EX-99.1
Published on November 9, 2023

Kiora Pharmaceu-cals, Inc. NASDAQ: KPRX Q4 2023 | Corporate Overview

2 Forward Looking Statements Some of the statements in this presentation are "forward-looking" and are made pursuant to the safe harbor provision of the Private Securities Litigation Reform Act of 1995. These "forward-looking" statements include statements relating to, among other things, the development and commercialization efforts and other regulatory or marketing approval efforts pertaining to Kiora's development-stage products, including KIO-301 and KIO-104, as well as the success thereof, with such approvals or success may not be obtained or achieved on a timely basis or at all, the potential ability of KIO-301 to restore vision in patients with RP, the expecting timing of enrollment, dosing and topline results for the ABACUS study, the ability to develop KIO-301 for Choroideremia and Stargardt Disease and KIO-104 for posterior non-infectious uveitis, the ability to utilize strategic relationships to develop certain product candidates, Kiora’s ability to draw on its equity line of credit, and Kiora's ability to achieve the specific milestones described herein. These statements involve risks and uncertainties that may cause results to differ materially from the statements set forth in this presentation, including, among other things, the ability to conduct clinical trials on a timely basis, the ability to obtain any required regulatory approvals, market and other conditions and certain risk factors described under the heading "Risk Factors" contained in Kiora's Annual Report on Form 10-K filed with the SEC on March 23, 2023, or described in Kiora's other public filings. Kiora's results may also be affected by factors of which Kiora is not currently aware. The forward-looking statements in this presentation speak only as of the date of this presentation. Kiora expressly disclaims any obligation or undertaking to release publicly any updates or revisions to such statements to reflect any change in its expectations with regard thereto or any changes in the events, conditions, or circumstances on which any such statement is based, except as required by law.
3 Kiora is developing re9nal therapeu9cs to improve sight in pa9ents with severe vision loss due to inherited or age-related diseases Sharpened Focus on Orphan Retinal Diseases Patient Perspective Individual’s burden of disease Physicians Perspec/ve Efficient, cost-effec8ve treatments Societal Perspective Pharma industry obligation to help
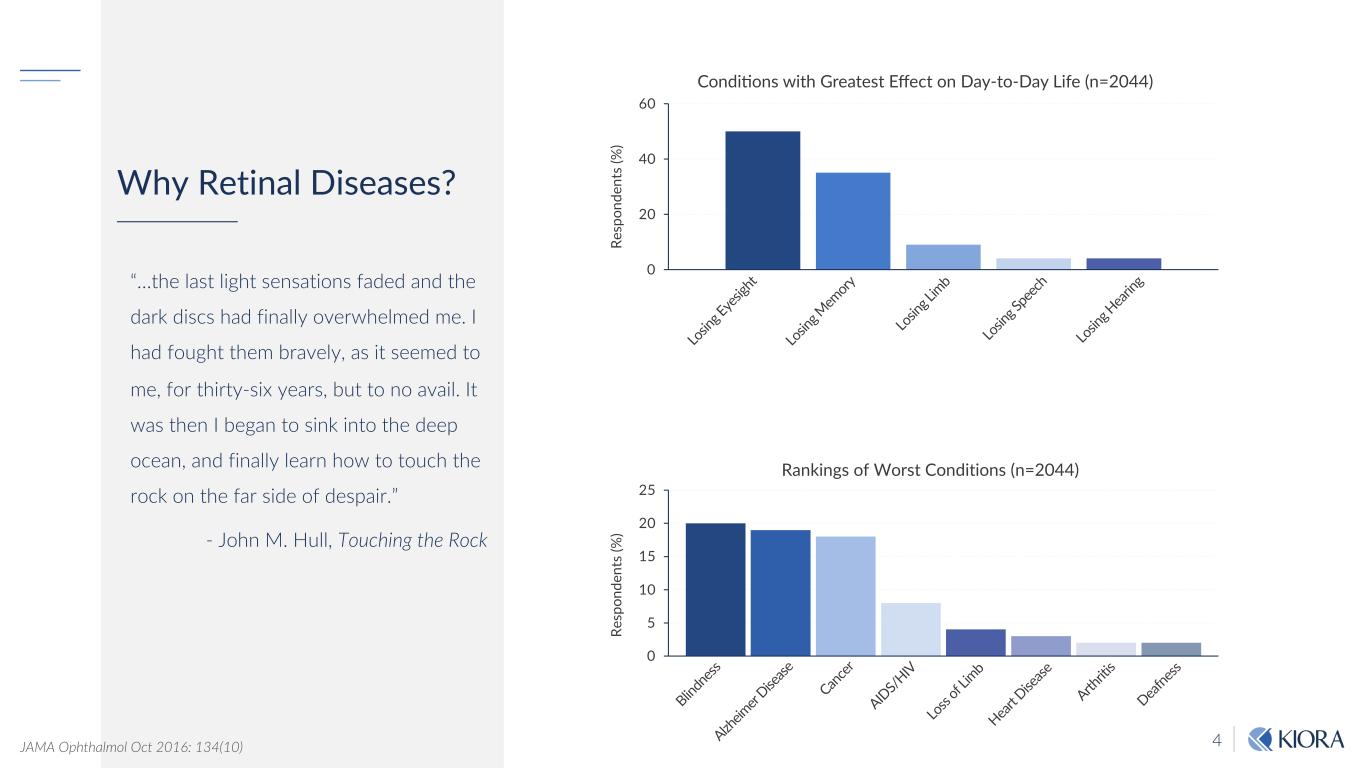
4 Why Retinal Diseases? “…the last light sensations faded and the dark discs had finally overwhelmed me. I had fought them bravely, as it seemed to me, for thirty-six years, but to no avail. It was then I began to sink into the deep ocean, and finally learn how to touch the rock on the far side of despair.” - John M. Hull, Touching the Rock JAMA Ophthalmol Oct 2016: 134(10) 0 20 40 60 0 5 10 15 20 25 Re sp on de nt s (% ) Re sp on de nt s (% ) Lo sin g E ye sig ht Lo sin g M em ory Lo sin g L im b Lo sin g S pe ech Lo sin g H ea rin g Blind ne ss Alzh eim er Dise ase Can cer AID S/H IV Lo ss of Lim b Hea rt D ise ase Arth riti s Dea fne ss Condi&ons with Greatest Effect on Day-to-Day Life (n=2044) Rankings of Worst Conditions (n=2044)
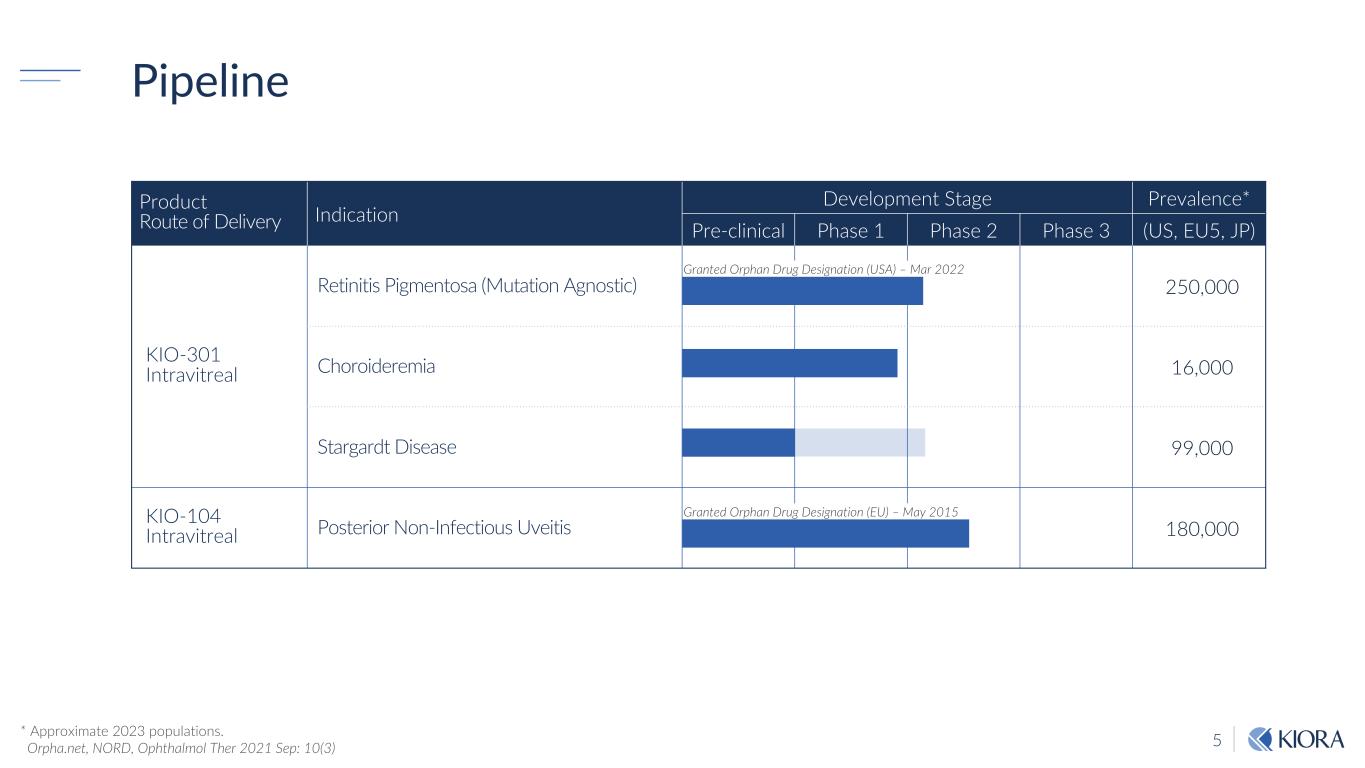
5 Pipeline Product Route of Delivery Indication Development Stage Prevalence* Pre-clinical Phase 1 Phase 2 Phase 3 (US, EU5, JP) KIO-301 Intravitreal Retinitis Pigmentosa (Mutation Agnostic) 250,000 Choroideremia 16,000 Stargardt Disease 99,000 KIO-104 Intravitreal Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis 180,000 Granted Orphan Drug Designation (USA) – Mar 2022 Granted Orphan Drug Designation (EU) – May 2015 * Approximate 2023 populations. Orpha.net, NORD, Ophthalmol Ther 2021 Sep: 10(3)
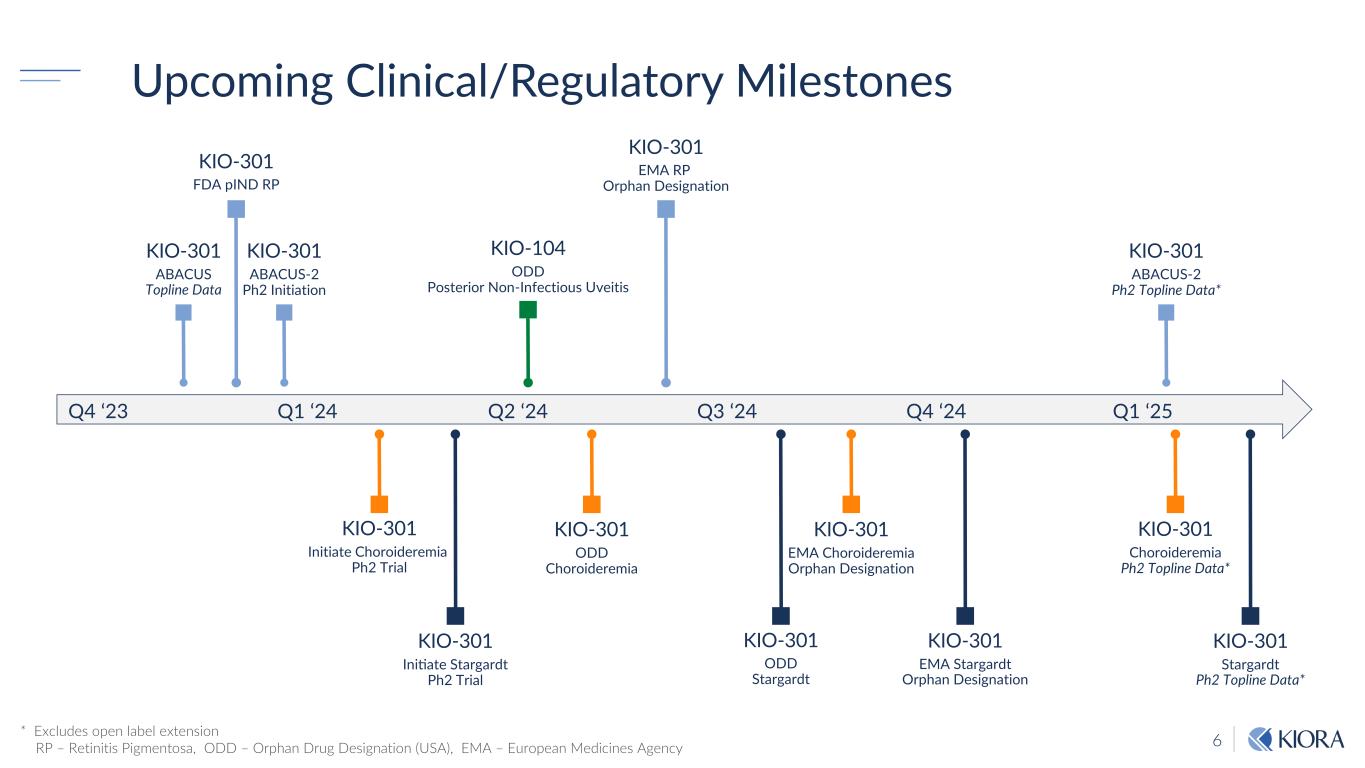
6 Q4 ‘23 Q1 ‘24 Q2 ‘24 Q3 ‘24 Q4 ‘24 KIO-301 ABACUS Topline Data KIO-301 ABACUS-2 Ph2 Initiation KIO-301 ABACUS-2 Ph2 Topline Data* KIO-301 Initiate Choroideremia Ph2 Trial KIO-301 Choroideremia Ph2 Topline Data* KIO-301 IniOate Stargardt Ph2 Trial KIO-301 FDA pIND RP KIO-301 Stargardt Ph2 Topline Data* KIO-104 ODD Posterior Non-Infectious Uveitis KIO-301 ODD Choroideremia KIO-301 ODD Stargardt Q1 ‘25 * Excludes open label extension RP – Retinitis Pigmentosa, ODD – Orphan Drug Designation (USA), EMA – European Medicines Agency Upcoming Clinical/Regulatory Milestones KIO-301 EMA RP Orphan Designation KIO-301 EMA Choroideremia Orphan Designation KIO-301 EMA Stargardt Orphan Designation

7 KIO-301 Small Molecule Targeting Vision Restoration Retinitis Pigmentosa, Choroideremia, Stargardt Disease
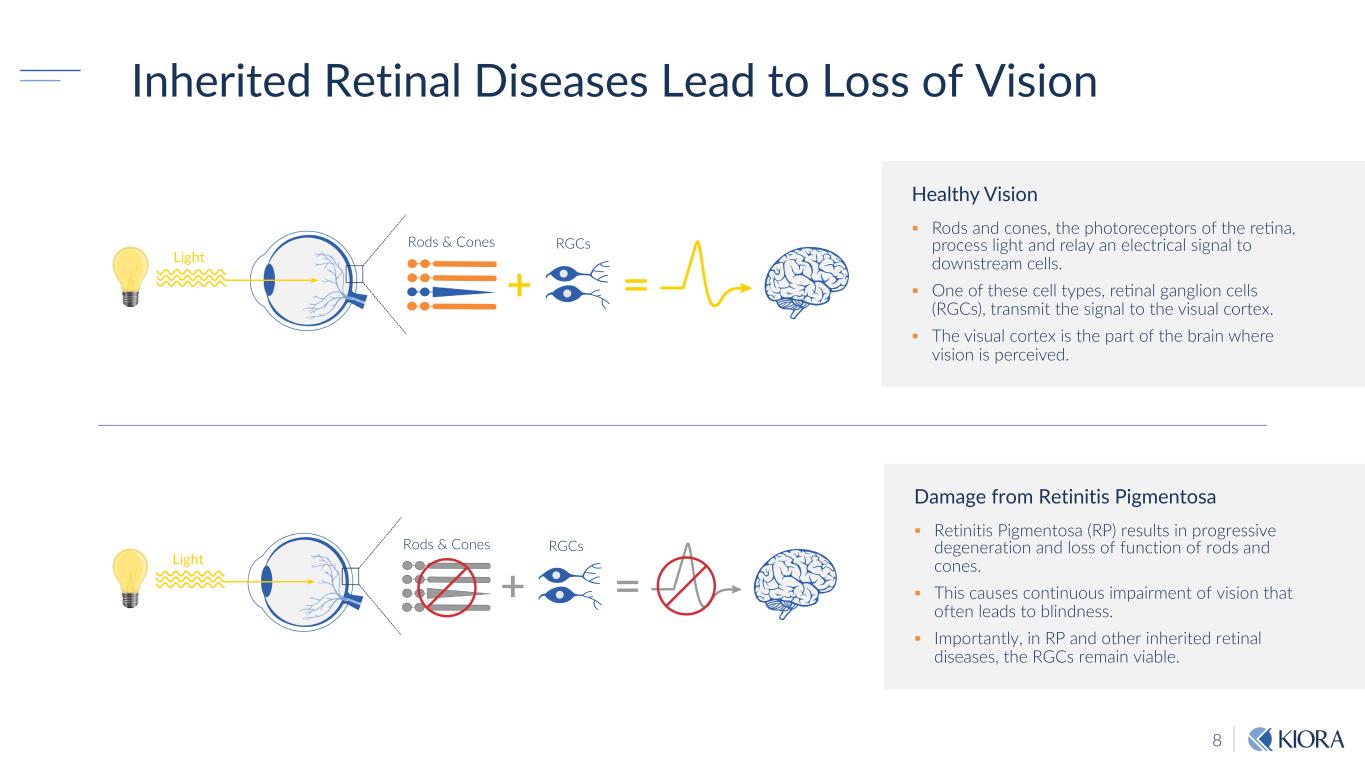
8 Inherited Retinal Diseases Lead to Loss of Vision Healthy Vision § Rods and cones, the photoreceptors of the re7na, process light and relay an electrical signal to downstream cells. § One of these cell types, re7nal ganglion cells (RGCs), transmit the signal to the visual cortex. § The visual cortex is the part of the brain where vision is perceived. Damage from Retinitis Pigmentosa § Retinitis Pigmentosa (RP) results in progressive degeneration and loss of function of rods and cones. § This causes continuous impairment of vision that often leads to blindness. § Importantly, in RP and other inherited retinal diseases, the RGCs remain viable. Rods & Cones Light RGCs Rods & Cones Light RGCs
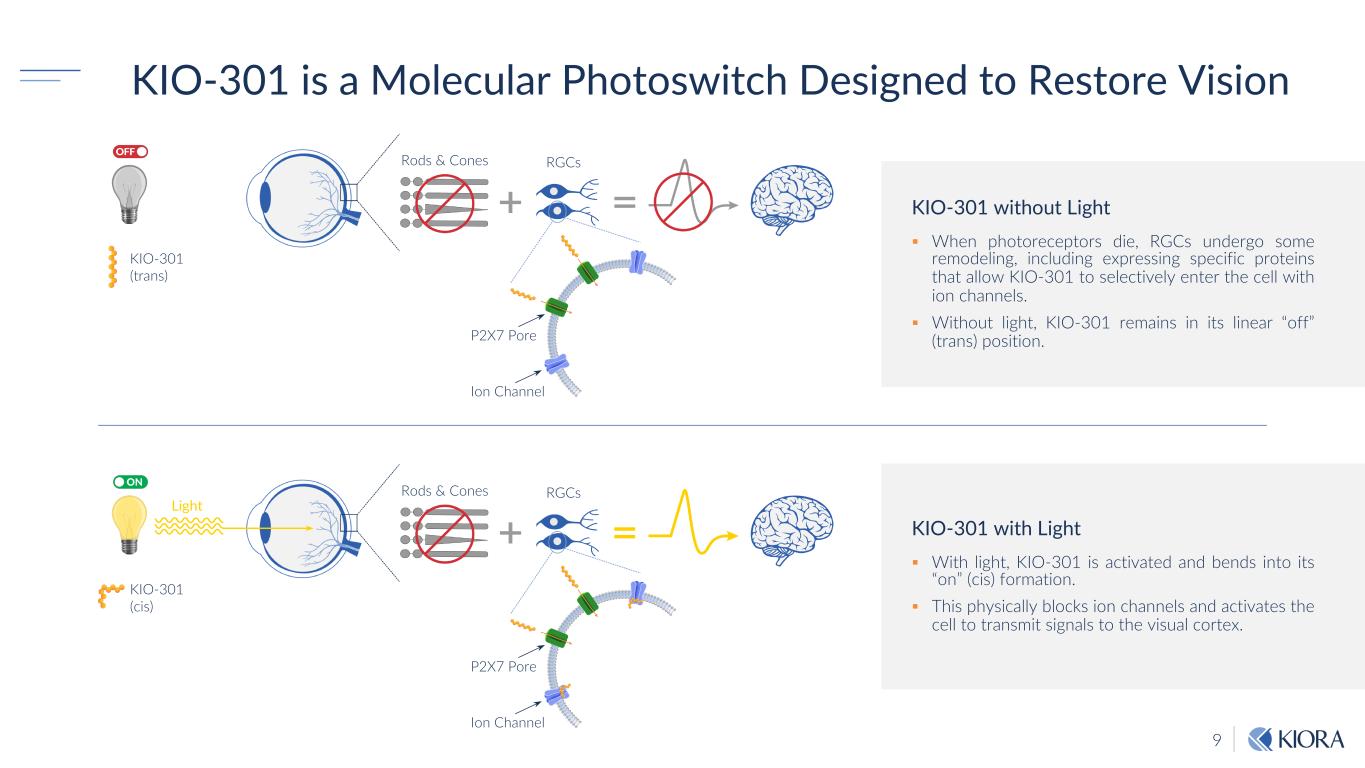
9 KIO-301 is a Molecular Photoswitch Designed to Restore Vision KIO-301 without Light § When photoreceptors die, RGCs undergo some remodeling, including expressing specific proteins that allow KIO-301 to selectively enter the cell with ion channels. § Without light, KIO-301 remains in its linear “off” (trans) position. KIO-301 with Light § With light, KIO-301 is activated and bends into its “on” (cis) formation. § This physically blocks ion channels and activates the cell to transmit signals to the visual cortex. Rods & Cones RGCs KIO-301 (trans) P2X7 Pore Ion Channel Rods & Cones Light RGCs KIO-301 (cis) P2X7 Pore Ion Channel

10 Clinical Presenta-on § Night blindness, reduced visual field range and eventual loss of central vision § Visual acuity declines § 50% of pa\ents are not qualified to drive by age 37 and legally blind by 55 E-ology § 50+ gene\cally dis\nct subtypes from 150+ muta\ons § Inherited disease Market Opportunity § ~100k pa\ents in US (Provider: Re\na Specialists [~3k]) § Es\mated total cost to US healthcare system in 2019: $3.7B Retinitis Pigmentosa A Disease with No Available Treatments Normal Vision Vision Declines over Time IOVS: Visual Field Progression in Retinitis Pigmentosa, American Academy of Ophthalmology, Clinical Ophthalmol 2021:15, 2855–2866
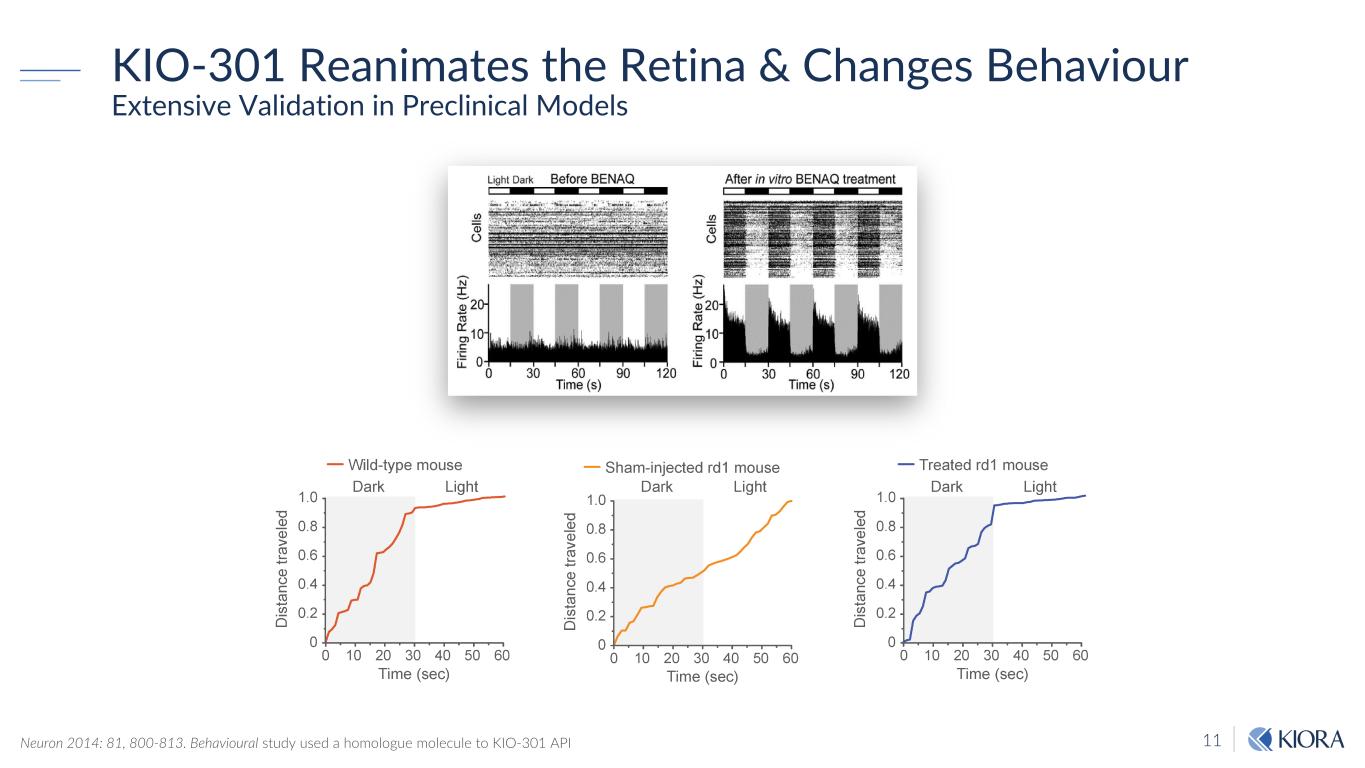
11 KIO-301 Reanimates the Retina & Changes Behaviour Extensive Validation in Preclinical Models Neuron 2014: 81, 800-813. Behavioural study used a homologue molecule to KIO-301 API
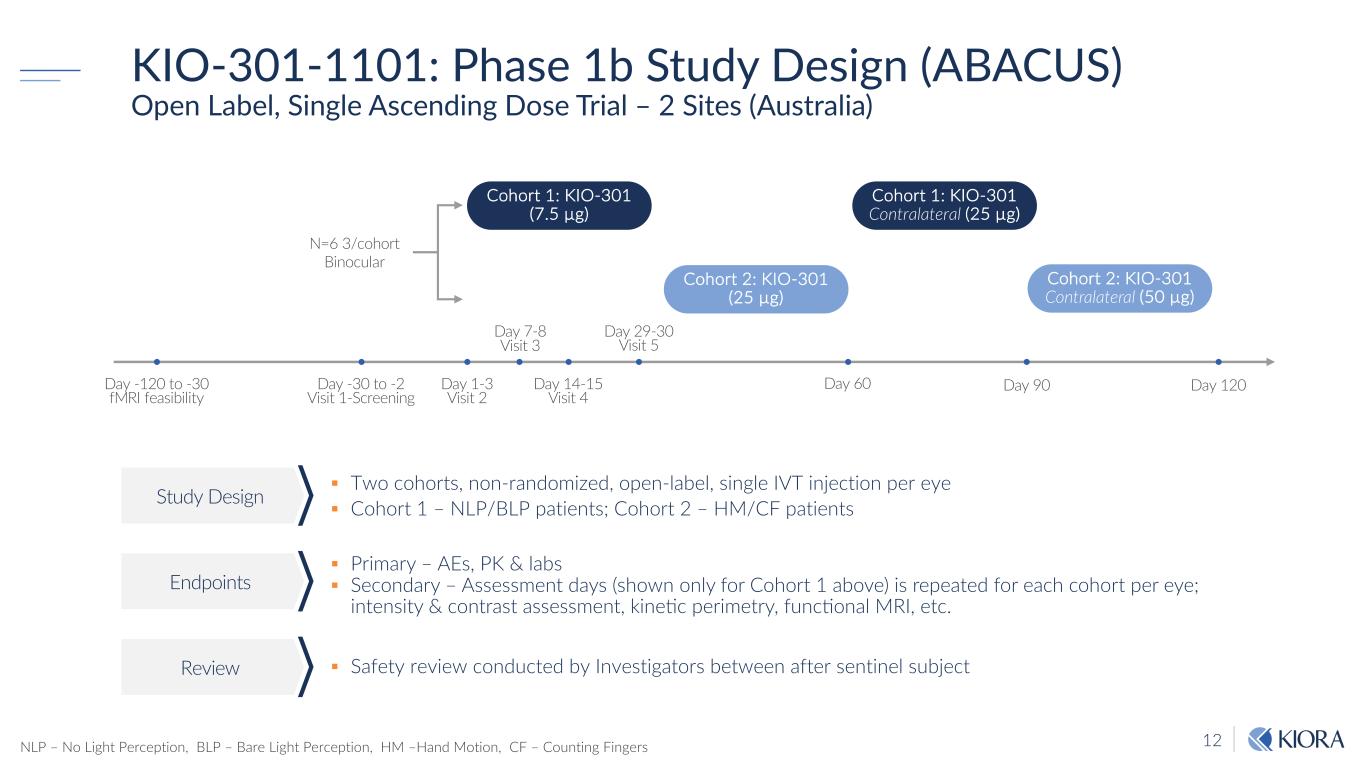
12 KIO-301-1101: Phase 1b Study Design (ABACUS) Open Label, Single Ascending Dose Trial – 2 Sites (Australia) § Two cohorts, non-randomized, open-label, single IVT injection per eye § Cohort 1 – NLP/BLP patients; Cohort 2 – HM/CF patients § Primary – AEs, PK & labs § Secondary – Assessment days (shown only for Cohort 1 above) is repeated for each cohort per eye; intensity & contrast assessment, kine8c perimetry, func8onal MRI, etc. § Safety review conducted by Investigators between after sentinel subject Study Design Endpoints Review N=6 3/cohort Binocular Day 90 Cohort 1: KIO-301 (7.5 µg) Day -30 to -2 Visit 1-Screening Day 29-30 Visit 5 Day 60 Day 120 Cohort 1: KIO-301 Contralateral (25 µg) Cohort 2: KIO-301 (25 µg) Cohort 2: KIO-301 Contralateral (50 µg) Day 1-3 Visit 2 Day 7-8 Visit 3 Day 14-15 Visit 4 Day -120 to -30 fMRI feasibility NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception, HM –Hand Motion, CF – Counting Fingers

13 Patient Testimonials Pa\ent 1-02 Baseline VA: NLP Cohort 1 Patient 2-05 Baseline VA: CF Cohort 2 VA – Visual Acuity, NLP – No Light PercepVon, CF – CounVng Fingers, HM – Hand MoVon Patient 1-03 Baseline VA: HM Cohort 2 Videos also available at: https://kiorapharma.com/technology/kio-301/
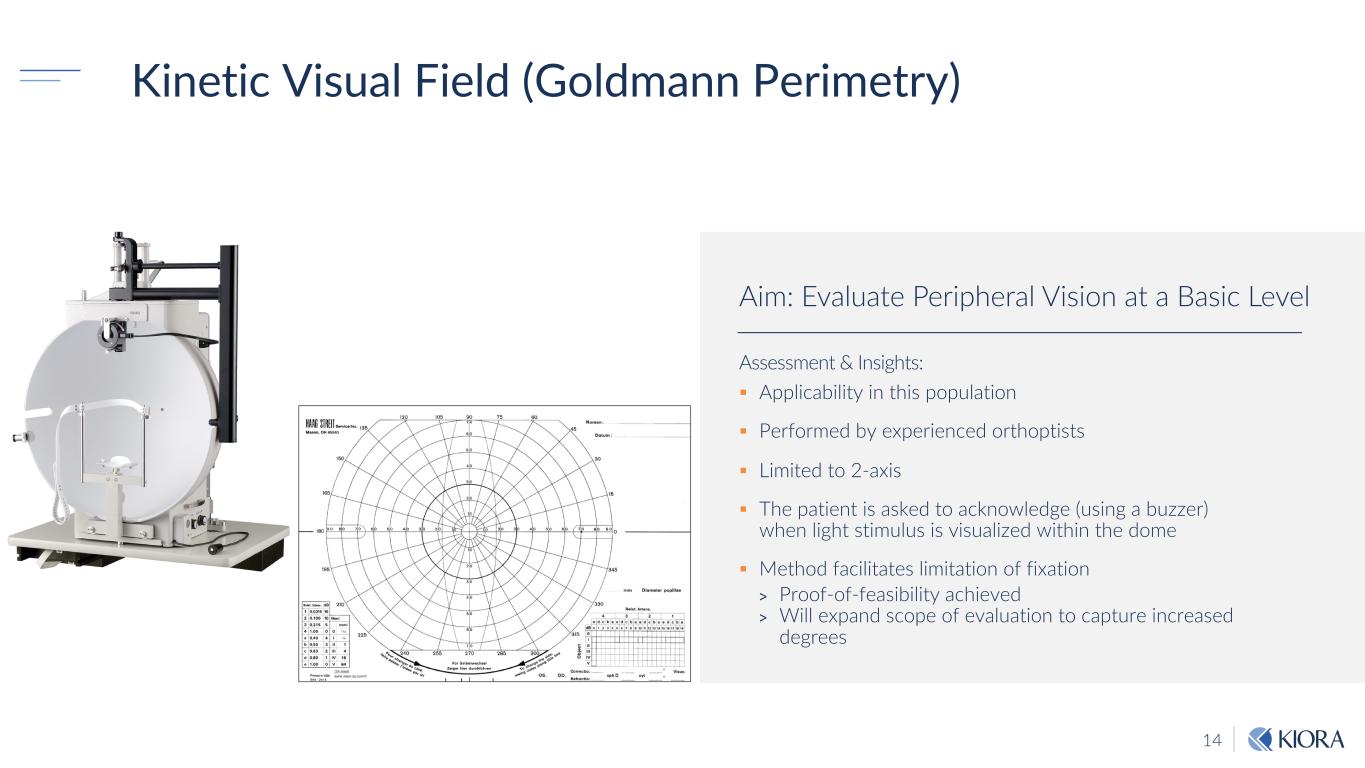
14 Kinetic Visual Field (Goldmann Perimetry) Assessment & Insights: § Applicability in this population § Performed by experienced orthoptists § Limited to 2-axis § The patient is asked to acknowledge (using a buzzer) when light stimulus is visualized within the dome § Method facilitates limitation of fixation > Proof-of-feasibility achieved > Will expand scope of evaluation to capture increased degrees Aim: Evaluate Peripheral Vision at a Basic Level
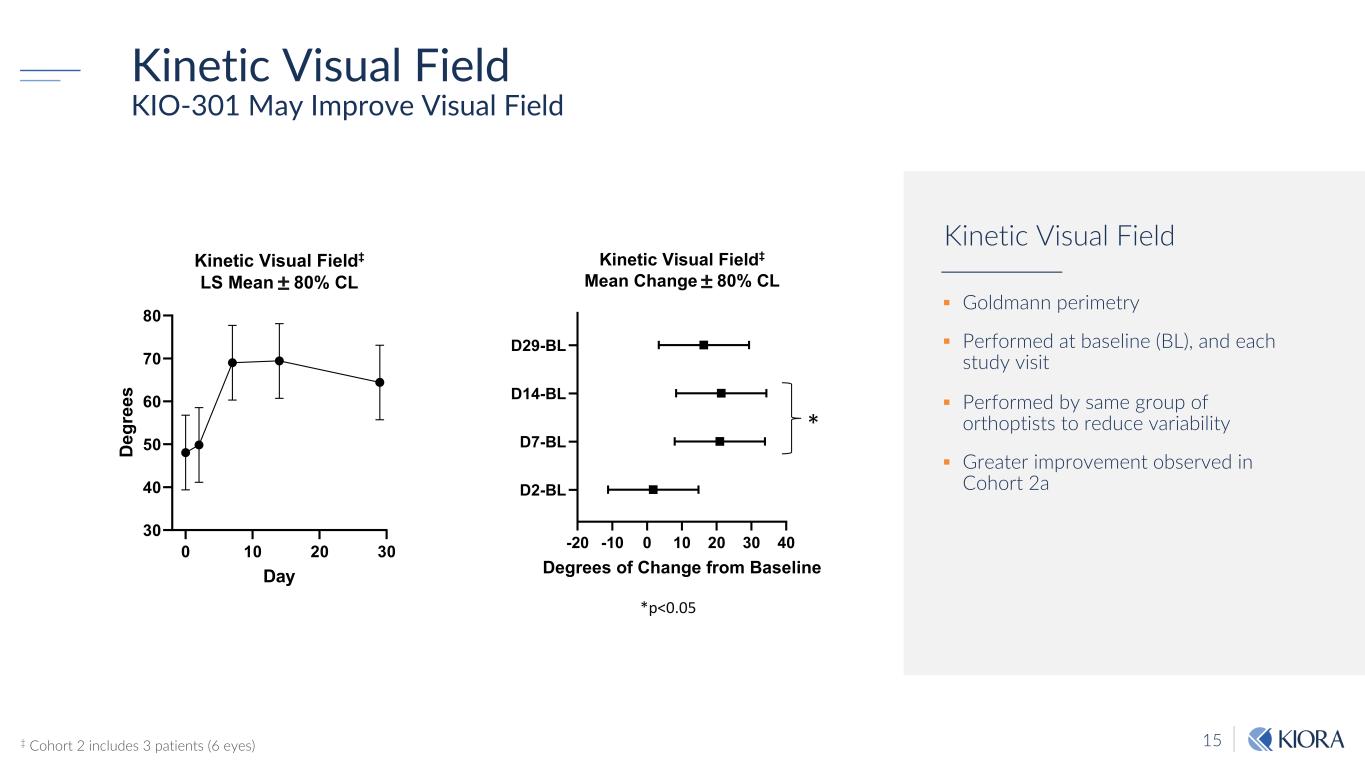
15 Kinetic Visual Field KIO-301 May Improve Visual Field 0 10 20 30 30 40 50 60 70 80 Kinetic Visual Field‡ LS Mean ± 80% CL Day D eg re es * -20 -10 0 10 20 30 40 D2-BL D7-BL D14-BL D29-BL Kinetic Visual Field‡ Mean Change ± 80% CL Degrees of Change from Baseline *p<0.05 ‡ Cohort 2 includes 3 patients (6 eyes) § Goldmann perimetry § Performed at baseline (BL), and each study visit § Performed by same group of orthoptists to reduce variability § Greater improvement observed in Cohort 2a Kinetic Visual Field
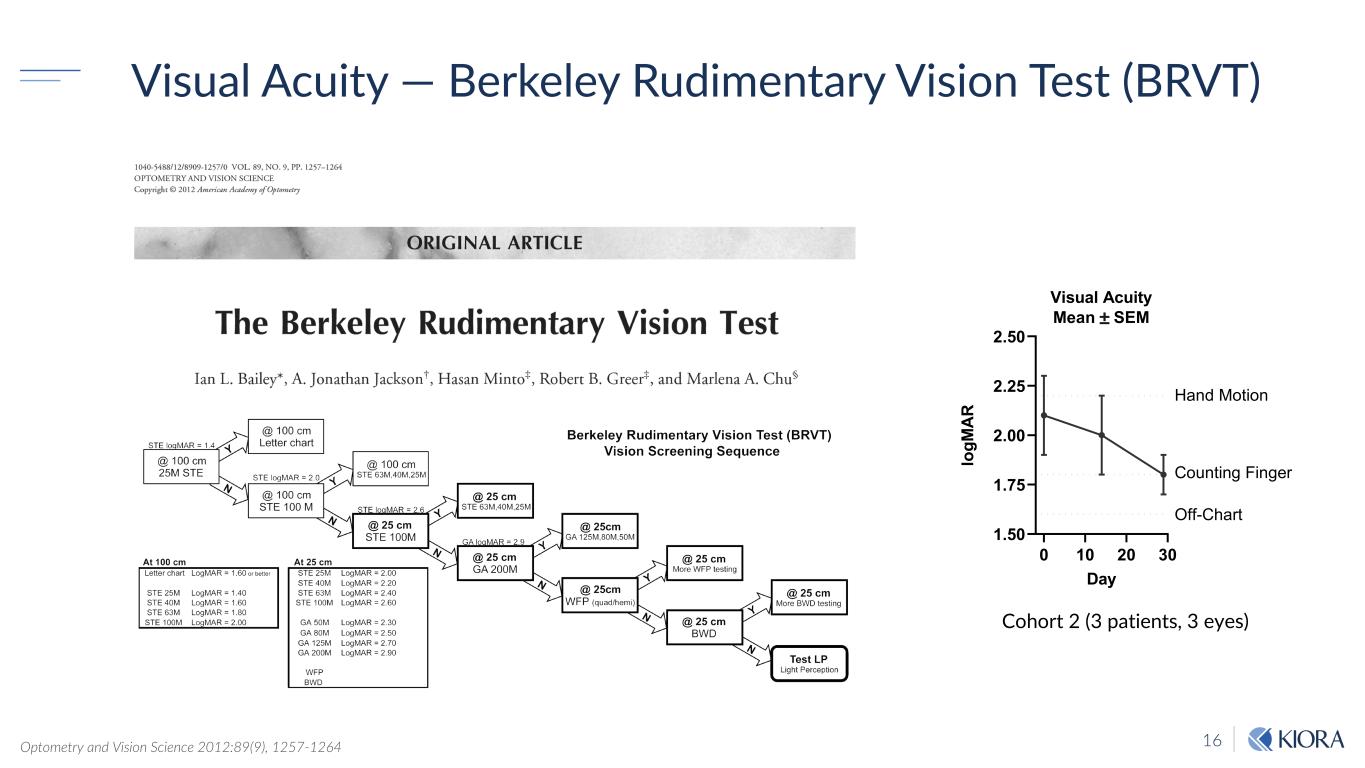
16 Visual Acuity — Berkeley Rudimentary Vision Test (BRVT) 0 10 20 30 1.50 1.75 2.00 2.25 2.50 Visual Acuity Mean ± SEM Day lo gM AR Off-Chart Counting Finger Hand Motion Optometry and Vision Science 2012:89(9), 1257-1264 Cohort 2 (3 patients, 3 eyes)

17 Light Perception (Intensity & Contrast Assessment) Assessment: § Series of visual s8muli (a series of lelers are presented on a screen to the pa8ent via a rear projector) § Binary outcome (yes/no) § The subject is asked to acknowledge (verbally and/or physically) when a change in light is perceived § Asked to also iden8fy object, if possible Aim: Evaluate Light Perception at a Basic Level
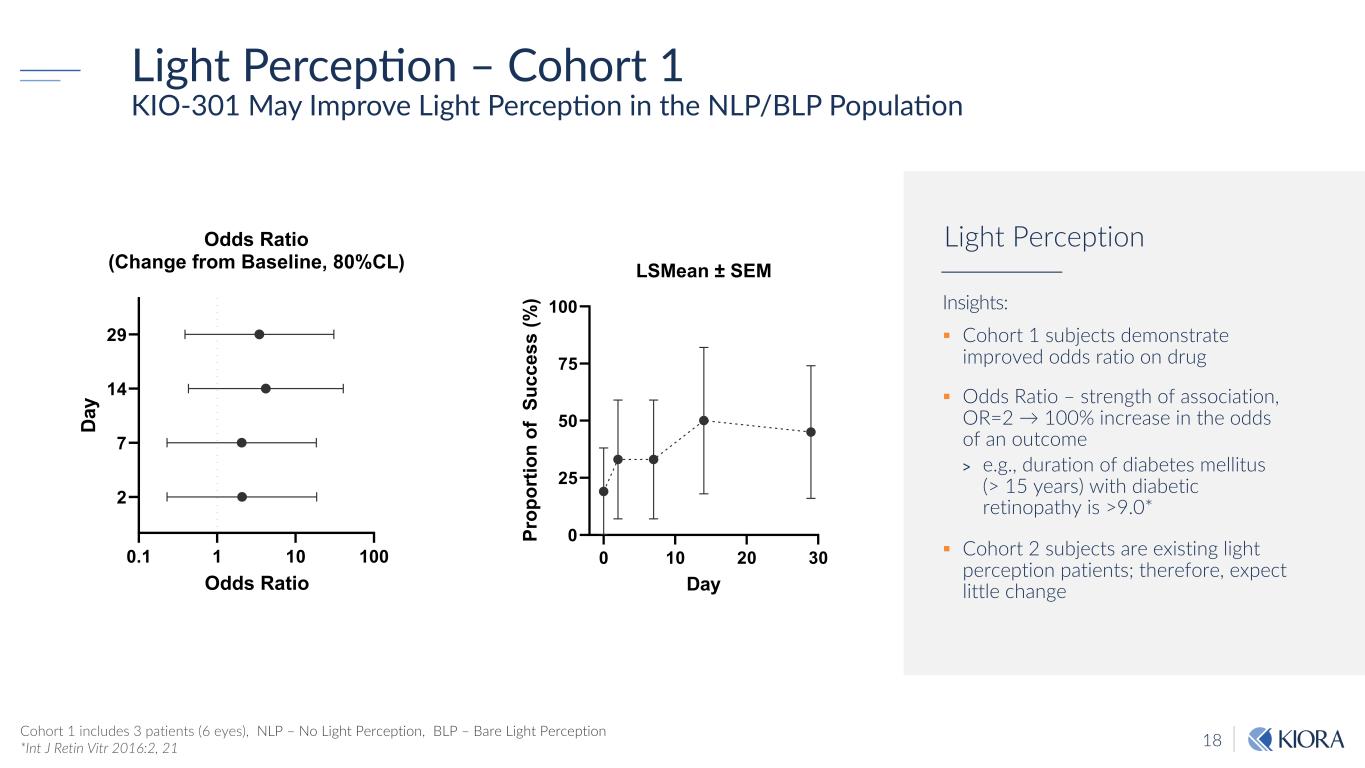
18 Light PercepSon – Cohort 1 KIO-301 May Improve Light PercepNon in the NLP/BLP PopulaNon Insights: § Cohort 1 subjects demonstrate improved odds ratio on drug § Odds Ratio – strength of association, OR=2 → 100% increase in the odds of an outcome > e.g., duration of diabetes mellitus (> 15 years) with diabetic retinopathy is >9.0* § Cohort 2 subjects are existing light perception patients; therefore, expect little change Light Perception Cohort 1 includes 3 patients (6 eyes), NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception *Int J Retin Vitr 2016:2, 21 0 10 20 30 0 25 50 75 100 LSMean ± SEM Day Pr op or tio n of S uc ce ss (% ) 0.1 1 10 100 2 7 14 29 Odds Ratio (Change from Baseline, 80%CL) Odds Ratio Da y
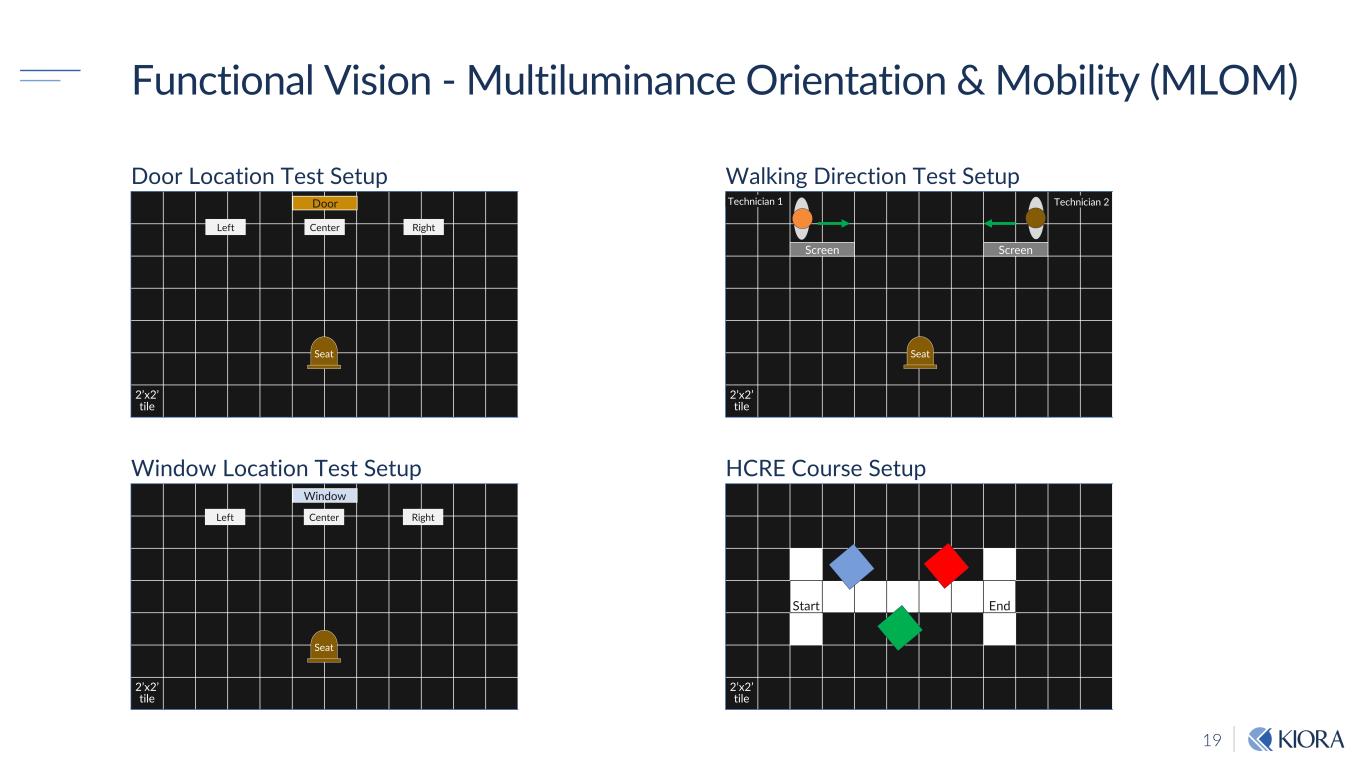
19 2’x2’ tile Door Location Test Setup Functional Vision - Multiluminance Orientation & Mobility (MLOM) 2’x2’ tile Window Location Test Setup 2’x2’ tile Walking Direction Test Setup Start End 2’x2’ tile HCRE Course Setup Screen Screen Technician 1 Technician 2Door Window Left Center Right Left Center Right Seat Seat Seat
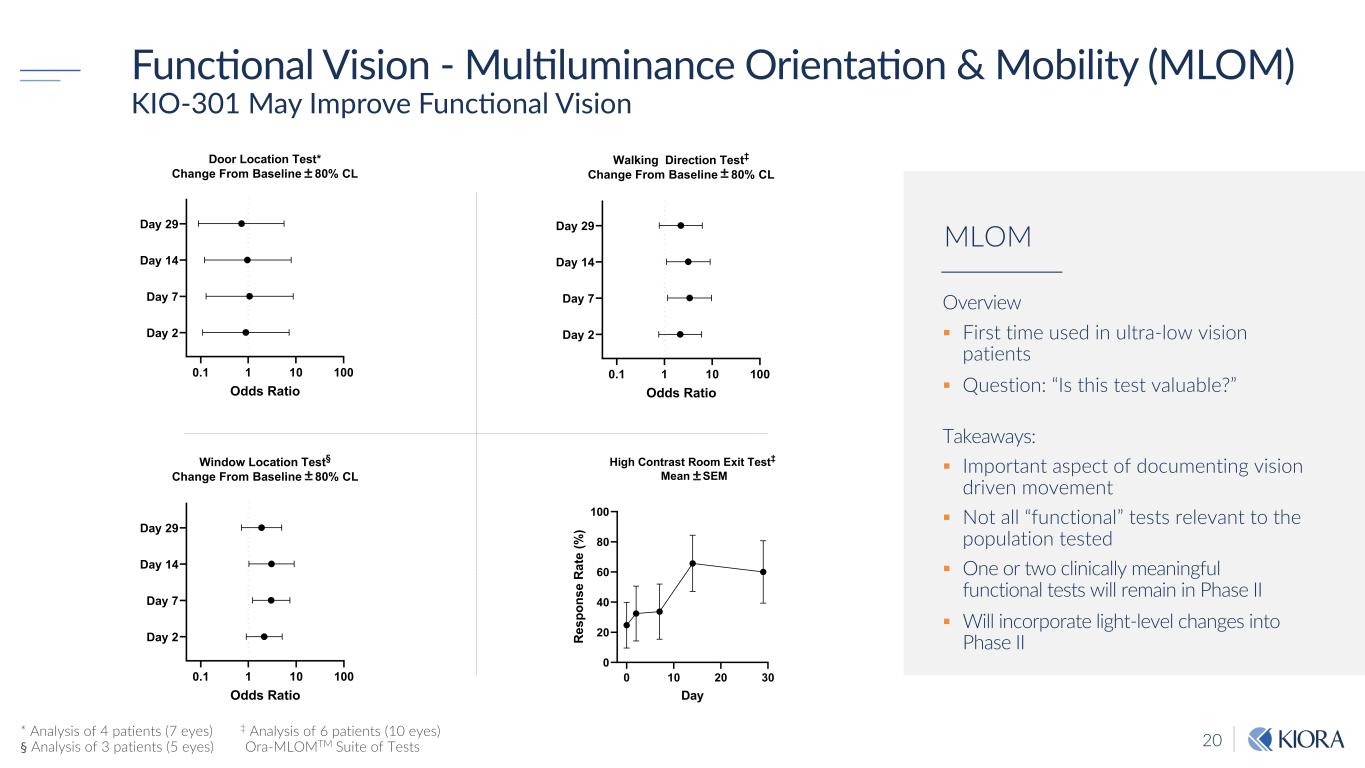
20 FuncEonal Vision - MulEluminance OrientaEon & Mobility (MLOM) KIO-301 May Improve FuncNonal Vision 0.1 1 10 100 Day 2 Day 7 Day 14 Day 29 Door Location Test* Change From Baseline ± 80% CL Odds Ratio 0.1 1 10 100 Day 2 Day 7 Day 14 Day 29 Walking Direction Test‡ Change From Baseline ± 80% CL Odds Ratio 0.1 1 10 100 Day 2 Day 7 Day 14 Day 29 Window Location Test§ Change From Baseline ± 80% CL Odds Ratio * Analysis of 4 patients (7 eyes) ‡ Analysis of 6 patients (10 eyes) § Analysis of 3 patients (5 eyes) Ora-MLOMTM Suite of Tests Overview § First time used in ultra-low vision patients § Question: “Is this test valuable?” Takeaways: § Important aspect of documenting vision driven movement § Not all “functional” tests relevant to the population tested § One or two clinically meaningful functional tests will remain in Phase II § Will incorporate light-level changes into Phase II MLOM 0 10 20 30 0 20 40 60 80 100 High Contrast Room Exit Test‡ Mean ± SEM Day R es po ns e R at e (% )
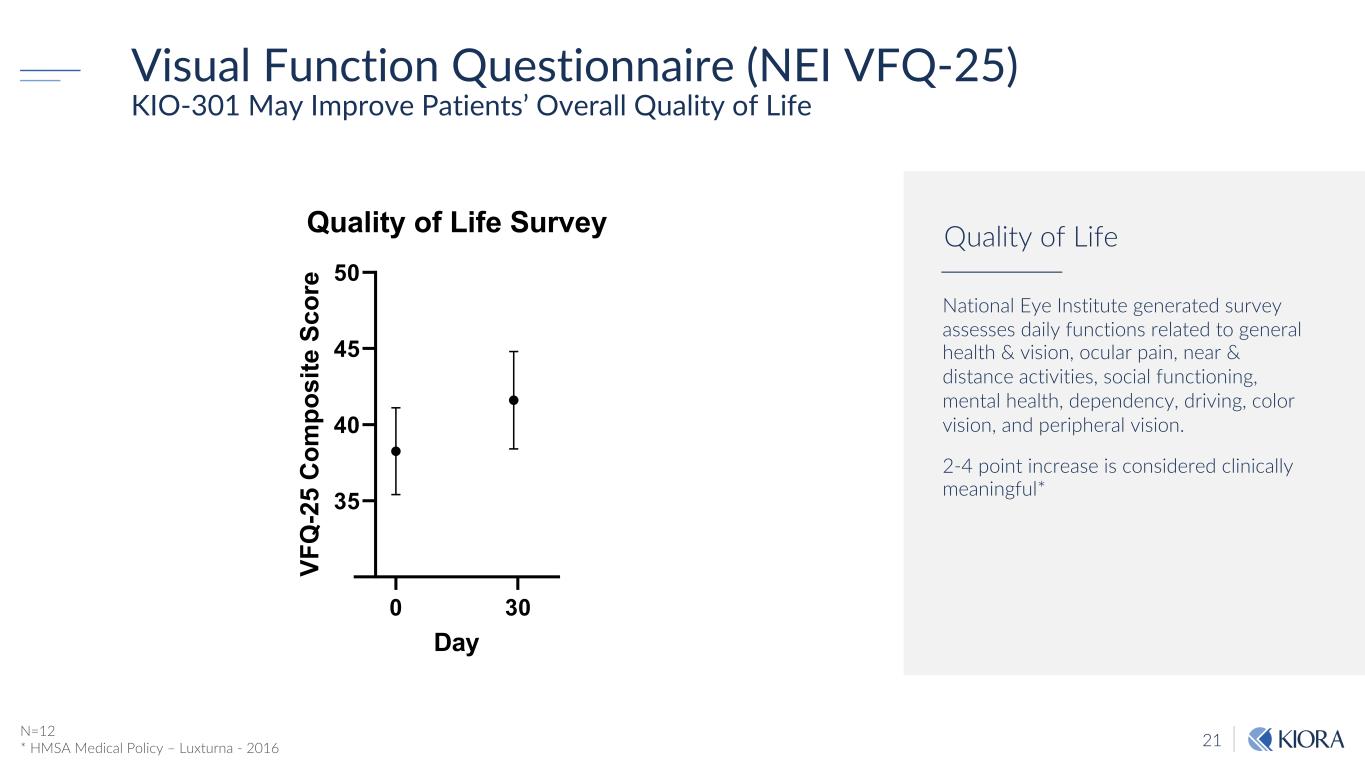
21 Visual Function Questionnaire (NEI VFQ-25) KIO-301 May Improve Patients’ Overall Quality of Life 0 30 35 40 45 50 Quality of Life Survey Day VF Q -2 5 C om po si te S co re N=12 * HMSA Medical Policy – Luxturna - 2016 National Eye Institute generated survey assesses daily functions related to general health & vision, ocular pain, near & distance activities, social functioning, mental health, dependency, driving, color vision, and peripheral vision. 2-4 point increase is considered clinically meaningful* Quality of Life
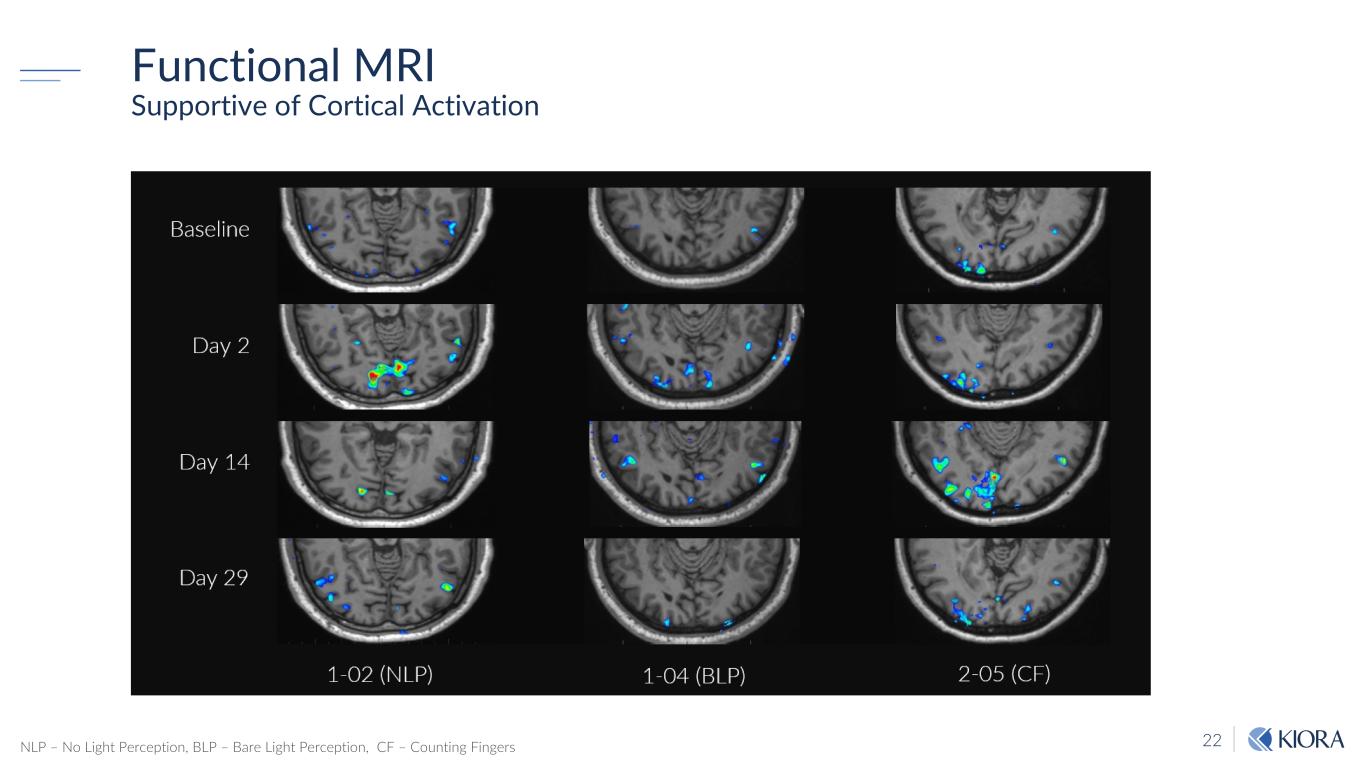
22 Functional MRI Supportive of Cortical Activation NLP – No Light Perception, BLP – Bare Light Perception, CF – Counting Fingers

23 ABACUS-1 Takeaways Patients report improvements in vision § Consistent with objective clinical assessments § Follow-on study will include sham group Pilot study limitations § Non-controlled § Small sample size Approvable outcome assessments need to be defined § US FDA pIND scheduled for Q4 2023 KIO-301 appears to reanimate the retina 4 3 2 1 No Safety & Tolerability Concerns

24 KIO-301-2101: Phase 2 Study Design (ABACUS-2) Sham Controlled, Masked, Randomized, Multiple Ascending Dose Trial – 4 Sites (Australia) 5 RP pts with NLP randomized to receive 50μg KIO-301 or sham (3:2) OU monthly for 3 months 5 RP pts with LP randomized to receive 50μg KIO-301 or sham (3:2) OU monthly for 3 months Patients randomized to control will be eligible to receive 50μg KIO-301 OU monthly for 3 months Cohort 2A Cohort 2B Open Label Extension *Subject to ongoing nonclinical tox results Study Design ABACUS-2 § Controlled § N=20 patients § Includes higher dose* (100µg) Key Elements Cohort 1A Cohort 1B Open Label Extension 5 RP pts with NLP randomized to receive 100μg KIO-301 or sham (3:2) OU monthly for 3 months 5 RP pts with LP randomized to receive 100μg KIO-301 or sham (3:2) OU monthly for 3 months Patients randomized to control will be eligible to receive 100μg KIO-301 OU monthly for 3 months § Multiple injections over 3 months § Binocular injections § Open label extension for controls § Endpoints incorporating US FDA feedback
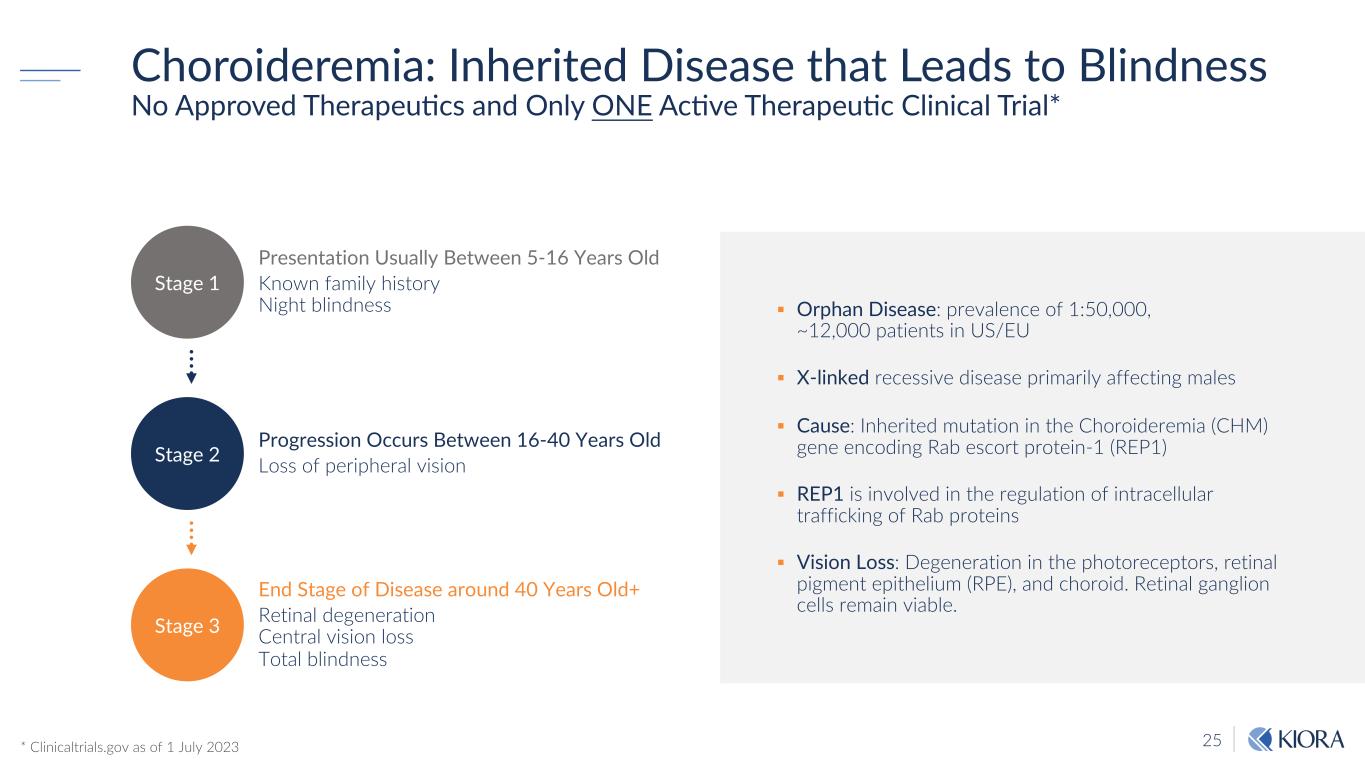
25 § Orphan Disease: prevalence of 1:50,000, ~12,000 patients in US/EU § X-linked recessive disease primarily affecting males § Cause: Inherited mutation in the Choroideremia (CHM) gene encoding Rab escort protein-1 (REP1) § REP1 is involved in the regulation of intracellular trafficking of Rab proteins § Vision Loss: Degeneration in the photoreceptors, retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), and choroid. Retinal ganglion cells remain viable. Choroideremia: Inherited Disease that Leads to Blindness No Approved TherapeuNcs and Only ONE AcNve TherapeuNc Clinical Trial* * Clinicaltrials.gov as of 1 July 2023 Stage 3 Presentation Usually Between 5-16 Years Old Known family history Night blindness Progression Occurs Between 16-40 Years Old Loss of peripheral vision End Stage of Disease around 40 Years Old+ Retinal degeneration Central vision loss Total blindness Stage 1 Stage 2
26 The Choroideremia Research Foundation (CRF) is the largest global not-for-profit organization focused on the search for a cure for Choroideremia (CHM). Partnership with the Choroideremia Research Foundation Education and Awareness of CHM and KIO-301 CHM KOL Network to Assist in Clinical Protocol Design CHM Patient Identification to Assist in Trial Enrollment Partnering on:
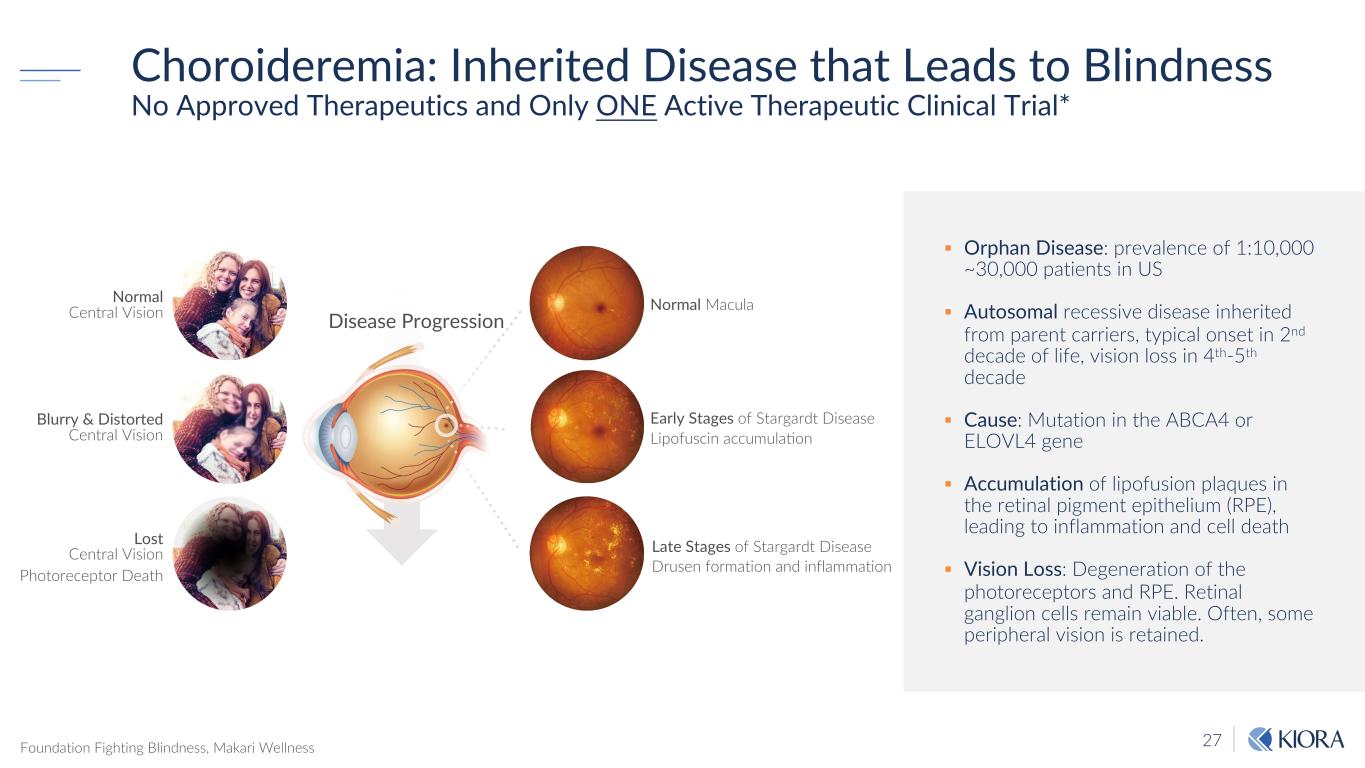
27 § Orphan Disease: prevalence of 1:10,000 ~30,000 patients in US § Autosomal recessive disease inherited from parent carriers, typical onset in 2nd decade of life, vision loss in 4th-5th decade § Cause: Mutation in the ABCA4 or ELOVL4 gene § Accumulation of lipofusion plaques in the retinal pigment epithelium (RPE), leading to inflammation and cell death § Vision Loss: Degeneration of the photoreceptors and RPE. Retinal ganglion cells remain viable. Often, some peripheral vision is retained. Choroideremia: Inherited Disease that Leads to Blindness No Approved Therapeutics and Only ONE Active Therapeutic Clinical Trial* Foundation Fighting Blindness, Makari Wellness Normal Central Vision Blurry & Distorted Central Vision Lost Central Vision Photoreceptor Death Normal Macula Early Stages of Stargardt Disease Lipofuscin accumulaMon Late Stages of Stargardt Disease Drusen formation and inflammation Disease Progression
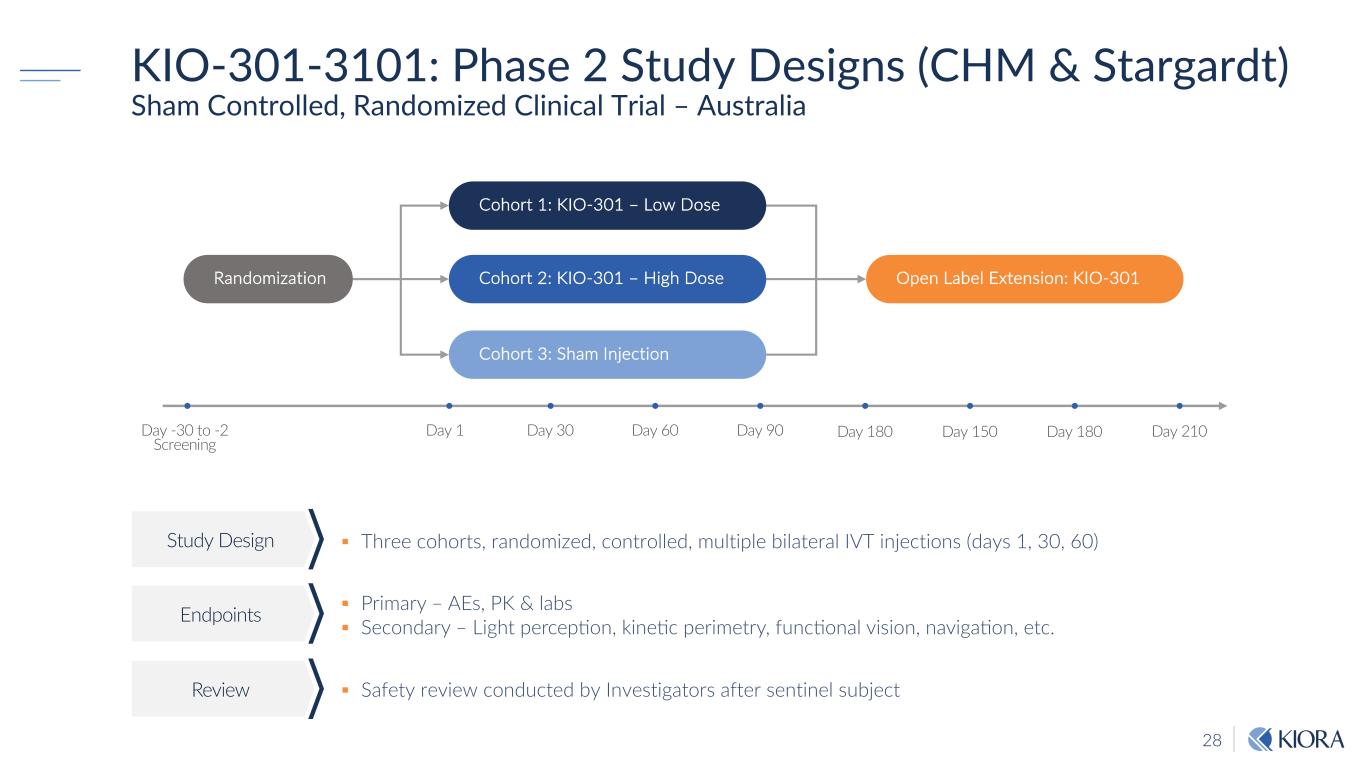
28 KIO-301-3101: Phase 2 Study Designs (CHM & Stargardt) Sham Controlled, Randomized Clinical Trial – Australia § Three cohorts, randomized, controlled, multiple bilateral IVT injections (days 1, 30, 60)Study Design Endpoints Review § Safety review conducted by Investigators after sentinel subject § Primary – AEs, PK & labs § Secondary – Light percep8on, kine8c perimetry, func8onal vision, naviga8on, etc. Day 150 Cohort 1: KIO-301 – Low Dose Day -30 to -2 Screening Cohort 3: Sham Injection Day 1 Day 30 Randomization Open Label Extension: KIO-301 Day 60 Day 90 Day 180 Day 210Day 180 Cohort 2: KIO-301 – High Dose

29 KIO-104 Intravitreal Small Molecule DHODH Inhibitor Steroid Sparing Approach to Retinal Inflammation

30 KIO-104 is an intravitreal, non-steroidal, novel small molecule which mitigates: § Metabolic activity and proliferation of T-cells § Secretion of IL-17, VEGF and IFN-𝛾 KIO-104 Overview (DHODH Inhibitor) O F F F F F F F NH O S OH O Existing immunosuppressive agents have a fundamentally different mode of action on T-cells compared to KIO-104 § KIO-104 is best-in-class inhibitor of DHODH (lowest IC50)* § KIO-104 is first-in-class in ophthalmology *1,000x more potent than Teriflunomide (Aubagio© — Sanofi) DHODH - dihydroorotate dehydrogenase
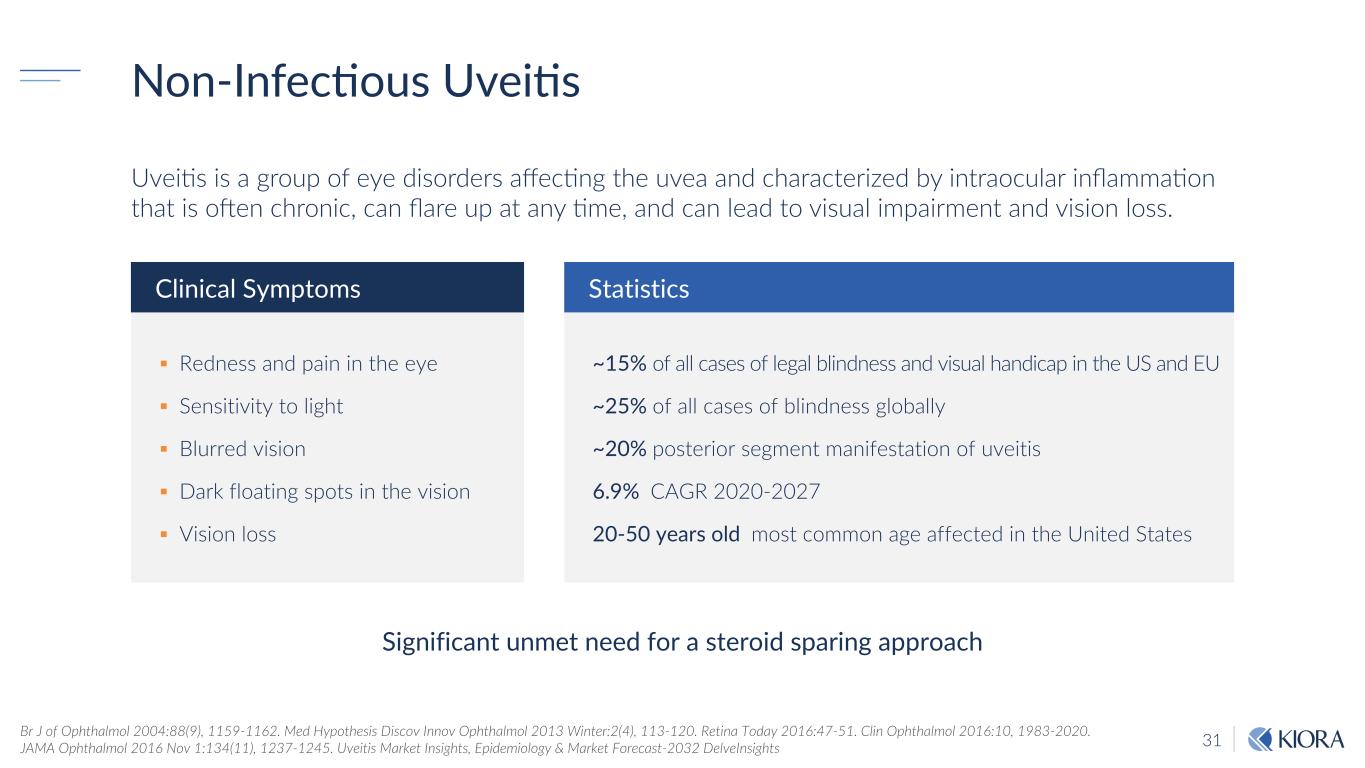
31 Non-InfecSous UveiSs Br J of Ophthalmol 2004:88(9), 1159-1162. Med Hypothesis Discov Innov Ophthalmol 2013 Winter:2(4), 113-120. Retina Today 2016:47-51. Clin Ophthalmol 2016:10, 1983-2020. JAMA Ophthalmol 2016 Nov 1:134(11), 1237-1245. Uveitis Market Insights, Epidemiology & Market Forecast-2032 DelveInsights § Redness and pain in the eye § Sensitivity to light § Blurred vision § Dark floating spots in the vision § Vision loss Clinical Symptoms Statistics ~15% of all cases of legal blindness and visual handicap in the US and EU ~25% of all cases of blindness globally ~20% posterior segment manifestation of uveitis 6.9% CAGR 2020-2027 20-50 years old most common age affected in the United States Uvei9s is a group of eye disorders affec9ng the uvea and characterized by intraocular inflamma9on that is o\en chronic, can flare up at any 9me, and can lead to visual impairment and vision loss. Significant unmet need for a steroid sparing approach
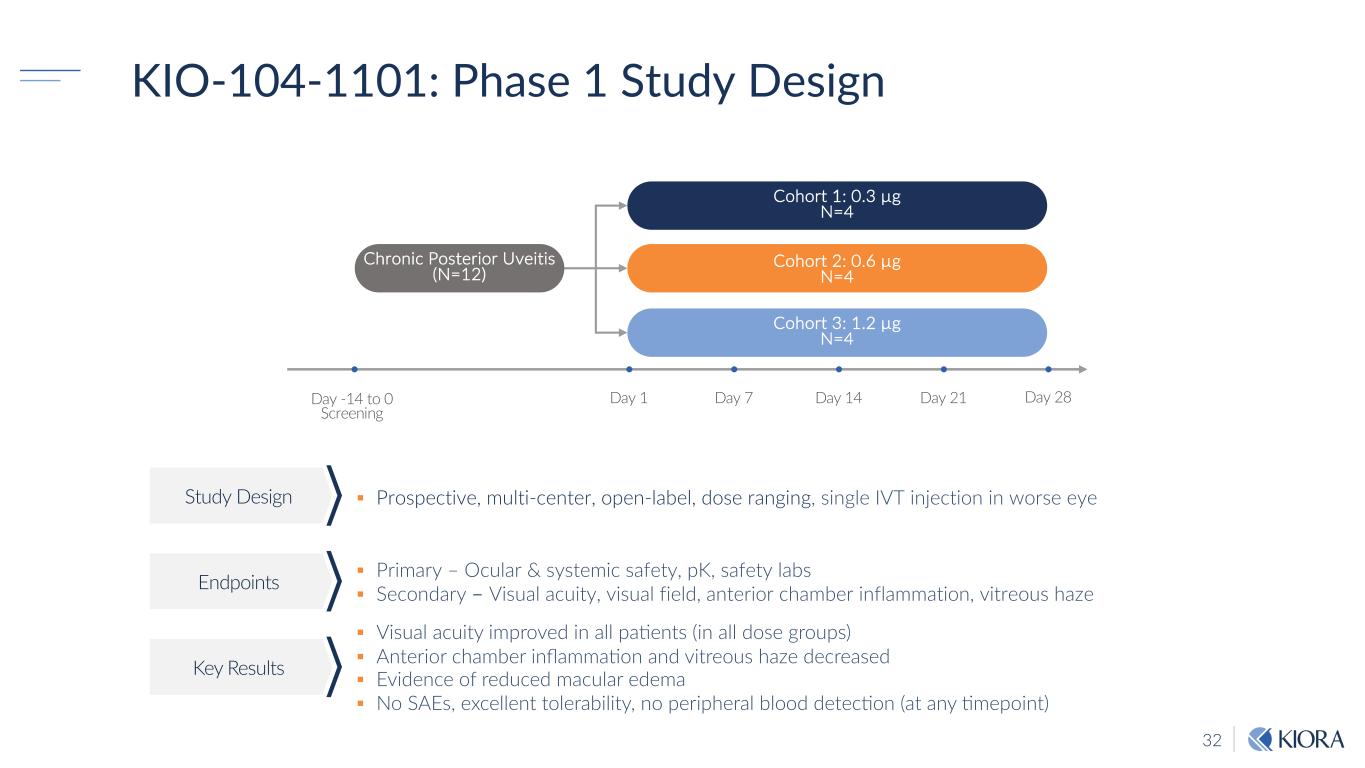
32 Day 28 Cohort 1: 0.3 µg N=4 Day -14 to 0 Screening Cohort 3: 1.2 µg N=4 Day 1 Day 7 Chronic Posterior Uveitis (N=12) Day 14 Day 21 Cohort 2: 0.6 µg N=4 KIO-104-1101: Phase 1 Study Design Study Design Endpoints Key Results § Prospective, multi-center, open-label, dose ranging, single IVT injection in worse eye § Visual acuity improved in all pa8ents (in all dose groups) § Anterior chamber inflamma8on and vitreous haze decreased § Evidence of reduced macular edema § No SAEs, excellent tolerability, no peripheral blood detec8on (at any 8mepoint) § Primary – Ocular & systemic safety, pK, safety labs § Secondary – Visual acuity, visual field, anterior chamber inflammation, vitreous haze
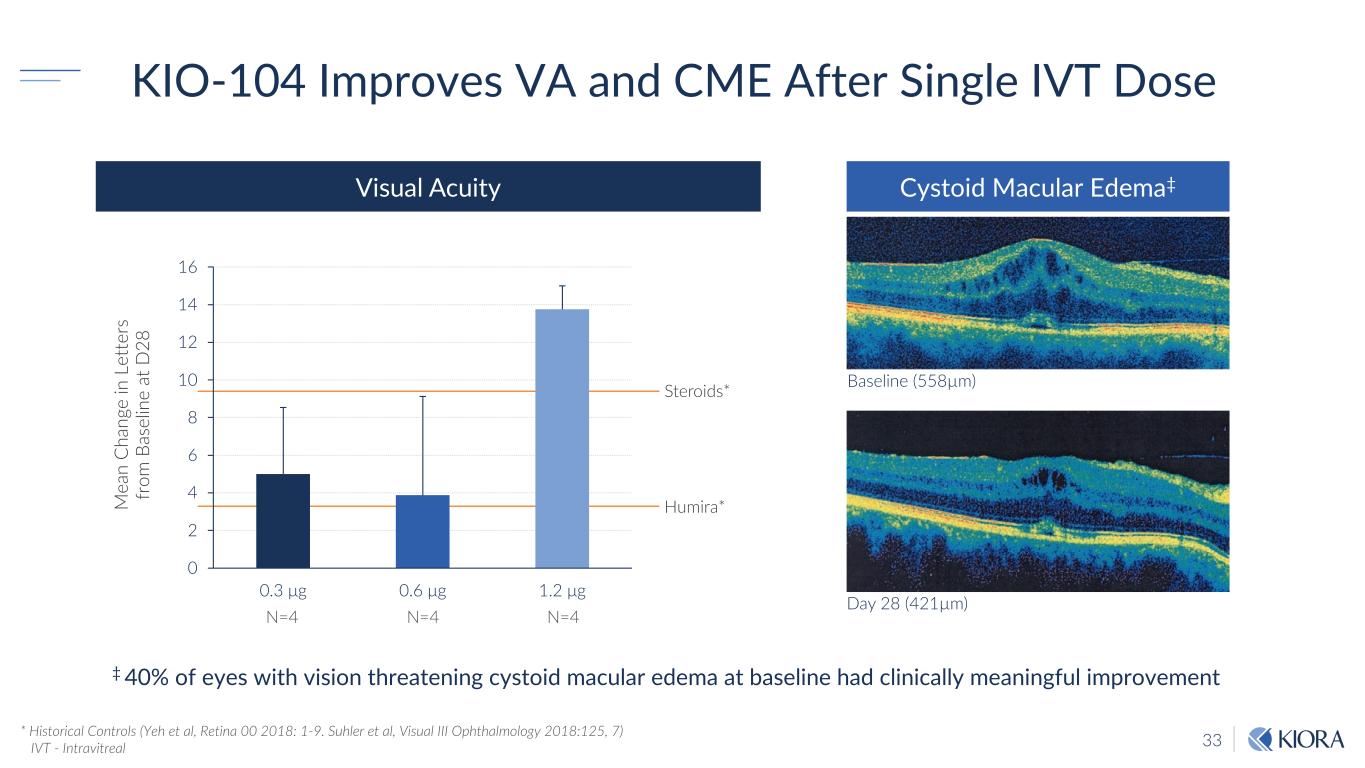
33 KIO-104 Improves VA and CME After Single IVT Dose * Historical Controls (Yeh et al, Retina 00 2018: 1-9. Suhler et al, Visual III Ophthalmology 2018:125, 7) IVT - Intravitreal 0 2 4 6 8 10 12 14 16 0.3 μg 0.6 μg 1.2 μg Steroids* Humira*M ea n C ha ng e in L et te rs fr om B as el in e at D 28 N=4 N=4 N=4 Day 28 (421µm) Baseline (558µm) Visual Acuity Cystoid Macular Edema‡ ‡ 40% of eyes with vision threatening cystoid macular edema at baseline had clinically meaningful improvement

34 CORPORATE OVERVIEW

35 Brian M. Strem, PhD President & CEO Eric J. Daniels, MD, MBA Chief Development Officer Melissa Tosca, CPA EVP – Finance Stefan Sperl, PhD EVP – CMC & Opera7ons Leadership Team

36 Board of Directors Brian M. Strem, PhD President & CEO Aron ShapiroKen Gayron Praveen Tyle, PhD Chairman David Hollander, MD, MBA Erin Parsons Carmine Stengone
37 Scientific Advisory Board Russel Van Gelder, MD, PhD Charlie Wykoff, MD, PhD Allen Ho, MD, PhD Chris/ne Kay, MD, PhD Vitreo Retinal ASSOCIATES Mark Pennesi, MD, PhD

Contact: info@kiorapharma.com