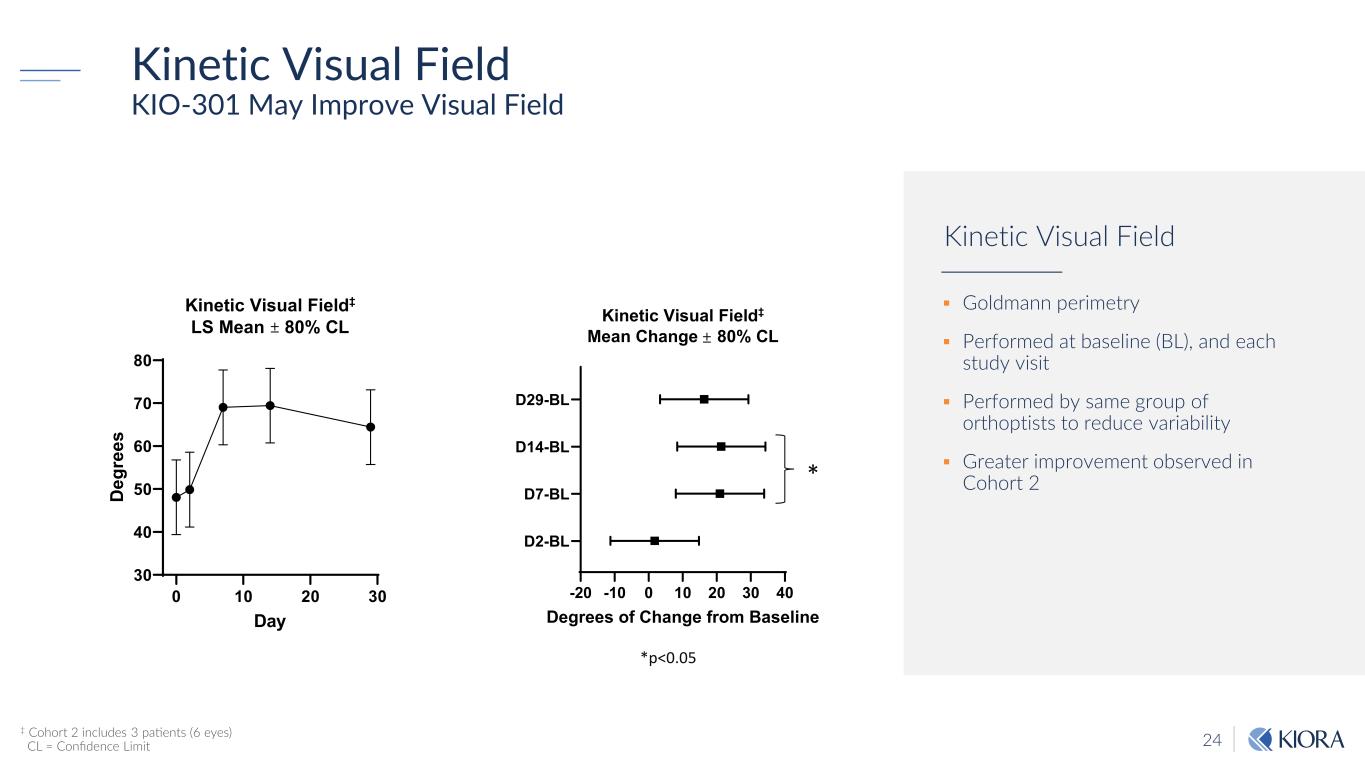
24 Kinetic Visual Field KIO-301 May Improve Visual Field ‡ Cohort 2 includes 3 patients (6 eyes) CL = Confidence Limit Goldmann perimetry Performed at baseline (BL), and each study visit Performed by same group of orthoptists to reduce variability Greater improvement observed in Cohort 2 Kinetic Visual Field -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 D2-BL D7-BL D14-BL D29-BL Kinetic Visual Field‡ Mean Change ± 80% CL Degrees of Change from Baseline * *p<0.05 0 10 20 30 30 40 50 60 70 80 Kinetic Visual Field‡ LS Mean ± 80% CL Day D eg re es
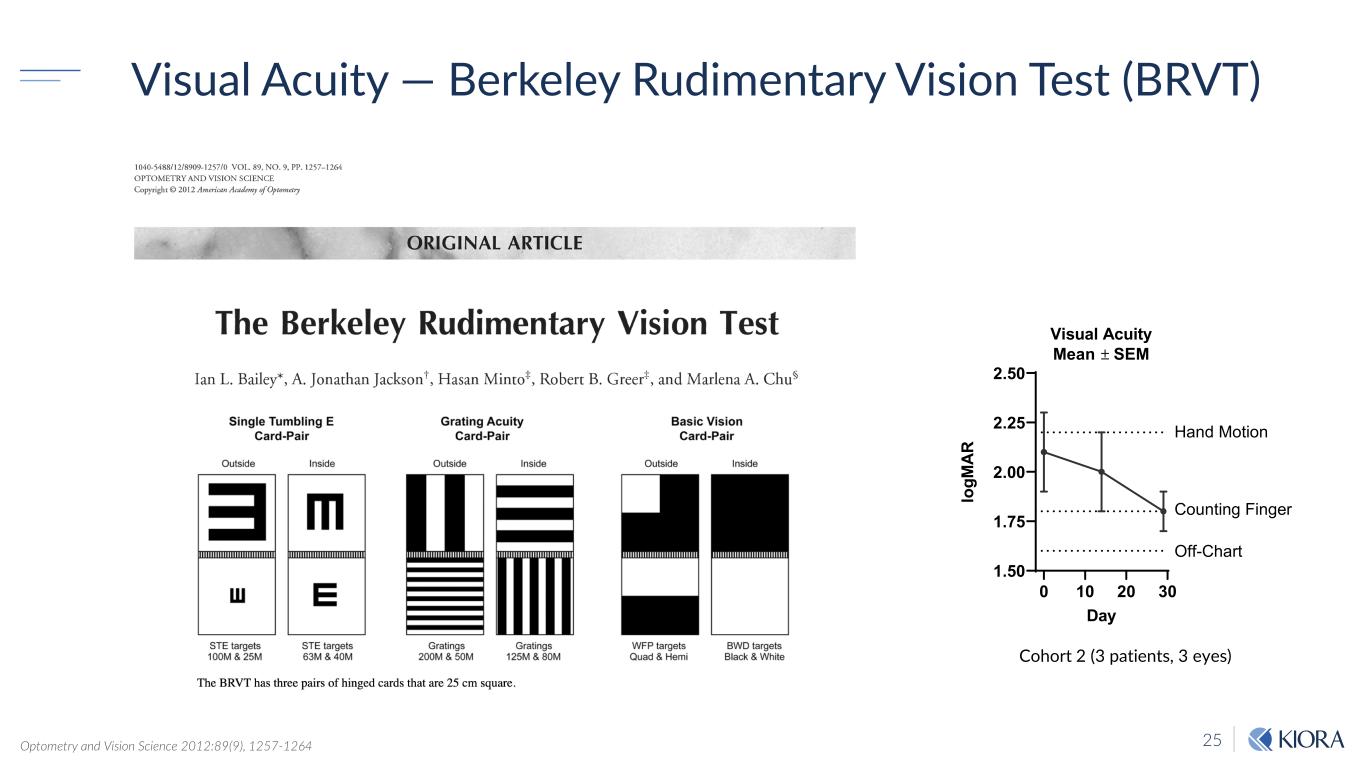
25 Visual Acuity — Berkeley Rudimentary Vision Test (BRVT) Optometry and Vision Science 2012:89(9), 1257-1264 Cohort 2 (3 patients, 3 eyes) 0 10 20 30 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 Visual Acuity Mean ± SEM Day lo gM AR Off-Chart Counting Finger Hand Motion

26 Light Perception (Intensity & Contrast Assessment) Assessment: Series of visual stimuli (a series of letters are presented on a screen to the patient via a rear projector) Binary outcome (yes/no) The subject is asked to acknowledge (verbally and/or physically) when a change in light is perceived Asked to also identify object, if possible Aim: Evaluate Light Perception at a Basic Level
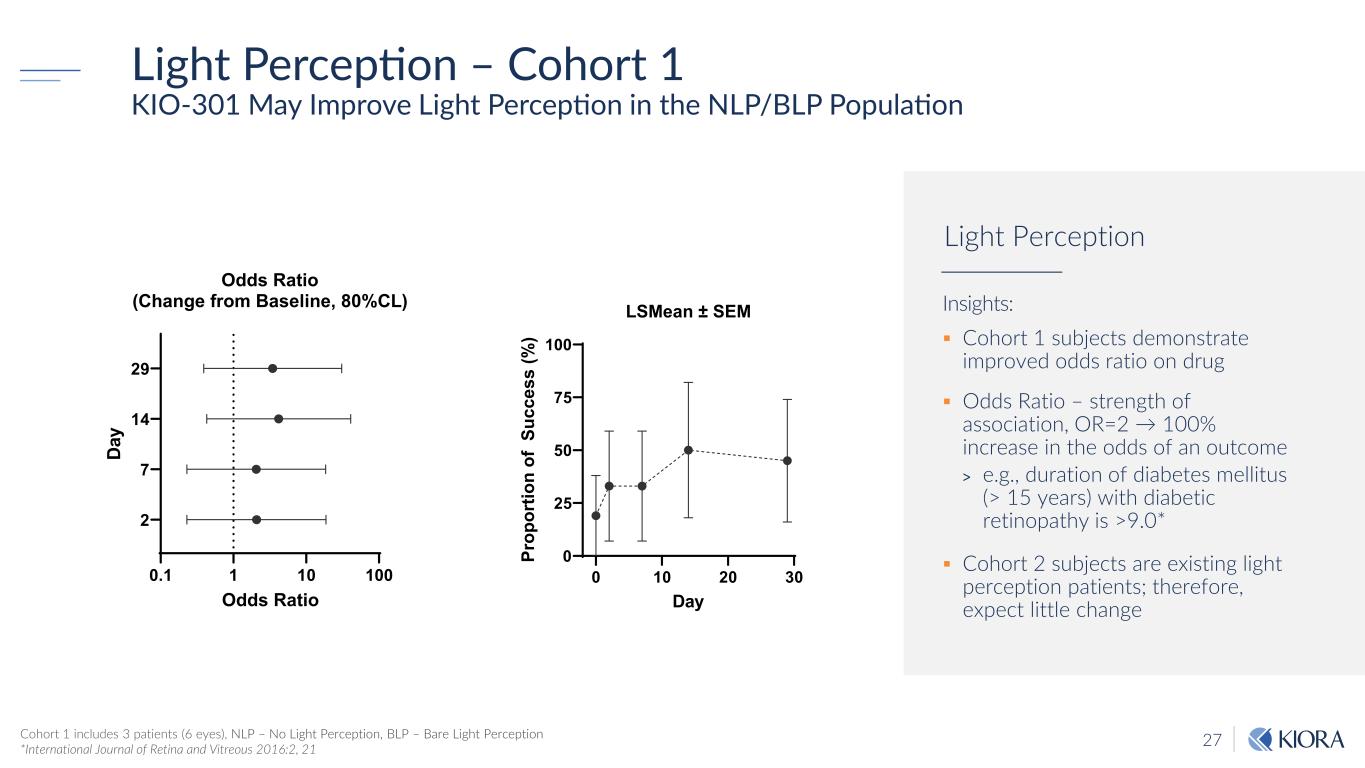
27 Light Perception – Cohort 1 KIO-301 May Improve Light Perception in the NLP/BLP Population Insights: Cohort 1 subjects demonstrate improved odds ratio on drug Odds Ratio – strength of association, OR=2 → 100% increase in the odds of an outcome > e.g., duration of diabetes mellitus (> 15 years) with diabetic retinopathy is >9.0* Cohort 2 subjects are existing light perception patients; therefore, expect little change Light Perception Cohort 1 includes 3 patients (6 eyes), NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception *International Journal of Retina and Vitreous 2016:2, 21 0 10 20 30 0 25 50 75 100 LSMean ± SEM Day Pr op or tio n of S uc ce ss (% ) 0.1 1 10 100 2 7 14 29 Odds Ratio (Change from Baseline, 80%CL) Odds Ratio Da y
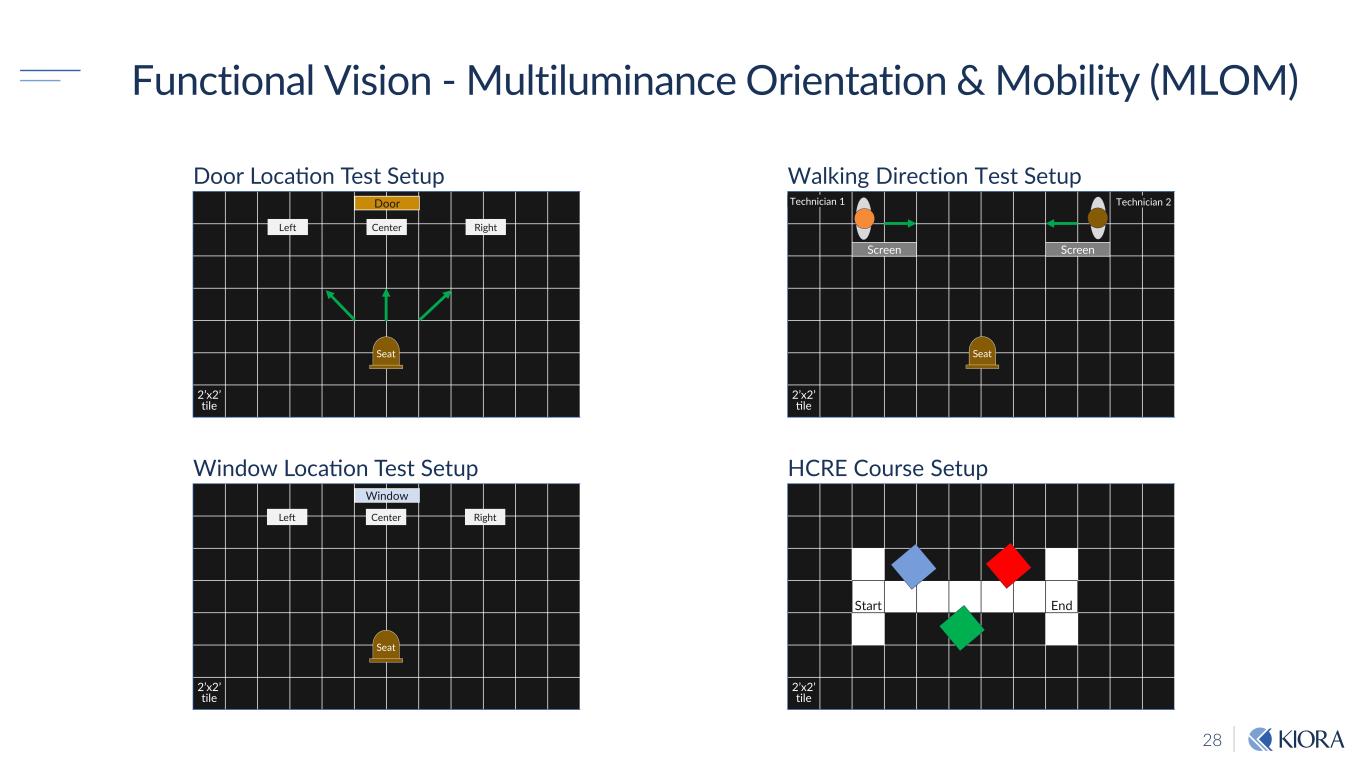
28 2’x2’ tile Door Location Test Setup Functional Vision - Multiluminance Orientation & Mobility (MLOM) 2’x2’ tile Window Location Test Setup 2’x2’ tile Walking Direction Test Setup Start End 2’x2’ tile HCRE Course Setup Screen Screen Technician 1 Technician 2Door Window Left Center Right Left Center Right Seat Seat Seat
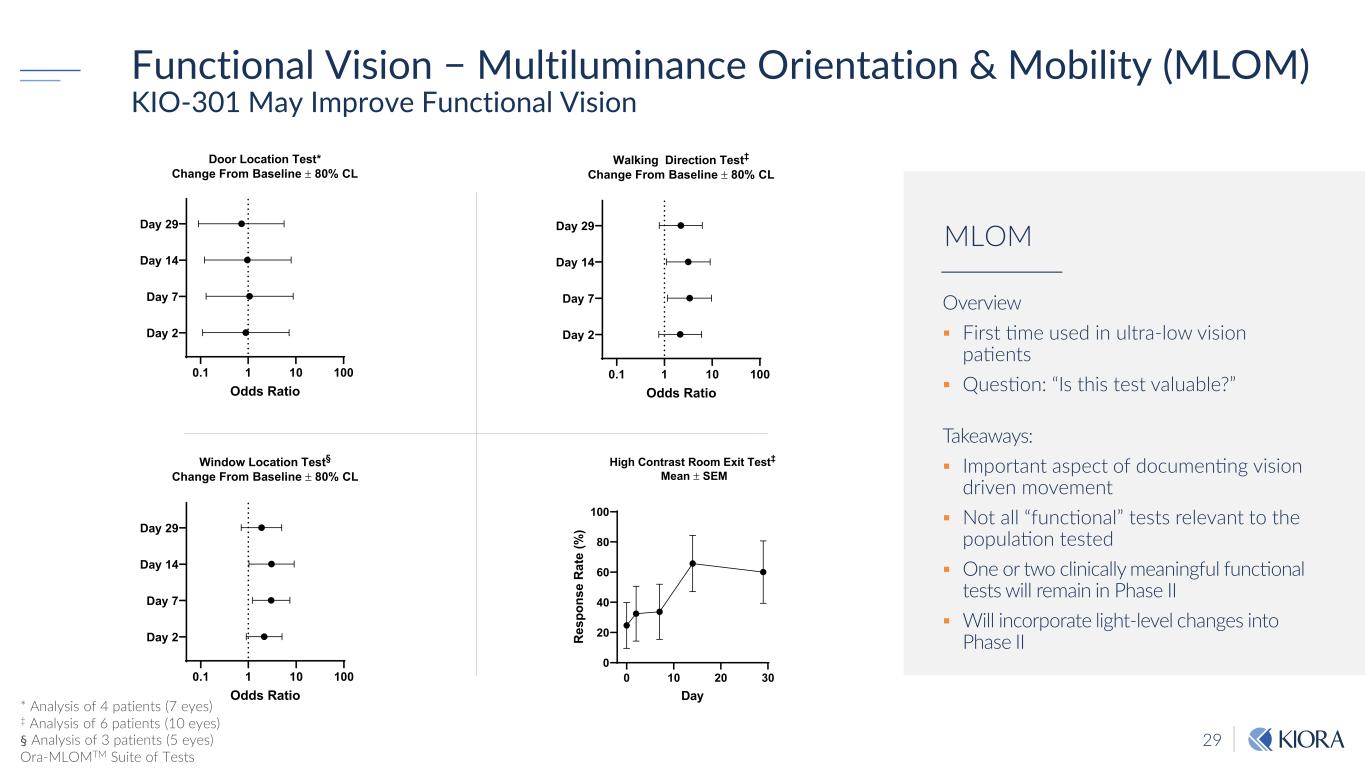
29 Functional Vision − Multiluminance Orientation & Mobility (MLOM) KIO-301 May Improve Functional Vision 0.1 1 10 100 Day 2 Day 7 Day 14 Day 29 Door Location Test* Change From Baseline ± 80% CL Odds Ratio 0.1 1 10 100 Day 2 Day 7 Day 14 Day 29 Walking Direction Test‡ Change From Baseline ± 80% CL Odds Ratio 0.1 1 10 100 Day 2 Day 7 Day 14 Day 29 Window Location Test§ Change From Baseline ± 80% CL Odds Ratio * Analysis of 4 patients (7 eyes) ‡ Analysis of 6 patients (10 eyes) § Analysis of 3 patients (5 eyes) Ora-MLOMTM Suite of Tests Overview First time used in ultra-low vision patients Question: “Is this test valuable?” Takeaways: Important aspect of documenting vision driven movement Not all “functional” tests relevant to the population tested One or two clinically meaningful functional tests will remain in Phase II Will incorporate light-level changes into Phase II MLOM 0 10 20 30 0 20 40 60 80 100 High Contrast Room Exit Test‡ Mean ± SEM Day R es po ns e R at e (% )

30 Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI VFQ-25) KIO-301 May Improve Patients’ Overall Quality of Life 0 30 35 40 45 50 Quality of Life Survey Day VF Q -2 5 C om po si te S co re n=12 *HMSA Medical Policy – Luxturna – 2016 National Eye Institute generated survey assess daily functions related to general health & vision, ocular pain, near & distance activities, social functioning, mental health, dependency, driving, color vision, and peripheral vision. 2-4 point increase is considered clinically meaningful* Quality of Life

31 Functional MRI Qualitative Supportive of Cortical Activation NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception, CF – Counting Fingers
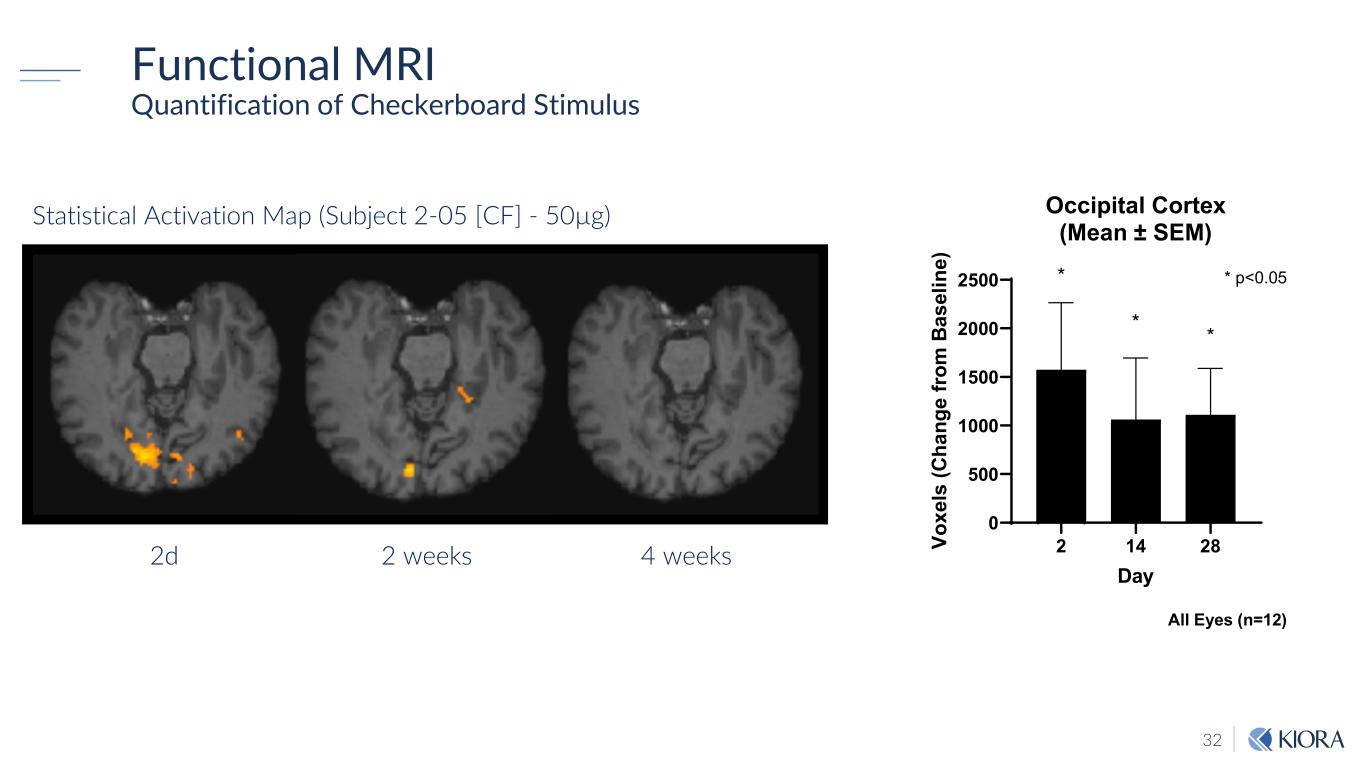
32 1-02 Checkerboard with arrow Statistical Activation Map (Subject 2-05 [CF] - 50µg) 2d 4 weeks2 weeks Functional MRI Quantification of Checkerboard Stimulus 2 14 28 0 500 1000 1500 2000 2500 Occipital Cortex (Mean ± SEM) Day Vo xe ls (C ha ng e fro m B as el in e) * * * * p<0.05 All Eyes (n=12)

33 “…in my last few months and years, my vision has been deteriorating fairly rapidly. It’s like a dimmer switch has been turned down and the rooms were getting darker. Going into areas would be like going into a cave. In my living room, there are two lights in the ceiling, cluster lights. I would have to look to find one, then look to find the other. When I sat down three days after the injection, I looked up and I could see both quite clearly and with better illumination (brightness)…” ~ Subject 1-03 - Baseline HM Patient Testimonials NLP – No Light Perception, HM – Hand Motion, CF – Counting Fingers Videos available at https://kiorapharma.com/inherited-retinal-diseases/ “Before the study, I had no light perception whatsoever. And at the start of the study, I had a couple of MRIs; and while I was there, they flashed lights there and I saw absolutely nothing. 48 hours after the drug, I had another MRI; and I think that was the first OMG moment, to say, that I can actually see flashing lights.” “We went for a walk, a couple of weeks ago, into the supermarket, and I thought I was in a sci-fi movie. I could see everything, and I could see every individual item which I would not have been able to do…”
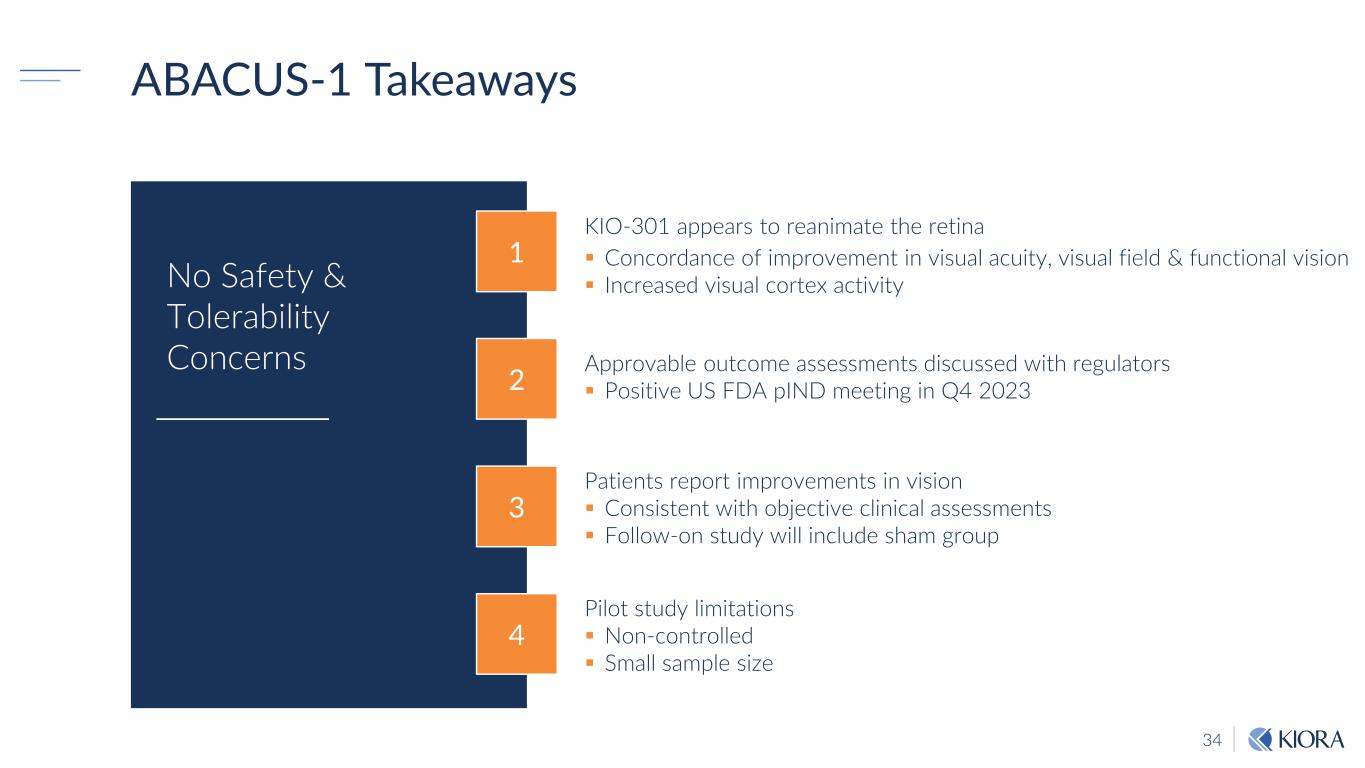
34 ABACUS-1 Takeaways Patients report improvements in vision Consistent with objective clinical assessments Follow-on study will include sham group Pilot study limitations Non-controlled Small sample size Approvable outcome assessments discussed with regulators Positive US FDA pIND meeting in Q4 2023 KIO-301 appears to reanimate the retina Concordance of improvement in visual acuity, visual field & functional vision Increased visual cortex activity 4 3 2 1 No Safety & Tolerability Concerns

35 Théa Open Innovation Partnership: Co-Development & Commercialization Transaction Highlights Théa Open Innovation (TOI) granted exclusive development & commercialization rights to KIO-301 for IRDs (≠ Asia) $16M cash upfront payment to Kiora Kiora eligible for up to an additional $285M in clinical development, regulatory and commercial milestones Kiora to conduct and be reimbursed for Phase 2 trials TOI to conduct and fund Phase 3 trials Kiora to receive tiered royalties up to low 20%
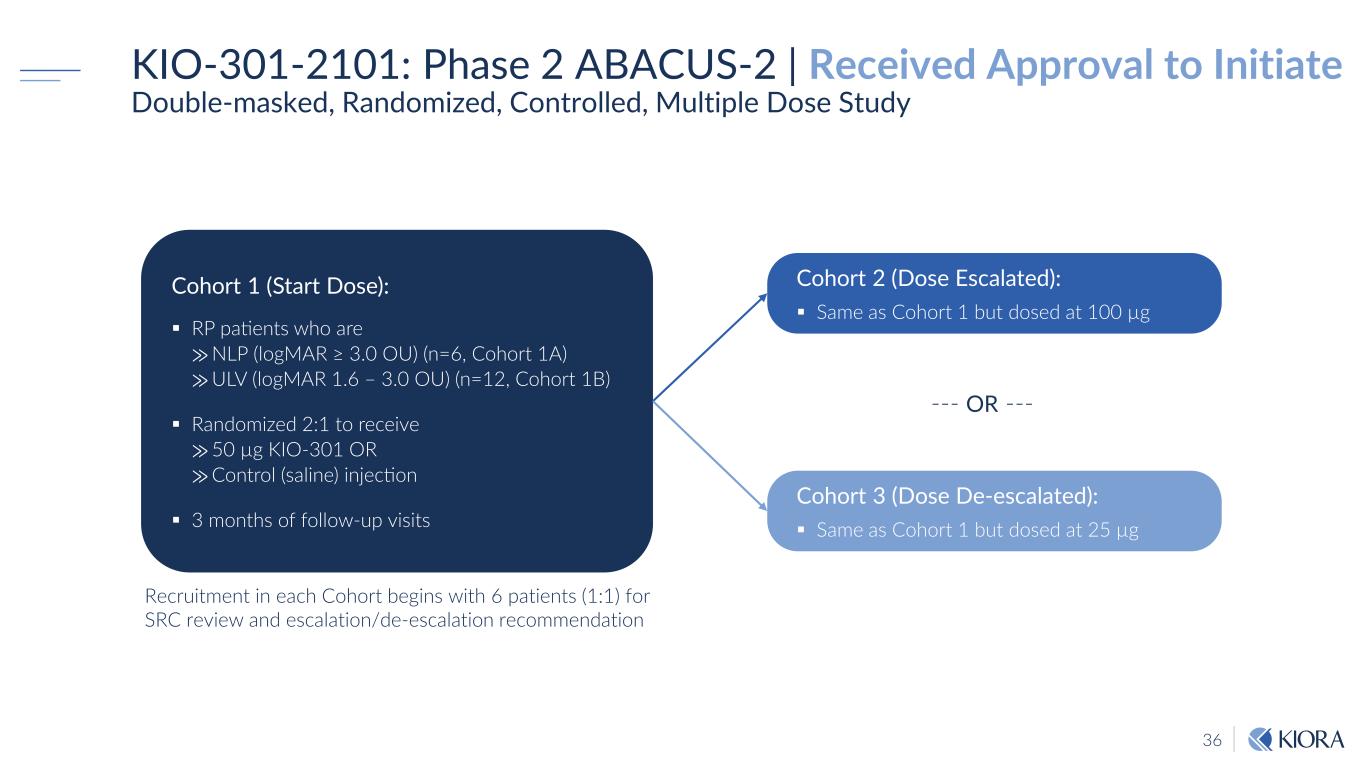
36 KIO-301-2101: Phase 2 ABACUS-2 | Received Approval to Initiate Double-masked, Randomized, Controlled, Multiple Dose Study Recruitment in each Cohort begins with 6 patients (1:1) for SRC review and escalation/de-escalation recommendation Cohort 2 (Dose Escalated): Same as Cohort 1 but dosed at 100 µg Cohort 1 (Start Dose): RP patients who are ⨠NLP (logMAR ≥ 3.0 OU) (n=6, Cohort 1A) ⨠ULV (logMAR 1.6 – 3.0 OU) (n=12, Cohort 1B) Randomized 2:1 to receive ⨠50 µg KIO-301 OR ⨠Control (saline) injection 3 months of follow-up visits Cohort 3 (Dose De-escalated): Same as Cohort 1 but dosed at 25 µg --- OR ---

37 ABACUS-2 (IVT Q6W for 3 Months) Double-masked, Randomized, Controlled, Multiple Dose Study – 5 Sites (Australia), 36 Patients St ud y A ss es sm en ts St ud y V is its Treatment Period Study visits occur every 3 weeks for study assessments with KIO-301 or control administered every 6 weeks (OU) for 3 consecutive doses Follow-up Period Four visits 3 weeks apart with the final, end-of-study visit occurring 3 months after the last dose of KIO-301 or control Safety Assessments Adverse events, vital signs , ECG, clinical chemistry & hematology, pharmacokinetics, SD-OCT, dilated fundoscopy, slit lamp, intraocular pressures Efficacy Assessments ⨠Visual acuity as measured by BRVT ⨠Visual field as measured by digitized Goldmann perimetry ⨠Ultra-low Vision Quality of Life Questionnaire ⨠Functional vision as measured by a validated • 360-degree door location exit test (patients with NLP) • 360-degree room light direction test (patients with NLP) • 360-degree object identification test (patients with ULV) • High contrast room exit test (patients with ULV) IVT – Intravitreal, OU – Both Eyes, Q6W – Once every 6 Weeks, NLP – No Light Perception, ULV – Ultra-Low Vision
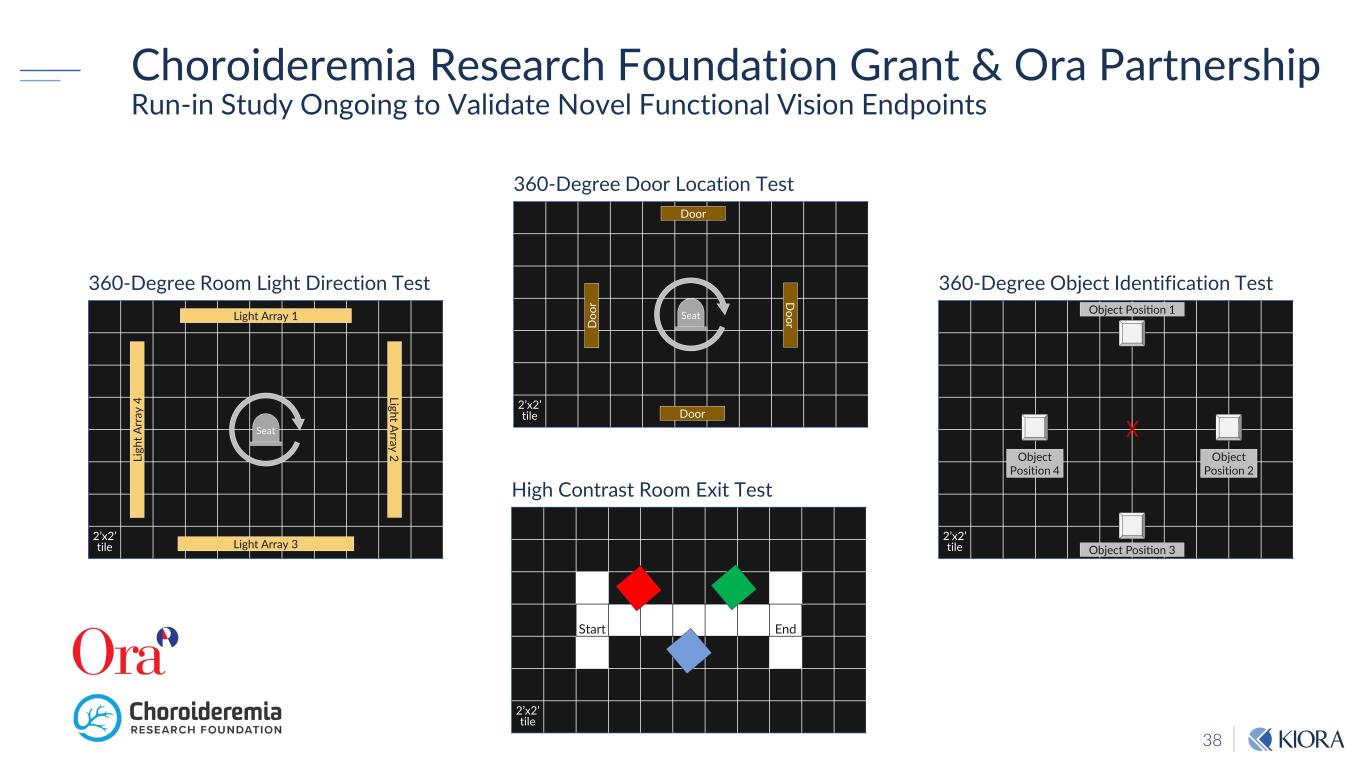
38 Choroideremia Research Foundation Grant & Ora Partnership Run-in Study Ongoing to Validate Novel Functional Vision Endpoints 2’x2’ tile 360-Degree Door Location Test Door Door D oorD oo r Start End 2’x2’ tile High Contrast Room Exit Test 2’x2’ tile 360-Degree Room Light Direction Test Light Array 2 Light Array 1 Li gh t A rr ay 4 Light Array 3 Seat 2’x2’ tile 360-Degree Object Identification Test Object Position 1 Object Position 3 Object Position 2 Object Position 4 Seat X

39 Brian M. Strem, PhD President & CEO Eric J. Daniels, MD, MBA Chief Development Officer Melissa Tosca, CPA Chief Financial Officer Stefan Sperl, PhD EVP – CMC & Operations Leadership Team

40 Upcoming Milestones Initiate ABACUS-2 Phase 2 clinical trial 2H 2024 Complete run-in study to validate novel functional vision endpoints Q1 2025 Complete enrollment of ABACUS-2 2H 2025 KIO-301 KIO-104 Round out non-clinical package Q4 2024 Initiate KLARITY Phase 2 clinical trial 1H 2025

Thank You NASDAQ: KPRX